Lambs Tongue Weed (Plantago lanceolata).
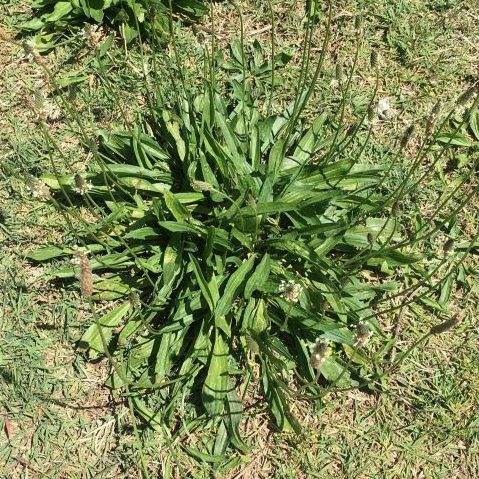
Lambs Tongue weed, is also known as Ribwort or Buckhorn Plantain. It is a common perennial weed of turf and lawns, and is found in all areas of Australia.
Buckhorn Plantain, is a weed that you should try and keep out of your turf. It has a large tap root, is hard to kill, and is relatively drought tolerant.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Ribwort or Buckhorn Plantain.
- Know its habitat.
- Know the best way to manage this weed.
The Ribwort Plantain (Plantago lanceolata) is an environmental weed in NSW, VIC and WA.
Why is Lambs Tongue Weed a Problem?
- It quickly spreads and forms dense populations. These compete with turf for water and nutrients.
- It produces large numbers of seeds that can establish quickly.
- The seeds can contaminate machinery. It can then spread to new areas.
- It thrives in a wide range of conditions, and tolerates drought periods.
- This weed has a very long dormancy period. Seeds can remain dormant in the soil for over 150 years.
Buckthorn Plantain is an Indicator Weed of dry, low nutrient status soils.
Our Weed ID Chart has more information on turf and grass weeds.
The distribution map is courtesy of The Living Atlas of Australia.
How to Identify Lambs Tongue Weed.
Buckhorn Plantain is easy to identify. It has distinct slender parallel veins on hairy leaves that form 1 or more rosettes. When it is young it looks similar to Wireweed.
- It spends the Winter as a rosette.
- The leaves, crown and its short below ground stem all act as storage organs.
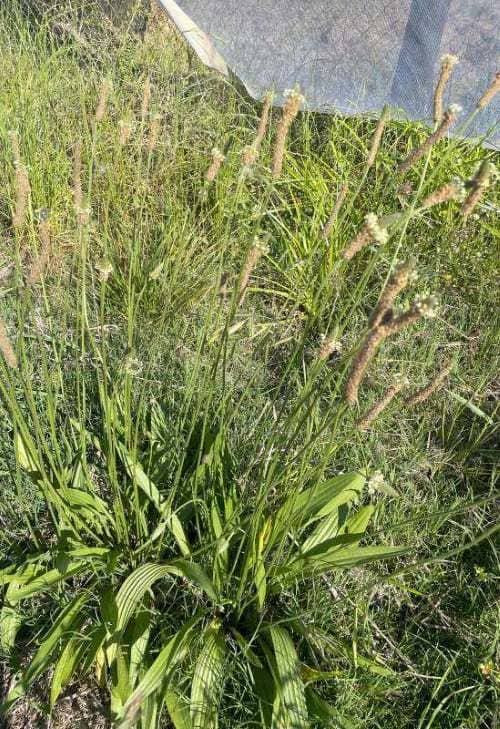
- Slender, long flower stems grow out from the rosettes.
- These flower stems have dense, brown, cylinder shaped seed heads.
- White anthers often stick out of the flowers.
- Because of its height, the seed quickly spreads via the wind.
- It tends to germinate in the cool months in the late Autumn and the early Winter.
Photosynthetic Pathway. Lambs Tongue Weed is a C3 weed. It is frost tolerant.
Leaf length: Its leaves are long and narrow, and are between 3 and 30 cm long.
Leaf Width: The leaves are 8 to 30 mm wide.
Comments: You often find that this weed grows close to the ground in lawns and sports turf situations. It tends to be much more open and spread when there is no competition.
Habitat: You often find Buckhorn or Ribwort Plantain in poor lawns, turf, gardens, and along roadsides.
How to Control Lambs Tongue Weed.
- A combination of cultural and chemical control will manage Ribwort or Buckhorn Plantain. However, if you rely entirely on cultural control it will not give 100% control of this weed in turf grass.
- Autumn is the best time to control of this perennial weed.
Cultural Control of Lambs Tongue Weed.
- This weed is not a great competitor. This means that if you maintain a thick, healthy turf cover it is a major step toward managing this weed.
- Use the right turf fertiliser. This helps to create a dense turf canopy that will discourage it.
- Mow at the right height for your turf type. This will favour the grass over the weed.
- You can hand pull plants if it isn’t widespread.
- It is easy to remove it by hand. Early removal of the seedlings works if you keep at it.
- Make sure that you pull out the whole plant. This includes its deep tap root. If you don’t, it quickly grows back after you pull it up.
Chemical Control of Lambs Tongue Weed.
Your choice of turf herbicide depends on:
- The turf type that is present.
- Cost.
- How easy it is to apply.
It is very important to use products at the right time and rate. Spot spraying also works if it’s practical. However, if this weed is widespread blanket treatment works better.
The best time to control this weed is once it germinate, and when it is actively growing.
Pre-emergents for Lambs Tongue.
Pre-emergents that prevent this weed in turf include:
- Indaziflam.
- Isoxaben.
- Mesotrione.
These are not necessarily registered for this weed in Australia. So always make sure that you read the label before you use them.
Overseas Research.
- Work shows that Specticle herbicide gives excellent pre-emergent control of Buckhorn Plantain.
- It does not control older plants that are already present.
- These will continue to grow after you use a pre-emergent.
Post Emergents for Lambs Tongue Weed.
There are three important things to consider with the post-emergent control of Ribwort Plantain.
- The best time to spray this weed is when it’s young, and not well established.
- Mixes of 2 or 3 actives will give better control than if you use one active by itself.
- You get the best control when you treat this weed in the Autumn.
- You will need several treatments to kill this perennial weed and any new seedlings.
- Once this weed matures it is difficult to control.
- Products that contain 2,4-D tend to work the best.
Other options include:
- Bromoxynil.
- Carfentrazone.
- Dicamba.
- Mesotrione. No current label for this weed in Australia.
- Penoxsulam. No current label for this weed in Australia.
- Quinclorac does gives some control of Buckthorn Plantain. However, it doesn’t work well on Broadleaf Plantain.
- MCPA will suppress, and not kill, Ribwort Plantain.
Suitable post emergents include:
- Casper Herbicide. Do not use this on Buffalo grass.
- Stature Herbicide. Not for home garden use.
- Quali-Pro Negate. Do not use this on Buffalo grass.
- ProForce Weed Blast MA. You can use this on Buffalo grass.
- Warhead Trio. You can use this on Buffalo grass.
- ProForce Contra M. Do not use this on Buffalo grass.
Table of post Emergents for Use in Turf.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | ||||
Casper Herbicide. | Prosulfuron + Dicamba | 2 and 4 | 800 g to 1 Kg | Use on weeds after they emerge in the Autumn to the early Spring. Use the high rates in cool months or if the weed pressure is high. Complete control may take 4 to 6 weeks & depends on growth stage & the soil and air temperature. Weed death takes longer when you use this in the Winter (May to August). Use a non-ionic surfactant like Optispread 1000 at a rate of 0.25 to 0.5% v/v. | ||||
Stature Herbicide. | MCPA + Dicamba + Diflufenican | 4 + 4 + 12 | 2 L | Use in 200 to 500 L water on actively growing weeds. Control may take 4 to 6 weeks. You may need to repeat the treatment in 4 to 6 weeks if you use low rates on high weed populations or in long germination periods. Use a surfactant. | ||||
Quali-Pro Negate. | Rimsulfuron + Metsulfuron-methyl | 2 | 110 g | Apply to actively growing weeds, and not to weeds under stress. | ||||
ProForce Weed Blast MA. | Bromoxynil + MCPA | 6 + 4 | 3 to 6 L | Apply evenly over the area. DO NOT mow turf for 2 days after use. Use a at least 500 L/Ha of water | ||||
Warhead Trio. | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | Use on actively growing weeds. Some discolouration may occur on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue couch. Do not overlap any areas that you spray. Use a surfactant. | ||||
ProForce Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Use on actively growing weeds, and on moist soil in 250-400 L of water. Do not use on Lippia, Strawberry Clover or Buffalo grass. Do not mow turf for 2 days before or after use. Do not fertilise within two weeks of a spray. | ||||
Non Selectives for Lambs Tongue Weed.
You cannot use any of these on lawns or turf to selectively control this weed.
- Glufosinate-ammonium controls this weed for 4 to 6 weeks. However, it will tend to grow back as it just burns off the top growth.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate, but if water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The products below are non-selective. They also have a long term residual, and will stop any re-growth of Ribwort Plantain.
- Renegade. Renegade stops the germination of Ribwort Plantain for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for repeat product applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives post and pre-emergent control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown. It then gives residual control for up to 3 months, and is safe to use near trees.
Table of Non-Selectives.
Product | Active Ingredient | Chemical Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole + Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000 L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |
In Conclusion
The key to manage Lambs Tongue weed is to maintain a healthy turf surface. You should do this before you spray any chemicals.