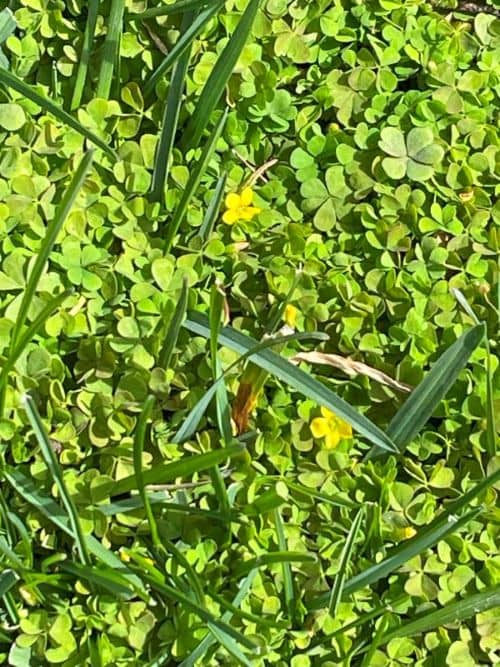
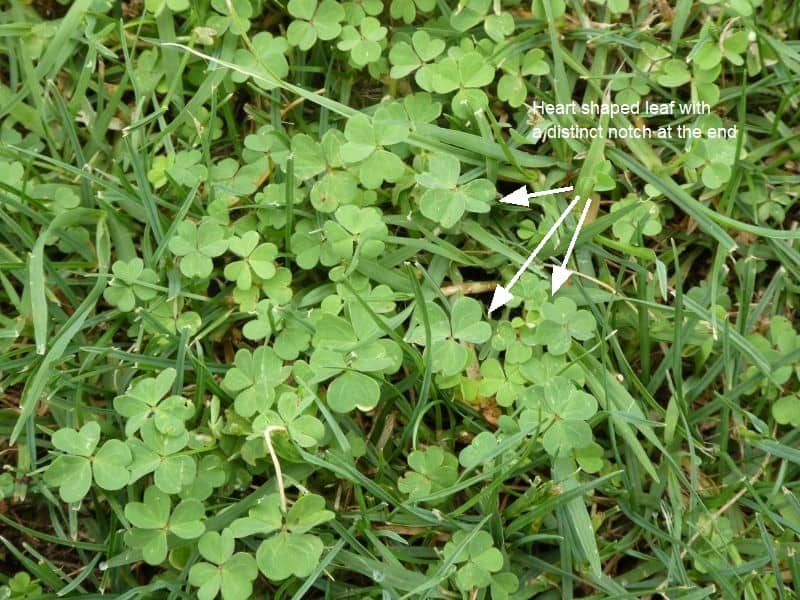
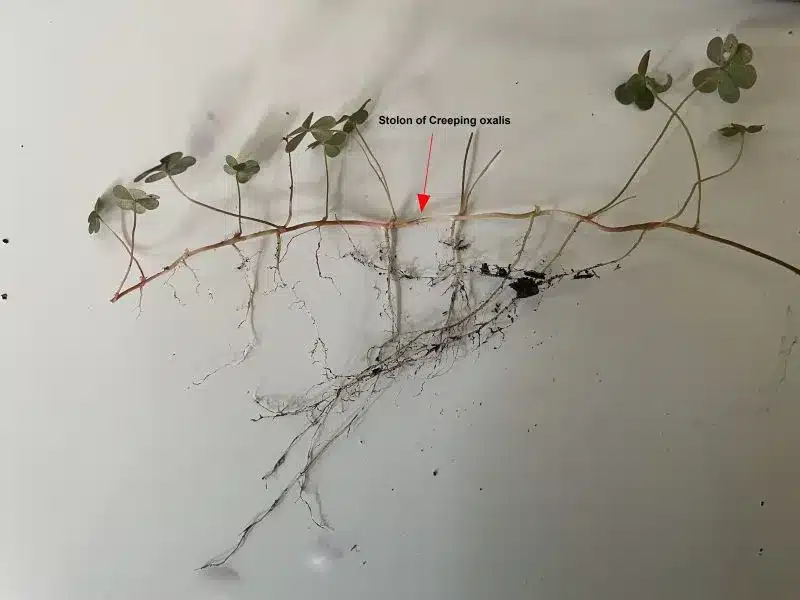
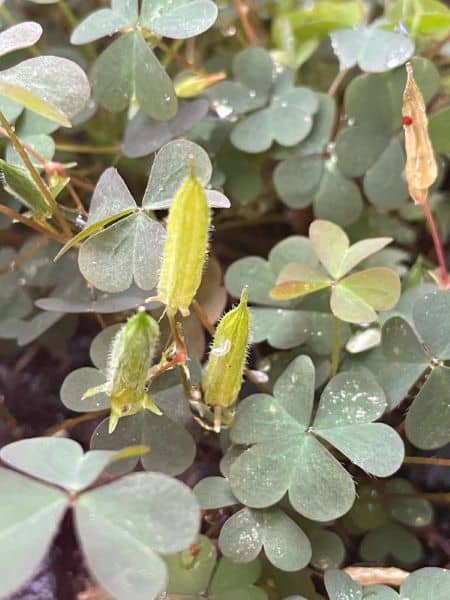
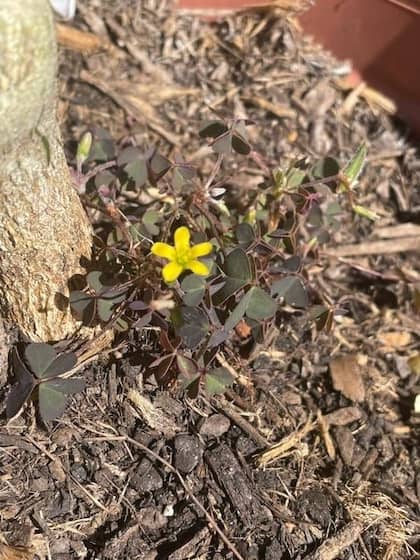
Creeping oxalis (Oxalis corniculata).
Why is Creeping Oxalis a Weed.
- Once it establishes Oxalis corniculata quickly spreads.
- It forms dense mats. These mats can choke out grass.
- It competes for soil nutrients, light and water.
- It spreads by seed and by stolons.
- This weed is hard to remove because of its root system.
- The leaves are hard to wet. This limits herbicide uptake.
- The small yellow flowers can be an issue with lawn care.
The leaves of this weed have a lemon flavour. You can use them to make a Vitamin C rich tea. However, it does contain large amounts of oxalic acid (hence its name) which blocks calcium uptake in the body.
How to Identify Creeping oxalis.
- It has three heart-shaped leaves.
- These alternate trifoliate leaves mean it is similar in appearance to White Clover.
- Its flowers are small and bright yellow.
- The stolons spread across the ground, They can be up to 60 mm long.
- It has light green to purple hairy stems.
There are two easy ways to tell this weed and White Clover apart:
- Oxalis corniculata has a small yellow flower. White Clover has pink or white flowers.
- White Clover has a distinct white mark on its leaves. Oxalis corniculata doesn’t have this.
- Soursob doesn’t have above ground stolons. It reproduces via bulbs.
- Wood Sorrel doesn’t have underground bulbs.
- The flowers of Soursob are larger.
- Soursob favours heavy, fertile, well-drained soils, and frost free areas. Creeping oxalis is more frost tolerant.
- Soursob flowers mainly in the Winter. It is dormant over the Summer.
Table of Differences Between Trifoliate Weeds.
Spreading | Trifoliate | Leaf Shape | Tooth at Tip of Leaf | Toothed Leaf Margins | Annual/ Perennial | Soil Conditions | Habitat | Flowers | |
Creeping Oxalis | Yes | Yes | Heart shape | No | Smooth | Perennial | High pH | Shade | Yellow with 5 petals |
White Clover | Yes | Yes | Smooth rounded | No | Yes | Perennial | High pH | Open areas | White |
Black Medic | Yes | Yes | Oval serrated | Yes | Yes | Summer Annual | Low pH | Full sun | Yellow |
Summary of Characteristics.
Reproduction of Creeping oxalis:
- This weed reproduces by seed, and also spreads by stolons.
- The seeds travel up to 5 metres out of seed pods.
- They can move on shoes, fur and machinery.
- The seeds germinate very quickly.
Removing Creeping oxalis.
- Cultural control is very difficult.
- An integrated approach is the best way to manage this weed.
- Once it establishes it is difficult to control.
- Autumn is an ideal time to control of this weed.
Cultural Control of Creeping oxalis.
- If you only rely on hand pulling or mowing you will not control Yellow Wood Sorrel.
- If you do hand weed, you must not leave any plant material behind in the soil.
- This is because it will regrow from its tap root.
- At a low height of cut it becomes more prostrate and grows across the surface.
Weed Calendar for Creeping oxalis.
Management Calendar for Creeping oxalis | ||||||||||||
Winter Annual sometimes Perennial | ||||||||||||
Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Active Growth | ||||||||||||
Flowering | ||||||||||||
Fruiting | ||||||||||||
Pre emergent herbicide | ||||||||||||
Post emergent herbicide | ||||||||||||
Chemical Control of Creeping oxalis.
- There are several broad leaf herbicides to control Yellow Wood Sorrel.
- As this weed is hard to wet, use Optispread 1000 to give good contact with the weed.
- For large areas, if you use a combination of pre and post-emergents you will get the best results.
- Pre-emergents prevent seed growth.
- You use post-emergents once you can see any weeds.
- Post-emergents tend to be more effective on small weeds, rather than older, more mature ones.
- Pre-emergents will not work if stolons, rhizomes, or root and stem fragments are left behind when you hand pull weeds.
Pre-Emergents for Creeping Oxalis.
- BASF Freehand Herbicide
- Echelon Duo.
- Indaziflam. This gives good pre and post emergent control in 2020 work.
Table of Pre-emergents.
Product | AI | FRAC Group | Rate per Ha | African Love grass | Annual Rye | Crabgrass | Creeping oxalis | Parramatta Grass | Paspalum | Summergrass | Winter Grass | Crowsfoot | White Clover | $ Cost / m2 | Longevity weeks |
Barricade | Prodiamine | 3 | 1 to 4 L | 143 to 572 | 24 | ||||||||||
Onset 10GR | Prodiamine | 3 | 50 to 150 Kg | 275 to 825 | 24 | ||||||||||
Echelon Duo | Oxadiazon | 14 | 300 to 400 Kg | 2100 to 2800 | 12 | ||||||||||
Dimension | Dithiopyr | 3 | 1.75 to 3.5L | 280 to 560 | 18 | ||||||||||
Freehand | Pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P | 3 + 15 | 100 Kg | 1585 | 12 | ||||||||||
Specticle | Indazaflam | 29 | 250 ml | 495 | 32 | ||||||||||
Pennmag | Metolachlor | 15 | 2 L | 45 | 8 |
Post Emergents for Creeping Oxalis.
- 2,4-D gives the best results vs this weed.
- The Sulfonylureas like Recondo and Duke, are also work against this weed.
- The best time to use post-emergents is in the daytime. This is because the leaves of Yellow Wood Sorrel fold downward in the evening.
- This is called nyctinasty. This also occurs with Gazania and Morning Glory.
- When the leaves fold down it makes it hard for chemicals to stick to the leaves.
Post emergents include:
- Dicamba. Do not use this on Buffalo grass.
- Pylex. Do not use this on warm season turf. Use this on actively growing Wood Sorrel. In some cases a single hit of Pylex may not give complete control. In this case you may need to use this again 21 to 28 days later.
- Warhead Trio. This is safe to use on Buffalo grass.
- Stature Herbicide. Do not use this in the home garden.
- Recondo Herbicide. Do not use this on Buffalo grass.
- Weed Blast MA. This is safe to use on Buffalo grass.
- Contra M. Do not use this on Buffalo grass
- Duke Herbicide. This is safe to use on most Buffalo varieties.
Table of Post Emergents for Creeping oxalis.
Product | Active | Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | ||||
Casper | Prosulfuron + Dicamba | 2 and 4 | 800 g to 1 Kg | Use from Autumn to Spring. Use high rates in cool months or if there is high weed pressure. Control takes 4 to 6 weeks. Use an NIS at a rate of 0.25 to 0.5% v/v. | ||||
Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Use in 250 to 400 L of water. Do not use on Buffalo grass. After use do not mow for 2 days before or afterwards or fertilise for two weeks. | ||||
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2 L + 3.2 L of 2,4-D Amine 625 g/L | Use a minimum of 1000 L/Ha of water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. | ||||
Duke | Iodosulfuron | 2 | 100 g | Always use an NIS or Overtake Oil. Use in 200 to 500 L/ha water. | ||||
Pylex | Topramezone | 27 | 0.375 mL/ 100 m2 in 4-6 L water + 0.5% MSO | Allpy twice 21 to 28 days apart. You may see bleaching of Bentgrass after 7 to 14 days. Do not water for 24 hrs post use. | ||||
Recondo | Trifloxysulfuron | 2 | 225 g | Use an NIS at 0.25% v/v (1000 g ai/L), 0.42% v/v (600 g ai/L) or Overtake Oil at 1% v/v. Ensure uniform placement onto leaves & into crowns. Water volume is 400 to 800 L/ha. You may need to reapply in 4 to 6 weeks. Allow at least 6 weeks before you overseed. You may see discolouration on Qld Blue and Zoysia. | ||||
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid any overlap. Use an NIS. | ||||
Weed Blast MA. | Bromoxynil + MCPA | 6 + 4 | 3 to 6 L | Apply in a minimum of 500 L/Ha water. DO NOT mow for 2 days after use. | ||||
Non-Selectives for Creeping oxalis.
- Glufosinate-ammonium gives control for 4 to 6 weeks. However, Oxalis corniculata will grow back due to the limited movement of this chemical.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate. If water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The chemicals below are non-selective. They also have a long term residual and stop re-growth of Yellow Wood Sorrel.
- Renegade. Renegade stops the germination of Oxalis corniculata for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for chemical applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives post and pre emergent control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown of this weed. It has a residual control of up to 3 months. It is also safe to use near trees.
Table of Non Selectives for Creeping oxalis.
Product | Active Ingredient | Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |