Bindii (Soliva sessilis).
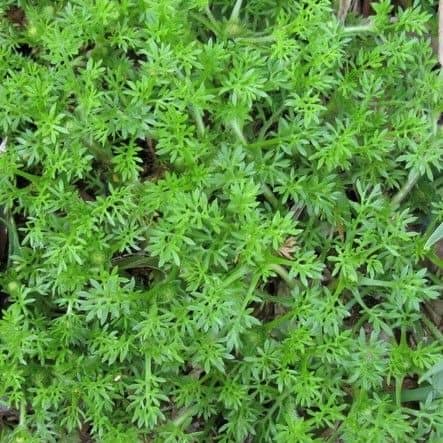
Bindii aka Jo-Jo Weed or Onehunga, is a member of the Daisy family. It is famous for its seeds that have tiny sharp seeds. It is a good indicator weed for compact soils.
Onehunga is an annual prostrate weed. It tends to appears from May to October, and spreads quickly. As temperatures fall in the Autumn if there is adequate soil moisture, it then germinates in thin or bare areas.
As an annual, it emerges from the previous year’s seed, grows, flowers, and then produces more seeds before it dies.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Bindii, Jo-Jo or Onehunga.
- Know the habitat of Bindii.
- Know the way to control Jo-Jo.
Why is Bindii a Problem Weed?
- It is a prolific seed producer.
- It can flower and set seed through the season. This gives it a competitive advantage.
- Bindii seeds have spiny burrs. These are difficult to remove and can puncture skin.
- It is difficult to control. Once the burrs form even when you kill this weed the burrs are left behind.
- Rapid spread. It quickly creates a dense carpet that smothers turf grass.
- Bindii causes bindii dermatitis, which is an irritant contact dermatitis.
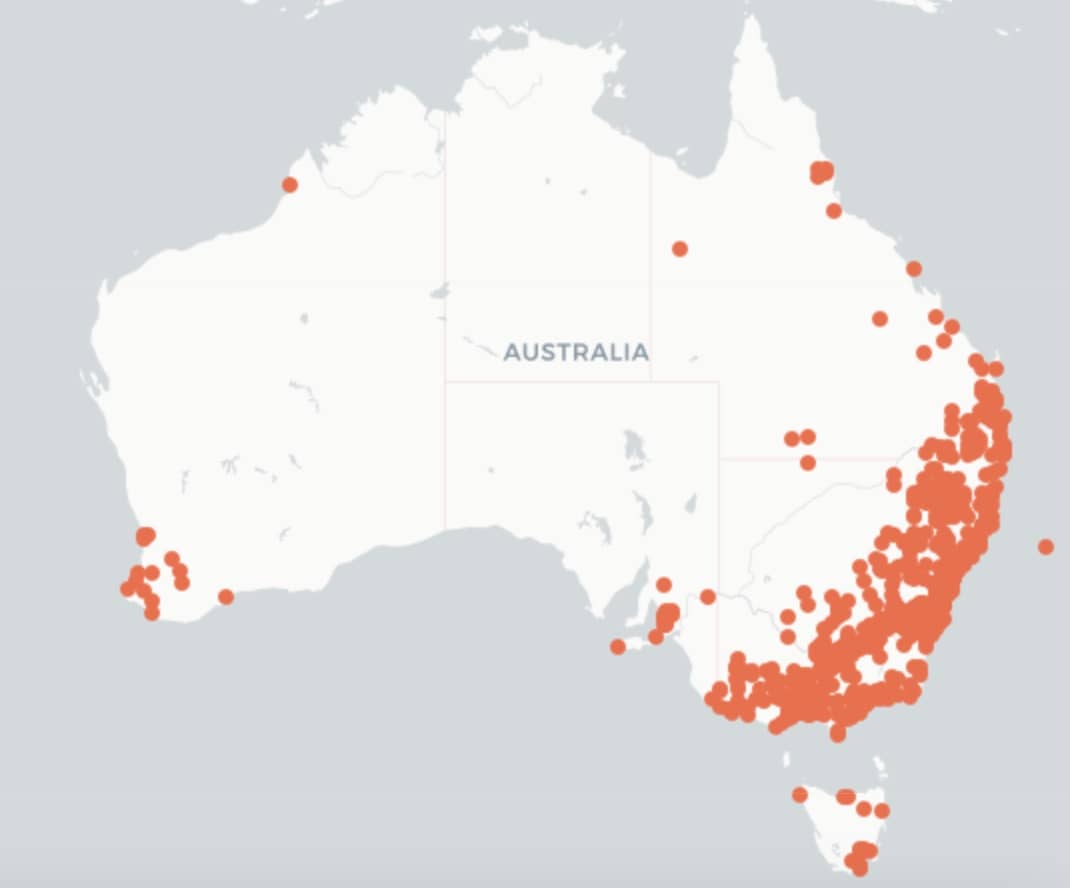
The distribution Map is courtesy of The Living Atlas of Australia.
For more information, please check out our weed ID chart.
Bindii Identification.
Onehunga is a low-growing and fast-spreading weed, and is often confused with Carrot Weed. However, the key difference is that Carrot Weed produces pale yellow flowers on the end of stalks in the early Winter. Bindii flowers much later, and has no flower stalks.

Leaves of Bindii or Soliva sessilis are shaped like parsley
Differences Between Bindii and Other Carrot Leaf Weeds.
Weed | Roots | Flowers | Smell when crush | Spiny Burrs |
Bindii | Fibrous | Green | No | Yes |
Carrot Weed | Weak taproot | Pale Yellow with no petals | No | No |
Swinecress | Strong taproot | Green | Yes | No |
It remains small and unnoticed over the Winter. However, once the temperatures start to increase in the early Spring, Bindii bursts into life. The young plants have a low-forming rosette, and its leaves look like the leaves of carrot or parsley.
As the plant matures, it spread sideways, and forms a low ground cover. Bindii matures very quickly, and it flowers soon after it germinates.
Its small, yellow flowers then form seedheads. It’s these that contain the small spiky seeds. Bindii produces 5 to 100 seeds per plant in the late Spring to Summer. At this stage, the seeds can move between sites by machinery, foot traffic and pets.
As the temperatures increase in the Summer, it dies out. The hard prickles then drop to the soil surface. When Bindii dies off it leaves patches of bare soil. These bare patches then act as an ideal habitat for it to germinate. Germination tends to happen when air temperatures reach 32°C.
Photosynthetic Pathway: Bindii is a C3 Weed.
Category: Jo-Jo is a Broadleaf (Dicot) weed.
Flower: Onehunga has small, bright yellow flowers that are not on stalks.
Height: It grows up to 50 mm in height.
Reproduction: Bindii reproduces only by seed.
Comments: Onehunga spreads up to 150 mm and has small, parsley-like leaves.
Habitat: Jo-Jo thrives in full sun or partial shade in compact, stressed, worn, or bare areas.
Management Calendar for Bindii.
Management Calendar for Bindii | ||||||||||||
Annual | ||||||||||||
Months | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Active Growth | ||||||||||||
Flowers | ||||||||||||
Pre emergent Herbicide | ||||||||||||
Post emergent herbicide | ||||||||||||
How to Remove Bindii.
Cultural Control of Bindii.
- Hand pull or use a weed tool. Make sure that when you pull up the entire plant you also pull up all of the roots. Do this before it seeds.
- As it favours compact soils, aeration helps deter this weed.
- Keep N fertiliser up to your grass. This helps the turf out compete this weed.
- Mowing is doesn’t work because of its prostrate growth habit.
Chemical Control of Bindii.
- Use pre-emergents in the Autumn. These include Dithiopyr, Prodiamine, Pendimethalin, Indaziflam, and Isoxaben. You need to apply these before the seeds start to grow.
- Try and apply a pre-emergents when the nights start to cool to around 13 to 16°C. If you apply a pre-emergent at this stage it effectively stops the Bindii seeds.
- If you miss the application window, then your next best option is to use a post emergent. Apply these in June, July or August.
Pre-Emergent Bindii Herbicides.
- Oxadiazon gives poor control of Bindii.
Post Emergent Herbicides for Bindii.
The most important factors to consider with control are:
- Apply post-emergents in the early Winter before the plant flowers and seeds. At this stage the weed is small and easy to control. It also hasn’t yet got any sharp burrs.
- Once the burrs form control is difficult.
- Control is not impossible in September, October and November. However, the spines will have already formed by this time, and will remain after the weed dies.
- Once the weed matures, you may need to make several herbicide applications, which increases the chances of turf grass injury.
- Treatment is best over the entire area rather than spot treating. The Bindii is dead 7-10 days after you spray.
There are several post-emergents for Bindii:
- 2,4-D.
- Dicamba. Do not use Dicamba on Buffalo grass.
- Duke 100WG.
- ProForce Recondo.
- Warhead Trio.
- Casper Herbicide. Do not use Casper on Buffalo grass.
- Contra M. Do not use Contra M on Buffalo grass.
- Pylex. Do not use on warm season turf.
- Quali-pro Negate.
Table of Selective Post Emergent Herbicides for Bindii.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | ||||
Casper | Prosulfuron + Dicamba | 2 and 4 | 800g-1Kg | Apply from Autumn to Spring. Use high rates in cool months or if high weed pressure. Control takes 4 to 6 weeks. Use an NIS at a rate of 0.25 to 0.5% v/v. | ||||
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2L + 3.2L of 2,4-D Amine 625g/L | Use a minimum of 1000L/Ha water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. | ||||
Duke | Iodosulfuron | 2 | 100g | Always use an NIS or Overtake Oil. Use in 200-500 L/ha water. | ||||
Pylex | Topramezone | 27 | 0.375 mL/ 100 m2 in 4-6 L water + 0.5% MSO | Make two applications 21-28 days apart. You may see bleaching of Bentgrass after 7-14 days. Do not water for 24 hrs post application. | ||||
Recondo | Trifloxysulfuron | 2 | 225g | Use an NIS at 0.25% v/v (1000 g ai/L), 0.42% v/v (600 g ai/L) or Overtake Oil at 1%v/v. Ensure uniform placement onto leaves & into crowns. Water volume is 400 to 800 L/ha. You may need a repeat application in 4 to 6 weeks. Allow at least 6 weeks before overseeding. You may see discolouration on Qld Blue and Zoysia. | ||||
Negate. | Rimsulfuron + Metsulfuron-methyl | 2 | 110g | Apply to growing weeds and not to stressed weeds. | ||||
Weed Blast MA. | Bromoxynil + MCPA | 6 + 4 | 3-6 L | Apply in a minimum of 500L/Ha water. DO NOT mow for 2 days after treatment. | ||||
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid overlapping. Use an NIS. | ||||
Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Apply in 250-400L water. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass. After use do not mow for 2 days before or after application or fertilize within two weeks. | ||||
Non Selective Bindii Herbicides.
Do not use any of these on lawns or turf areas to selectively remove Bindii.
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks. However, but it will recovers due to the limited movement of glufosinate.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate but if water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
These are non-selective. They also have a long term residual and stop any re-growth.
- Renegade. Renegade stops germination of Jo-Jo for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for multiple herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives post and pre emergent Onehunga control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown, and residual control for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use around trees.
Table of Non Selective Herbicides for Bindii.
Product | Active | Group | Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |