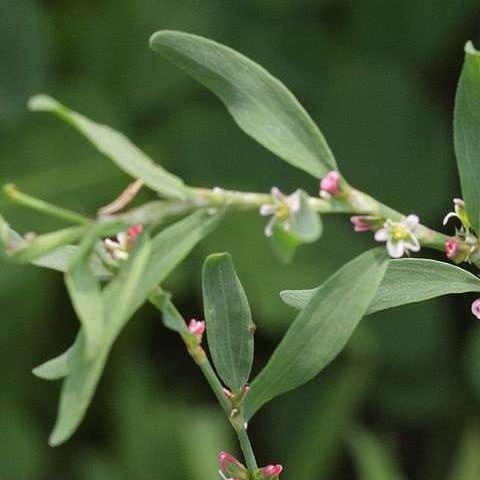
Wireweed (Polygonum aviculare).
Wireweed (Polygonum aviculare) is also known as Prostrate Knotweed, and Knotgrass. It is a common weed of amenity turf, and favours worn, and compact soils. Wireweed control of this weed can be very difficult.
- It favours areas that are irrigated.
- Is very wear resistant, and
- you often find it in compact goal mouths on sports fields.
After you read this you will be able to:
- Identify this weed.
- Know its habitat and lifecycle.
- Know the best options for Wireweed control.
Why is Wireweed a Problem?
- It forms dense vegetative mats, and has a strong, deep taproot.
- Knotweed germinates the earliest of all the Summer annual weeds. Because if it’s early germination, it is able to use resources and invade damaged areas before desirable grasses begin to grow.
- This weed spreads quickly, and outcompetes other plants for water, nutrients, and light.
- Once it establishes, Wireweed control is difficult.
- It produces large numbers of seeds. These remain viable for several years.
- It tends to be a problem at the most awkward times. It often germinates when you try to establish turf.
- This weed is inhibits seed germination, and the growth of seedlings.
- It is often mistaken for Spotted Spurge or Common Purslane. This can make control of this weed even more difficult.
- Knotweed causes dermatitis in sheep and humans. Horses and stock that eat large amounts of seed may develop enteritis.
Table Showing Differences between Wireweed, Spurge and Purslane.
Weed | Spreading | Leaves | Leaf shape | Leaf Hairs | Milky Sap | Flower Colour | Reproduction |
Knotweed | Yes | Alternate | Lanceolate or elliptic to oblong | None | No | White to green | Seed |
Prostrate Spurge | Yes | Opposite. Often has a dark spot in the centre of the leaf. | Small and oval | None | Yes | White | Seed |
Purslane | Yes | Alternate or opposite | Club shaped and fleshy | None | No | Yellow | Seed and stem fragments |
- This weed favours a soil pH > 5, and is found in a range of soils.
- It favours compact soils and heavy N use.
- It tolerates drought and low fertility soils.
- Knotweed is a good indicator weed for soil compaction.
Wireweed Identification.
This is an aggressive, low-growing Summer annual or biennial dicot weed.
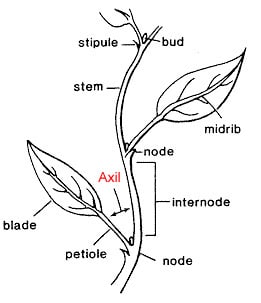
- Knotweed has small oval leaves. These have a purple sheath around their base.
- The branch leaves are about half the size of the stem leaves.
- The stems root at the nodes.
- It flowers mainly in the Autumn and the Spring. This is when you can see a large numbers of flowers along the base of the leaves.
- The stems have several branches and look “wiry”.
Photosynthetic Pathway: This is a C3 weed.
How Does it Reproduce?
- It only grows from seeds and produces around 50 seeds per plant.
- Seed densities can reach 200 to 5,000 seeds /m2. The seeds tend to be in the top 5 cm of the soil.
- The seeds can remain viable for up to 60 years.
- They need soil moisture to germinate.
- The deeper the seeds are in the soil profile the less likely they are to germinate.
The need for moisture to germinate explains why this weed is a problem if you disturb the soil and irrigate. When you disturb the existing seed bank in the soil, the seeds then germinate and grow rapidly.
You often see this happen when you re-surface sports fields or fairways.
- It is often mistaken for a grass when it germinates. This is because it has long, dark green leaves.
- In warm weather it grows rapidly.
- Any of the seeds that don’t germinate in the Spring, then go into a secondary dormancy period.
- It doesn’t tend to germinate over the Summer months.
- The leaves have no hairs.
- This weed has a strong, deep, fibrous tap root.
- It tends to germinate when soil temperatures are around 4 °C.
- The stems do not end in a flower head. Instead the small flowers occur in the leaf axils.
Wireweed Control.
Weed Management Calendar for Knotgrass.
Management Calendar | ||||||||||||
Summer Annual or Biennial | ||||||||||||
Months | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Active Growth | ||||||||||||
Flowering | ||||||||||||
Pre-emergent | ||||||||||||
Post emergent | ||||||||||||
What is its Treatment Threshold?
Cultural Wireweed Control.
Here are some tips on cultural options to control this weed in turf.
- It thrives in compact soils. This means, if you relieve any soil compaction it creates conditions that don’t favour it.
- It has a thin taproot. This taproot isn’t very strong and you can remove this by hand.You are best to do this when it the plant is young and the soil is moist.
Chemical Wireweed Control.
- Chemical control is best in the Spring. This is when the weed is actively growing.
- You must manage this weed before it produces seeds. If you don’t then control becomes even more difficult.
Pre-emergents For Knotweed.
- Aim to apply these in the late Autumn to the early Winter.
- You may need to make several applications to get this weed under control.
- UK research estimates that you will need to treat it for 4 to 7 years to exhaust any seedbank.
Table of Pre-emergent Herbicides.
Product Name | Active Ingredient | Rate | Safe Turf Types | Target Weeds | Duration | |
Barricade | Prodiamine 480 g/L | 1 to 4 L/Ha | Couch, Kikuyu, Buffalo, Zoysia, Paspalum, Queensland Blue. | Winter Grass, Summergrass, Crowsfoot Grass, African Lovegrass, Parramatta Grass, Crabgrass, Paspalum. | Up to 6 months | Group 3 |
Spartan | Prodiamine 480 g/L | 1 to 4 L/Ha | Kikuyu, Buffalo, Couch, Zoysia, Seashore Paspalum, Queensland Blue. | Winter Grass, Summergrass, Crowsfoot Grass, African Lovegrass, Parramatta Grass, Crabgrass, Paspalum. | Up to 6 months | Group 3 |
Specticle | Indaziflam 200 g/L | 125 to 250 ml/Ha | Couch, Kikuyu, Buffalo, Zoysia | Winter Grass, Summer Grass, Crowsfoot, Annual grasses & broadleaf weeds | Up to 8 months | Group 29 |
Pennmag | Metolachlor 960 g/L | 2 L/Ha | Turf | Summer Grass, Crowsfoot, Winter grass | 3 to 4 months | Group 15 |
Battalia | Pendimethalin 435 g/L | 2.3 to 3.4 L/Ha | Couch, Kikuyu, Buffalo | Winter Grass, Summer Grass, Crowsfoot Grass, Broadleaf weeds | 4 to 5 months | Group 3 |
Ronstar | Oxadiazon 20 g/Kg | 150 to 200 Kg/Ha | Couch, Kikuyu, Zoysia, Buffalo. | Winter Grass, Crowsfoot Grass, Summer Grass, Sorrel, Oxalis. | Up to 3 months | Group 14 |
Dimension EW | Dithiopyr 240 g/L | 1.75 to 3.5 L/Ha | Couch, Kikuyu, Kentucky Bluegrass, Buffalo, Ryegrass, Zoysia | Crabgrass, Winter Grass, Crowsfoot, Chickweed, Summer Grass. | 4 to 6 months | Group 3 |
BASF Freehand | 10 g/kg Pendimethalin 7.5 g/kg Dimethenamid-P | 100 Kg/Ha | Couch, Kikuyu, Queensland Blue, Buffalo, Zoysia | Amaranth, Annual ryegrass, Bittercress, Mexican clover, Chickweed, Crowsfoot grass, Dandelion, Deadnettle, Fat hen, Black Pigweed, Mustard, Pigweed, Prickly lettuce, Shepherd’s purse, Summer grass, Toad rush, Wireweed | 4 to 6 months | Group 3 |
Post Emergent Control.
- Control with post emergents works best when Knotweed is young. Ideally it should still be in the seedling stage.
- Once it establishes and hardens off, it is more difficult to control.
- When Knotweed is less than 75 mm in diameter, you can control it with 2,4-D. However, even after this it may grow back from buds on the crown of the plant.
- In agricultureTopramezone is used to control Knotweed up to the 6- leaf stage.
- Products that contain Dicamba usually provide better results. However, you can’t use these safely on Buffalo Grass.
Post Emergent Options:
- 2,4-D. This tends to burn the top off Knotweed but it then grows back.
- Warhead Trio. Warhead is safe to use on Buffalo grass.
- Contra M herbicide. Don’t use Contra M on Buffalo grass.
- Weed Blast MA. This is safe to use on Buffalo grass.
- Casper Turf. Don’t use Casper Turf on Buffalo grass.
- Dicamba. Don’t use Dicamba on Buffalo grass.
- Stature. Stature Turf Herbicide is safe on all established cool and warm season grasses. However it is not for home garden use. For best results use this with a non-ionic surfactant.
Table of Post Emergent Herbicides for Knotweed Control.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | |
2,4-D | 2,4-D | 4 | 1.8 to 3.2 L | Wet the foliage. DO NOT mow lawn for 1 week before and after use. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass (WA only). | |
Casper | Prosulfuron + Dicamba | 2 + 4 | 800g to 1 Kg | Use from the Autumn to the Spring. Use high rates in cool months or if there is high weed pressure. Control takes 4 to 6 weeks. Use an NIS at 0.25 to 0.5% v/v. | |
Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Apply in 250 to 400 L of water. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass. Do not mow for 2 days before or after use or fertilise within two weeks. | |
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2 L + 3.2 L of 2,4-D Amine 625 g/L | Use a minimum of 1000 L/Ha water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. | |
Stature | MCPA + Bromoxynil + Diflufenican | 4 + 6 + 12 | 2 L | Use to actively growing weeds. Control may take 4 to 6 weeks. You may need to reapply in 4 to 6 weeks. Use a surfactant for difficult to wet weeds. Use in 200 to 500 L of water. Transient discolouration may occur up to 21 days after use. | |
Weed Blast MA | Bromoxynil + MCPA | 6 + 4 | 3 to 6 L | Use in a minimum of 500 L/Ha of water. DO NOT mow for 2 days after use. | |
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid any overlap. Use an NIS. | |
Post emergent Herbicide Research.
- Among 18 herbicide treatments, only six control Knotweed over 80%.
- These include: 2,4-D, Dicamba, Metsulfuron, and Chlorsulfuron.
- Bromoxynil, Triclopyr, Clopyralid, Quinclorac, Metribuzin, Rimsulfuron, Foramsulfuron, and Trifloxysulfuron, do not give good control in couch.
- Diflufenican, the active in Warhead Trio, acts as a long-term pre-emergent against this weed.
Non Selectives For Wireweed Control.
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks. However, it will grow back due to the limited movement of glufosinate.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate but if water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The following are non-selective. They also have a long term residual and stop any re-growth.
- Renegade. Renegade stops germination for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for chemical treatments.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown. It also has a residual that lasts for up to 3 months, and is safe to use near trees.
Table of Non Selectives for Wireweed Control.
Product | Active Ingredient | Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |