How to ID and Remove Chickweed.
Chickweed (Stellaria media) is an annual weed of the lawn and garden. It is able to quickly spread, and outcompete plants, and produces large numbers of seeds that germinate quickly. These then form dense mats and choke out desirable vegetation.
We discuss the identification of this weed and recommend products to control this weed in turf grass.
Both the annual Common Chickweed (Stellaria media) and perennial Mouse-Ear Chickweed (Cerastium fontanum) look very similar. However, they have different leaf and stem characteristics.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Common and Mouse Ear Chickweed.
- Know their habitat.
- Know the best options to manage them.
Why is Common Chickweed a Problem Weed?
- It spreads and reproduces quickly.
- It produces thousands of seeds.
- This weed competes with plants for sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- It forms dense mats that smother young seedlings and established plants.
- The dense mats can smother or shade young seedlings and established plants.
- You can hand remove individual plants. However, the sheer number of seeds they produce means that their management must be ongoing.
More information on turf weeds is in our weed ID chart.
How to Identify Common Chickweed.
Common Chickweed is often mistaken for Mouse Ear Chickweed.
Common Chickweed.
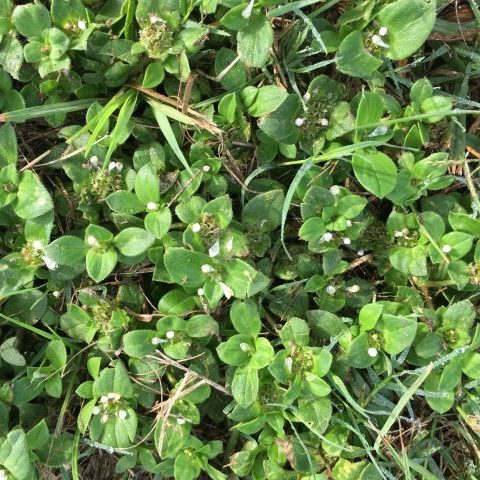
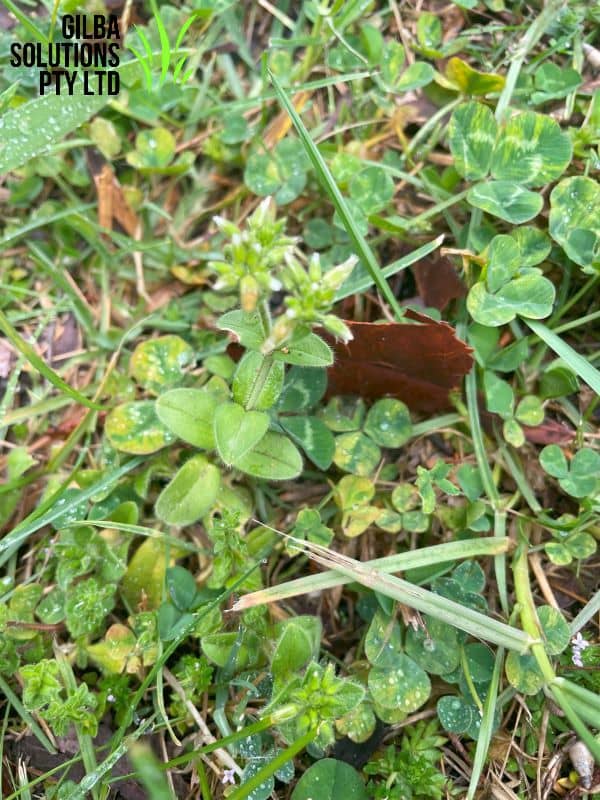
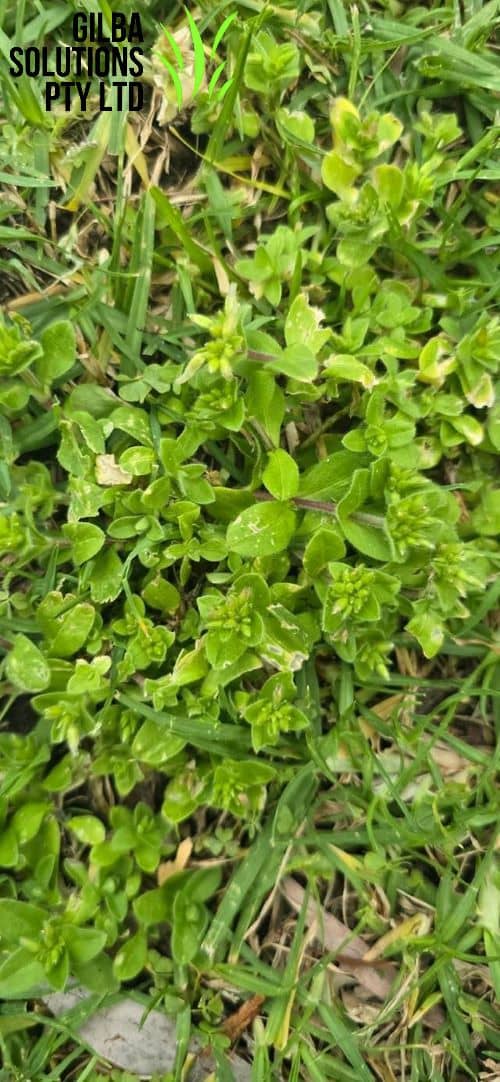
- It is a low-growing, bright green Winter annual. It has small white flowers that have five-petals.
- Unlike most cool season annuals, it persists through the Summer if it is not exposed to heat and drought.
- It forms large, dense patches but becomes upright if it isn’t mowed.
- The hairy stems often form mats that choke out turf grass.
- The prostrate stems can root at the nodes.
- The leaves have no hairs, and a single line of hairs on the stem.
- It grows in dense shade, and at much lower temperatures than many other weeds.
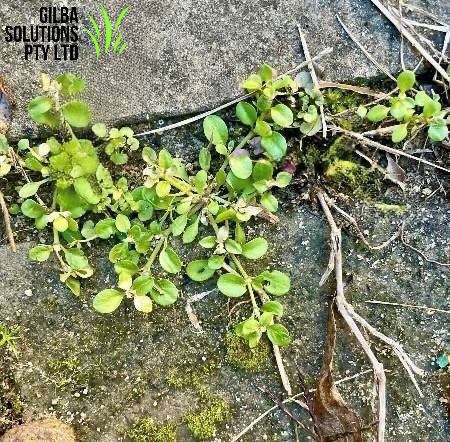
Mouse-Ear Chickweed.
- Mouse-ear Chickweed is a perennial weed.
- It has a similar growth habit to Common Chickweed but it is less common in turf grass.
- Its leaves often have an oblong shape, and it has hairy stems and leaves.
Table Showing Differences Between Common and Mouse Ear Chickweed.
Plant | Leaf colour | Leaf Hairs | Stems | Growth Habit | Flowers |
Common | Bright Light Green | Hairless or on one edge | One line hairs on either side | Annual | Petals deeply notched |
Mouse-Ear | Dark to grey green | Cover soft hairs | Forked and hairy | Perennial | Slightly notched |
- A good way to distinguish this plant from other plants is if you pull the stem until it breaks. With Chickweed the stem doesn’t break but stretches.
- It reproduces by seeds and by creeping stems which root at the nodes. While the plants can grow upright, they are more likely to form prostrate mats.
Category: This is a broadleaf (Dicot) weed.
Reproduction of Chickweed.
- It tends to germinate in the Autumn and the early Spring when temperatures are between 14 to 20°C.
- However, in shady, moist conditions it will germinate and grows through the season.
- Its seeds often germinate straight after they mature.
- Plants then grow vigorously, flower and set seed all within 5 weeks of emerging.
- Most seedlings emerge from the soil at depths of less than 25 mm. They dont emerge from depper than 50 mm.
Seed:
- This weed produces from 750 to over 30,000 seeds per plant, with an average of 2,500 seeds per plant.
- The seeds cling to fur, feathers and clothes, and also disperse by water, maintenance equipment, and in contaminated soil.
- The seeds are viable in the soil for over 10 years.
Comments: It has fibrous shallow roots.
- Chickweed grows vigorously in cool weather, and produces seeds through the Winter in mild regions.
- It flowers and seed within 2 to 3 months of germination.
- Mouse-ear Chickweed is a problem in lawns, where it can grow rapidly to infill damaged areas.
How to Remove Common Chickweed.
Both cultural and chemical control can manage this weed.
Cultural Control of Common Chickweed.
- Fertilize properly to maintain turf density.
- Mow at the right height,
- Irrigate appropriately for the turf type and time of year.
- Mowing is not effective. Close mowing encourages the plants to adopt a vigorous low growing growth habit.
- Hand removal works well as the weed pulls out easily. You must try to remove the entire plant before it seeds.
- You get the best results if the soil is moist when you hand pull it.
- Make sure to bag off the plants and remove any material off site.
- Chickweeds re-root from stem nodes in moist areas.
- Healthy, shade tolerant turf grass will outcompete this weed.
- Grass selection is also important. If you choose the wrong turf seed or grass type it makes management even more difficult.
- Improve the drainage and deal with any wet areas.
Chemical Control of Common Chickweed.
- Chemical control is best in the Autumn and the early Spring when plants are small.
- It is difficult to remove in cool weather, when the plants are large, or they develop a dense vegetative mat.
- Sulfonylurea resistance exists in the UK. So remember to rotate your chemistry.
- MCPA and 2,4-D are not very effective.
Pre-Emergent Control of Common Chickweed.
- Prodiamine (Onset 10GR, Spartan, or Barricade).
- S-Metolachlor (Pennmag).
- Propyzamide (ProForce Checkpoint).
- Pendimethalin (ProForce Battalia 435).
- BASF Freehand Herbicide.
- Esplanade Herbicide.
Post Emergent Control of Common Chickweed.
- ProForce Warhead Trio.
- Stature Herbicide.
- Dicamba. Do not use on Buffalo grass.
- Casper Turf Herbicide is registered in South Africa. Do not use on Buffalo grass
- Duke Herbicide.
- ProForce Contra M. Do not use on Buffalo grass.
- Recondo Herbicide.
Table of Post Emergent Herbicide Rates for Common Chickweed.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | ||||
Casper | Prosulfuron + Dicamba | 2 and 4 | 800g-1Kg | Apply from Autumn to Spring. Use high rates in cool months or if high weed pressure. Control takes 4 to 6 weeks. Use an NIS at a rate of 0.25 to 0.5% v/v. | ||||
Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Apply in 250-400L water. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass. After use do not mow for 2 days before or after application or fertilize within two weeks. | ||||
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2L + 3.2L of 2,4-D Amine 625g/L | Use a minimum of 1000L/Ha water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. | ||||
Stature | MCPA + Bromoxynil + Diflufenican | 4 + 6 + 12 | 2L | Apply to actively growing weeds. Complete control may take 4 to 6 weeks. A repeat application maybe needed in 4 – 6 weeks. Use a surfactant for difficult to wet weeds. Apply in 200 to 500 L of water. Transient discolouration may occur up to 21 days following application. | ||||
Duke | Iodosulfuron | 2 | 100g | Always use an NIS or Overtake Oil. Use in 200-500 L/ha water. | ||||
Recondo | Trifloxysulfuron | 2 | 225g | Use an NIS at 0.25% v/v (1000 g ai/L), 0.42% v/v (600 g ai/L) or Overtake Oil at 1%v/v. Ensure uniform placement onto leaves & into crowns. Water volume is 400 to 800 L/ha. You may need a repeat application in 4 to 6 weeks. Allow at least 6 weeks before overseeding. You may see discolouration on Qld Blue and Zoysia. | ||||
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid overlapping. Use an NIS. | ||||
Non Selective Control.
You cannot use any of these on lawns or turf areas to selectively remove this weed.
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks. However, it will tend regrow due to the limited movement of glufosinate.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate but if water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
These are non-selective but also have a long term residual and stop any re-growth.
- Renegade. Renegade stops germination for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for multiple herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives post and pre emergent control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown, and residual control for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use near trees.
Table of Non Selective Herbicides.
Product | Active Ingredient | Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |