Capeweed (Arctotheca calendula).
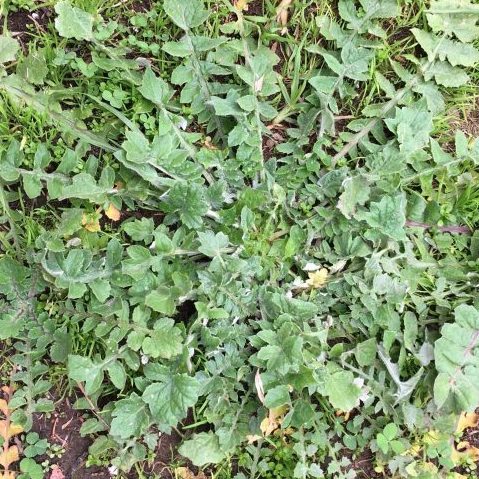
Capeweed, is also known as the Cape Dandelion. It is a low growing annual weed with a flat rosette of leaves.
It is very difficult to control, poisonous and indigestible if eaten in large quantities. In livestock, it causes respiratory issues, and stringhalt in horses.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify the Cape Dandelion.
- Know its habitat.
- Know the best options to control it.
Why is Capeweed a Problem?
- It has a deep taproot. This enables it to survive in dry conditions.
- The Cape Dandelion produces a lot of seeds. These can remain viable for several years. In good conditions it produces over 4,000 seeds a season.
- These seeds move by human activity, animals, wind, water and in grass clippings.
- The rosettes are large. This means that the plants are able to compete strongly with turf.
- It is very competitive for water, nutrients and light.
- In cool, cloudy weather, toxic levels of nitrates can occur in the Cape Dandelion. These nitrates suppress the plant uptake of Magnesium. This reduces plant iodine levels and causes grass tetany.
- When dairy cattle eat this weed it can also taint milk.
During its vegetative stages, you can confuse this weed with Dandelion, Catsear, Sowthistle and Fleabane.
Table of the Differences between Rosette Weeds.
Plant | Rosette | Annual or Perennial | Stems | Leaves | Flower Colour | Comments |
Dandelion | Yes | Perennial | Single unbranched and hollow. None or have minimal leaves. | Deeply toothed or lobed (point backwards). | Single Yellow flower per stalk, made of many small florets | When the stem or leaves are cut exudes sap. Open up when the sun is out, and then close at night. |
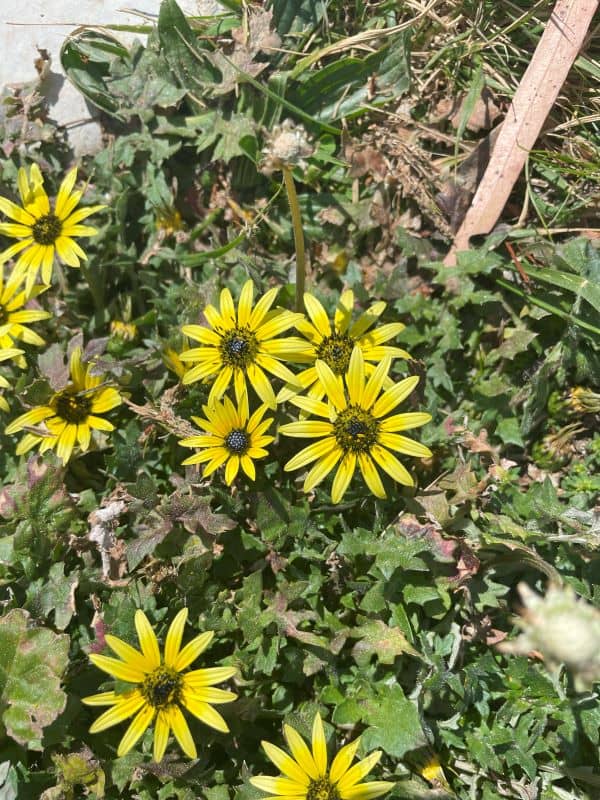
Capeweed | Yes | Annual | Several branches with a hollow core | Hairy undersides | Yellow with black centre | |
Catsear | Yes | Perennial | Multiple, branches. None or have minimal leaves. | Club shaped and sometimes hairy | Yellow. Made up of numerous tightly packed florets. | Has milky sap in its stems and leaves. Needs the sun for the flowers to open in the morning. Once open can't close for at least 3 hours. |
Gazania | Yes | Annual | No leaves | Hairless on the upper surface, woolly white hairy underneath. | Yellow | |
Fleabane | Yes | Annual, Biennial or short lived Perennial | Starts as a rosette and then grows tall, upright flower stems. | Elongated with bluntly toothed to deeply lobed margins. | Small tufted white daisy like flowers | |
Oriental Hawksbeard | Yes | Annual | Single leafy, branched main stem. | Hairy and emit a milky sap | Yellow | |
Sowthistle | Yes | Annual, biennial or perennial | Several branches, hollow stalks | Adult leaves are serrated and deeply lobed. They have a major triangle-shaped lobe at the tip of the leaf. | Yellow with several flowers per stalk | Open up when the sun is out, and then close at night. |
How to Identify Capeweed.
- The Cape Dandelion is an annual weed.
- It germinates in the Autumn and the Winter.
- After it rains, most of the seeds germinate within a few weeks.
- In warm weather, Capeweed seedlings grow quickly. They then smother other plants in the early Winter.
- The rosette grows close to the ground and is up to 60 cm across. These large plants are difficult to control with herbicides.
- It has broad, deeply lobed, succulent, leaves.
- The leaves have a cover of white furry hairs on their underside.
- It has distinctive flowers with yellow petals.
Category: The Cape Dandelion is a Broadleaf (Dicot) weed.
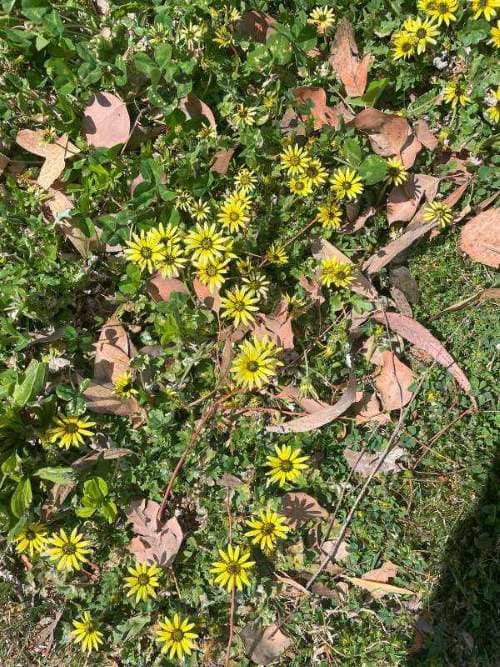
Flower: This weed flowers in the late Winter and the Spring. You can often see it in Canberra by the side of roads as a bright flush of yellow flowers.
The flower head look like a Daisy, and it is made up of several small yellow flowers. It is 15 mm across and has a black-to-brown centre. The flowers are on individual stalks about 200 mm long.
Height: It grows up to 30 cm in height.
Leaf length: The leaves are 5 to 25 cm long.
Leaf width: The leaves are 2 to 6 cm wide.
How Does Capeweed Reproduce?
- It spreads by seeds. A single plant produces over 4,500 seeds in a season.
- If you don’t carry out regular control measures, this weed quickly spreads.
- When it dies off over the Summer, Capweed seedlings can re-establish in the bare areas.
- The woolly seeds stick to clothes. They also spread by the wind.
- This woolly seed coat helps with its early season germination.
Habitat: This weed is present on most soil types but prefers sandy soils and loams. Its presence is a good indicator of high soil P or N.
More on lawn and turf grass weeds is in our weed ID chart.
How to Control Capeweed?
Cultural Control of Capeweed.
- If you have a small or new infestation, you can simply dig it up by hand.
- Make sure that you remove all the plants before they flower. They then can’t drop any seed.
- Cape Dandelion seeds can germinate the following year, and up to seven years after that.
- To prevent re-growth, make sure that you cut the fleshy taproot well below the ground level.
- Mowing is only effective if you repeat it regularly. If you mow at a low height of cut it prevents the weed from producing flowers.
Weed Management Calendar for Capeweed.
Management Calendar for Capeweed | ||||||||||||
Annual | ||||||||||||
Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Seeding | ||||||||||||
Active Growth (Rosette) | ||||||||||||
Flowering | ||||||||||||
Seeding | ||||||||||||
Dies Off | ||||||||||||
Pre emergent | ||||||||||||
Post emergent Herbicide | Post emergent (when rosettes form, and before it flowers) | |||||||||||
Chemical Control of Capeweed.
- This weed is difficult to control with post emergent herbicides. This is because of its cover of wooly hairs that make it hard to wet.
- When you use post emergents you need a wetter to give good chemical contact. Use Optispread 1000.
Pre-Emergent Herbicides for Capeweed Control.
- There are several pre-emergents that either suppress or control this weed. Be aware that you can’t use Envu Esplanade on turf grass.
Suppression.
- Pendimethalin (ProForce Battalia 435) suppresses the Cape Dandelion.
Control.
- Prodiamine. Syngenta Barricade or Spartan Herbicide
- Envu Esplanade.
- Envu Specticle.
Post Emergent Herbicides for Capeweed.
Several post-emergent herbicides are available. These include Dicamba and MCPA. Once it is present in lawns, you get the best control with herbicides that contain dicamba. However, you can’t use these on Buffalo grass.
- You can kill the young rosettes with MCPA or 2,4-D.
- ProForce Warhead Trio. This is safe to use on Buffalo grass.
- Weed Blast MA. This is safe to use on Buffalo grass.
- Casper Turf Herbicide. Don’t use Casper Turf Herbicide on Buffalo grass.
- ProForce Contra M. Don’t use Contra M on Buffalo grass.
Table of Post Emergent Herbicide Rates for Capeweed.
Product | Active | Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | ||||
Casper | Prosulfuron + Dicamba | 2 and 4 | 800 g to 1 Kg | Use from Autumn to Spring. Use high rates in cool months or if high weed pressure. Control takes 4 to 6 weeks. Use an NIS at a rate of 0.25 to 0.5% v/v. | ||||
Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Apply in 250-400 L water. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass. Do not mow for 2 days before or after USE or fertilise within two weeks. | ||||
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2 L + 3.2 L of 2,4-D Amine 625 g/L | Use a minimum of 1000 L/Ha water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. | ||||
MCPA | MCPA | 4 | 930 ml -1.8 L | Use in a high water volume to actively growing weeds. DO NOT mow for 2 days before use. Some transitory damage may occur to fine turf grass | ||||
2,4-D | 2,4-D | 4 | 1.8 to 3.2 L | Wet foliage. DO NOT mow lawn for 1 week before and at least 1 weed after use. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass (WA only). | ||||
Weed Blast MA | Bromoxynil + MCPA | 6 + 4 | 3-6 L | Use in a minimum of 500 L/Ha water. DO NOT mow for 2 days after use. | ||||
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid any overlap. Use an NIS. | ||||
Non Selective Control of Capeweed.
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks. Be aware that it will re-grow after this due to the limited movement of glufosinate.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate. However, if water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The list below are non-selective. They have a long term residual, and will stop re-growth of Cape Dandelion.
- Renegade. Renegade stops seed germination for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown of the Cape Dandelion. It also has a 3 month residual, and is also safe to use near trees.
Table of Non Selectives for Capeweed.
Product | Active Ingredient | Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |