How to Control White Clover (Trifolium repens).
White Clover (Trifolium repens) is one of the most persistent lawn weeds in Australia. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to identify and manage this weed in your turf, including both chemical and non-chemical methods.
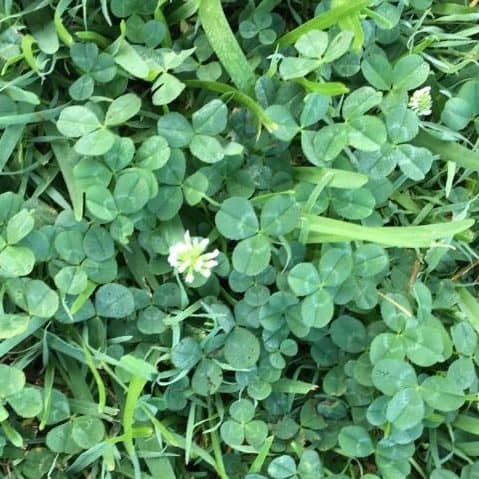
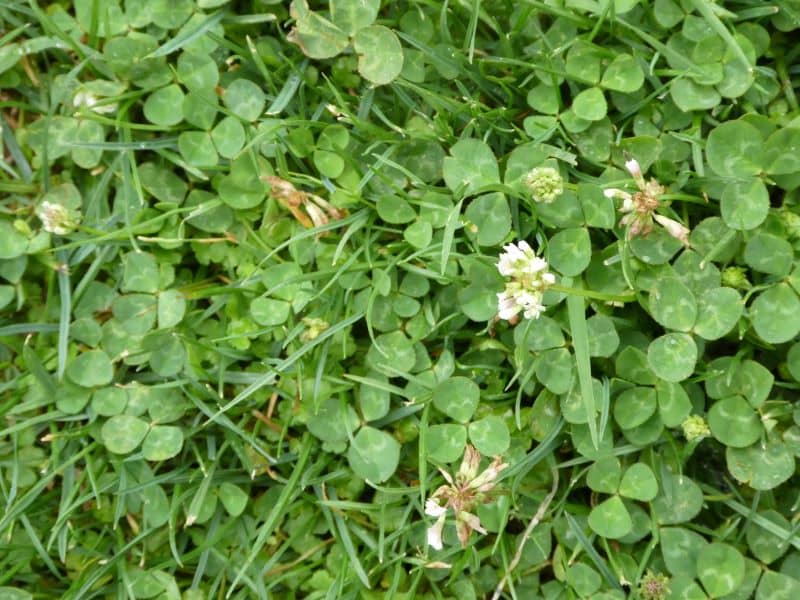
This is a common prostrate perennial weed of turf grass. You tend to see it in the Spring, Summer and Autumn, and it is easy to identify by its distinctive green, trifoliate compound leaves.
The distribution map is courtesy of The Atlas of Living Australia.
Why is White Clover a Problem Weed.
- It spreads rapidly and outcompetes existing turf.
- Once it establishes it spreads rapidly.
- It forms dense mats that choke out any existing turf grass.
- Triflolium repens competes with turf for soil nutrients.
- This weed is difficult to kill due to its root system, and the fact that it spreads by stolons.
- It is a legume and can fix N from the air. This means it thrives in N-deficient soils, which makes it more competitive vs turf grass.
- Clover is a persistent weed. It produces seeds that lie dormant in the soil for several years.
How to Identify White Clover.
Category: This is a broadleaf (Dicot) weed.
Photosynthetic Pathway: It is a C3 weed.
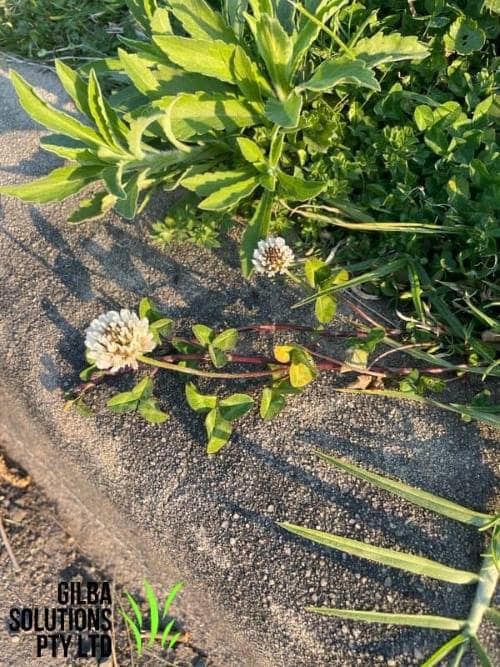
Flower: The flowers of Trifolium repens are white to pink, and look like a small pea. They tend to extend above the height of the leaves. It flowers from the Spring to the Autumn.
Height: This weed haș a prostrate growth habit.
Leaf length: The leaves have no hairs, have an oval to heart shape, and are 5 to 20 mm long.
Leaf width: The leaves are 5 to 14 mm wide.
Reproduction: It reproduces by seeds, and creeping stems that root at the nodes.
Comments: The leaf margins are slightly jagged. Each leaf has a distinct white crescent. This crescent encircles the base of each leaf, and forms a central white ring.
The trifoliate leaves cause cause it to be mistaken for Creeping oxalis, Spotted Medic, Black Medic and Burr Medic. There are several easy ways to tell these weeds apart.
Table Showing The Differences Between White Clover and Other Trifoliate Weeds.
Spreading | Leaf Marking | Trifoliate | Leaf Shape | Tooth at Tip of Leaf | Toothed Leaf Margins | Annual/ Perennial | Soil Conditions | Habitat | Flowers | |
White Clover | Yes | A pale green or whitish "V" or crescent shape. | Yes | Smooth rounded | No | Yes | Perennial | High pH | Open areas | White |
Spotted Medic | Yes | Yes. Distinct dark, heart-shape spot on each leaflet | Yes | Oval serrated | Yes | Yes | Winter Annual | Prefers slightly acidic to neutral soils (pH 5.5-7.0). | Full sun or partial shade | Yellow |
Black Medic | Yes | No | Yes | Oval serrated | Yes | Yes | Summer Annual | Prefers alkaline soils (pH of 6.5 to 7.8). | Full sun | Yellow |
Creeping Oxalis | Yes | No | Yes | Heart shape | No | Smooth | Perennial | High pH | Shade | Yellow with 5 petals |
Habitat: This is a very common turf weed, and you often find it in low N soils. This is because it is able to fix atmospheric N which gives it a compettiive advantage.
Once it establishes it tends to grow quickly and outcompete existing turf. It is a good indicator of low N soils but it does not tolerate droughty soils as it has a shallow root system. It prefers cool, moist weather on well-drained soils.
More on lawn and turf grass weeds is in our weed ID chart.
How to Control White Clover.
How to Manage White Clover?
- Once it establishes it is hard to hand remove.
- If you do hand pull it, you must make sure to remove all the roots and dispose of them to avoid any re-growth.
- The best way to do this is to grip the plant close to the ground and gently pull it up.
- For large patches, use a small garden spade or fork.
- Mow your turf at the right height. This is an effective non-chemical tool. It stops it from seeding, and encourages your turf to thicken up.
- If you fertilize your turf with N, it encourages the turf and not the weed. If you feed your turf it counters the ability of this weed to fix N.
- Don’t over water your turf. Trifolium repens likes moist soils.
The key to non chemical control is to have a dense, healthy turf cover. If you do this the turf outcompetes this weed and prevents it from spreading.
SUMMARY
- Trifolium repens is a very common turf weed in Australia
- The key to managin it is to maintain a healthy, dense grass cover.
- It is an indicator of low N soils.
- There are several pre and post emergent herbicides to manage this weed.
- Warhead Trio, Weedblast MA, Duke herbicide and MCPA are all afe to use on Buffalo grass.
Quick ID.
- It is a perennial weed.
- It is low growing and prostrate.
- The leaves are a distinctive green, and trifoliate.
- Each leaf has a distinct white crescent. This crescent encircles the base of each leaf, and forms a central white ring.
- They are hairless, and have an oval to heart shape.
- The flowers are white to pink, and look like a small pea.
- It flowers from the Spring to the Autumn.
- Often mistaken for Creeping oxalis, Spotted Medic, Black Medic and Burr Medic.
Chemical Control of White Clover.
Pre-Emergents For White Clover.
Trifolium repens is a perennial weed, which means that it will come back unless you kill it with a post-emergent herbicide. A pre-emergent only prevents the germination of seeds.
These stop new weeds from growing but won’t kill existing plants.
| Product | Active Ingredient | Rate per Ha | Cost per 100 m² | How Long It Works |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barricade | Prodiamine | 1 to 4 L | $143-572 | 24 weeks |
| Onset 10GR | Prodiamine | 50 to 150 Kg | $275-825 | 24 weeks |
| Dimension | Dithiopyr | 1.75 to 3.5 L | $280-560 | 18 weeks |
| Freehand | Pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P | 100 Kg | $1585 | 12 weeks |
| Specticle | Indazaflam | 250 ml | $495 | 32 weeks |
Post Emergents For White Clover.
These kill weeds that are already growing.
Important: Some products harm Buffalo grass. Check the table below.
| Product | Active Ingredients | Rate per Ha | Safe on Buffalo? | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,4-D | 2,4-D | 1.8 to 3.2 L | No (WA only) | Don’t mow 1 week before/after |
| Casper | Prosulfuron + Dicamba | 800 g to 1 Kg | No | Use Autumn to Spring |
| Contra M | Dicamba + MCPA | 6.5 L | No | Don’t mow 2 days before/after |
| Duke | Iodosulfuron | 100 g | Yes | Always add surfactant |
| MCPA | MCPA | 930 ml to 1.8 L | Yes | May damage fine grasses |
| Negate | Rimsulfuron + Metsulfuron | 110 g | No | Do not overlap |
| Recondo | Trifloxysulfuron | 300 g | No | Allow at least 6 weeks before overseeding. |
| Stature | MCPA + Bromoxynil + Diflufenican | 2 L | Yes | Safe on all cool and warm season turf. Not for home garden use |
| Weed Blast MA | Bromoxynil + MCPA | 3 to 6 L | Yes | Don’t mow 2 days after |
| Warhead Trio | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 5 L | Yes | May discolour some grasses |
| Quinstar | Quinclorac | 4.1 L | No | Cool season turf only |
| Pylex | Topramezone | 0.375 mL /100m² | No | Two treatments needed |
How to Use Post-Emergent Herbicides.
- Timing matters – Spray when Triolium repens is actively growing.
- Add surfactant – Most products need this.
- Don’t mow – Wait before and after spraying
- Be patient – Control takes from 4-6 weeks
- Repeat if needed.
Non-Selectives For White Clover.
These kill everything they touch. Use them carefully.
| Product | Active Ingredient | Rate per Hectare | How Long It Lasts | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 1 to 6 L | 4 to 6 weeks | This weed then tends to regrow due to the limited movement of glufosinate. |
| Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg | Short term | White clover can be tolerant to glyphosate. If water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray. |
| Numchuk Quad | Multiple ingredients | 20 to 25 L | 12 months | Long term knockdown and pre-emergent control |
| Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 7 L/1000L | 3 months | Safe to use near trees. |
| Renegade | Bromacil | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg | 12 months | Renegade stops germination for up to 12 months. |
Key Tips for Success.
- Maintain healthy turf – The best control is thick, well-fed grass.
- Spring and Autumn is the best time to treat – Treat when Trifolium repens is growing.
- Read the label – Always follow the label directions.