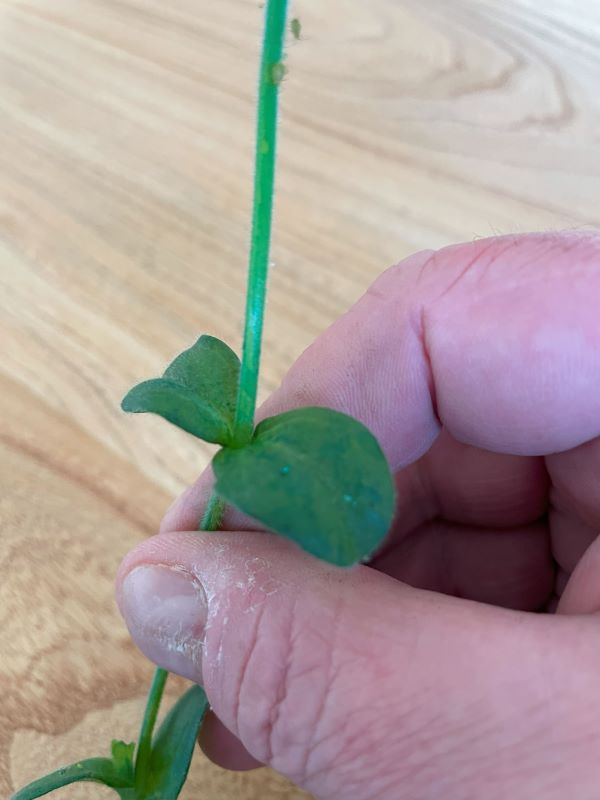
Mouse Ear Chickweed (Cerastium glomeratum)
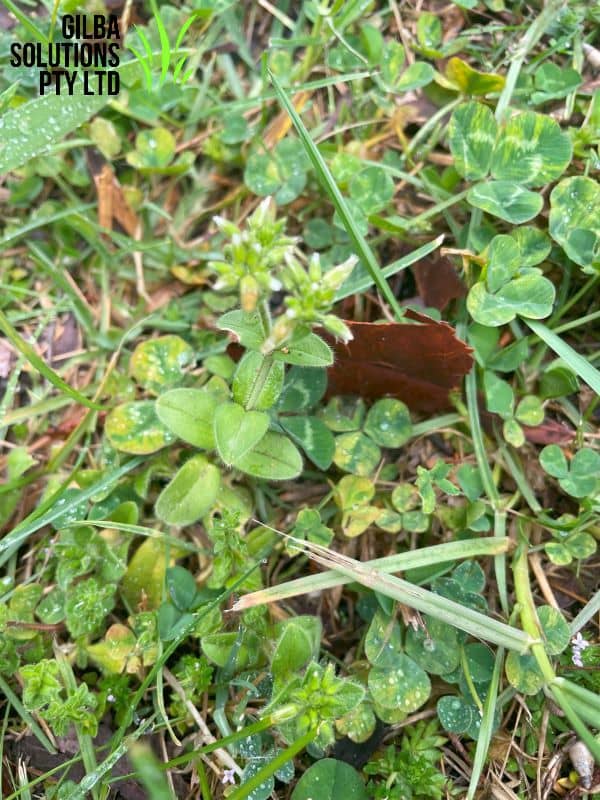
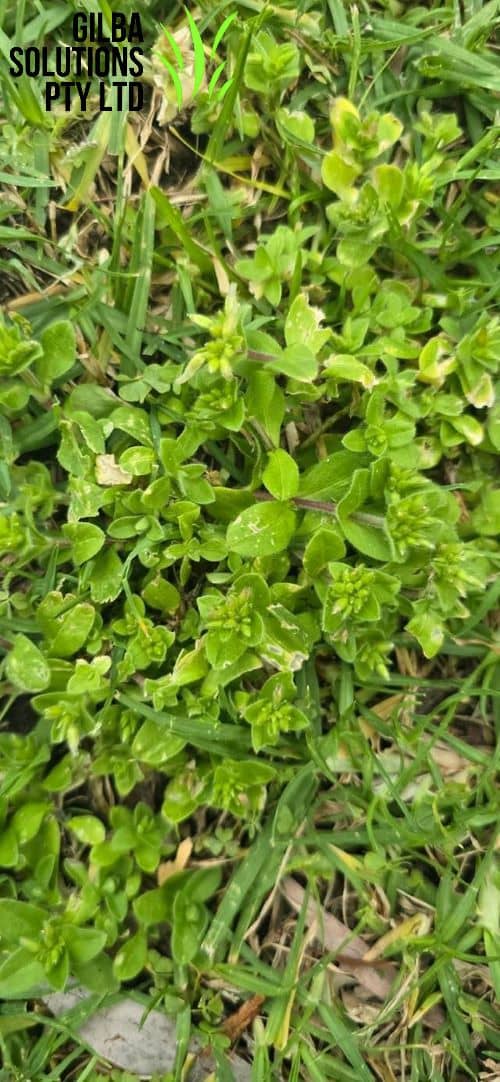
Mouse Ear Chickweed (Cerastium glomeratum) aka Sticky Mouse-Ear Chickweed is an invasive, low-growing annual that easily competes with other plants. It is common throughout Australia, but favours temperate areas like the Southern Highland and Central Tablelands of NSW and the ACT.
Mouse Ear Chickweed is an upright annual weed, and is similar to Common Chickweed (Stellaria media) but has a more erect habit. It is a highly unpalatable and a competitive weed in the grazing industry.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Mouse Ear Chickweed.
- Know its habitat.
- Know the best cultural and chemical options to control this weed.
Why is Mouse Ear Chickweed a Weed?
- Mouse Ear Chickweed reproduces by seeds and also quickly spreads vegetatively.
- The root system spreads and removes nutrients and moisture from the soil.
- It forms dense, mat, which smother other plants.
- It is very competitive and thrives in a wide range of conditions, and outcompetes native plants.
- Mouse Ear Chickweed seeds remain viable in the soil for several years.
- The leaves and stems have a cover of sticky hairs which make it difficult to remove.
Cerastium glomeratum is a problem in irrigated lawns and turf areas across Australia.
Mouse Ear Chickweed is a good indicator weed of moist soils, and in a turf situation it often indicates poor turf density.
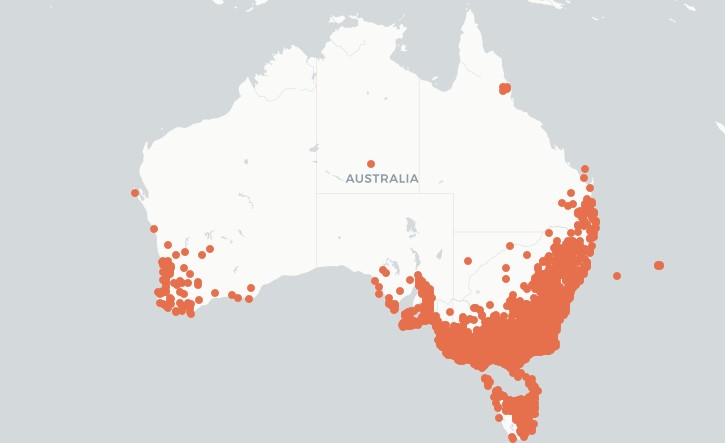
Thanks to The Atlas of Living Australia for the distribution map.
More information on turf weeds is in our weed ID chart.
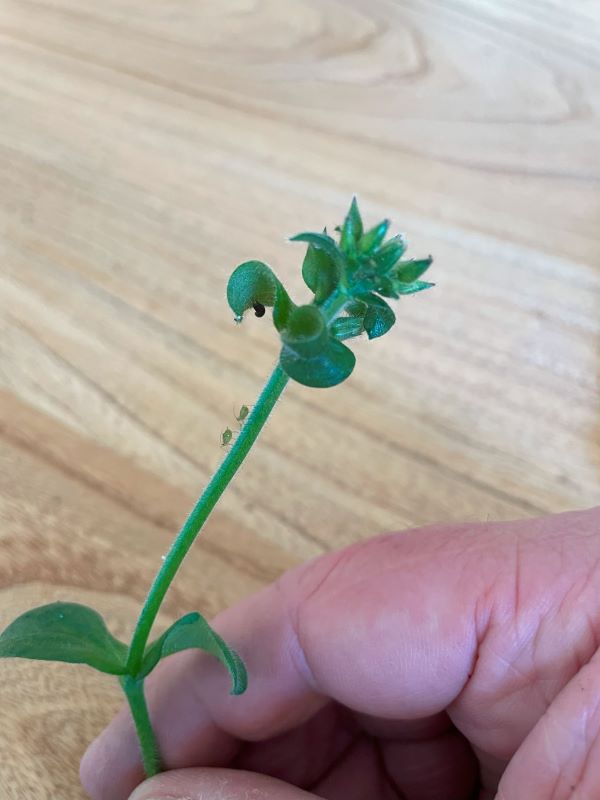
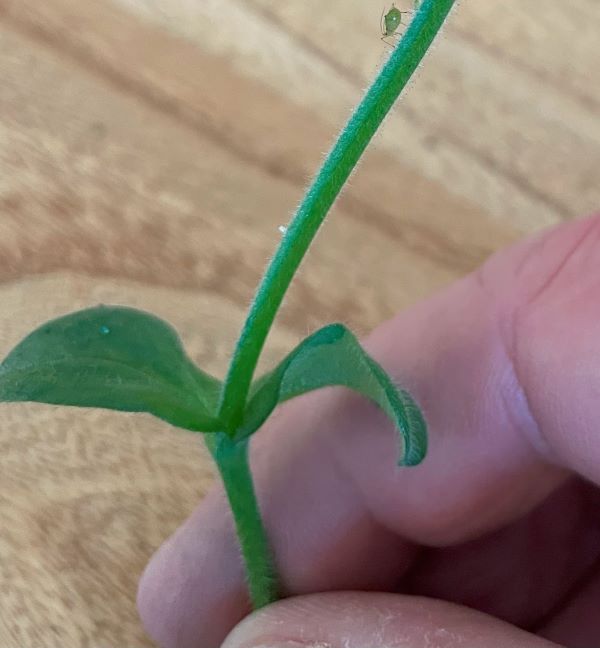
How to Identify Mouse Ear Chickweed.
A good way to distinguish Mouse Ear Chickweed from other plants is if you pull the stem until it breaks. With Mouse Ear Chickweed the stem doesn’t break but stretches.
Reproduction: Mouse Ear Chickweed reproduces only by seed. These seeds are spread by wind, water, vehicles, in mud and in agricultural produce. Some form of disturbance is essential for it to establish.
The seeds germinate when soil temperatures reach about 15°C; the optimal temperature being from 12° to 20°C. However, if the soil is very moist, seeds germinate at much higher temperatures.
The seeds tend to germinate at or very near to the soil surface, and germinate in large numbers after irrigation or rain. The deeper the seeds are buried or the drier the soil, the less likely it is that the seeds will germinate or the seedlings will survive. The lifecycle of this weed is 5 to 6 weeks.
Comments: The stems are 2.5 to 5 cm long.
Habitat: Mouse ear Chickweed is common along roadsides, in lawns and adjacent grasslands.
How to Manage Mouse Ear Chickweed.
Both cultural and chemical control can control this weed.
Cultural control of Mouse Ear Chickweed.
- Maintain turf density by fertilizing, mowing at the right height of cut, and irrigating appropriately.
- Hand weeding works well but you must make sure that you remove the entire plant and that includes the roots to prevent re-growth.
- Grass selection is also important. If you choosing the wrong turf seed or grass type it has serious implications in Mouse Ear Chickweed (Cerastium glomeratum) management in the future.
Chemical Control of Mouse Ear Chickweed.
- Chemical control of Cerastium glomeratum is best in the Autumn and the early Spring when the plants are small, and before they flower.
- Mouse Ear Chickweed is difficult to control in cool weather, when plants are mature, and when they develop into a dense vegetative mat.
- Sulfonylurea herbicide resistance in Chickweed exists. So remember to regularly rotate your chemistry.
- MCPA and 2,4-D are not very effective against Mouse Ear Chickweed.
Pre-Emergent Control of Mouse Ear Chickweed.
Oxadiazon is NOT effective against this weed.
- Prodiamine (Onset 10GR, Spartan, or Barricade).
- S-Metolachlor (Pennmag).
- Propyzamide (ProForce Checkpoint).
- Pendimethalin (ProForce Battalia 435).
- BASF Freehand Herbicide.
- Esplanade Herbicide in NZ and Australia.
Post Emergent Control of Mouse Ear Chickweed.
- ProForce Warhead Trio.
- Stature Herbicide. Not for Home use.
- Dicamba. Do not use on Buffalo grass.
- Casper Turf Herbicide is registered in South Africa. Do not use on Buffalo grass
- Duke Herbicide.
- ProForce Contra M. Do not use on Buffalo.
- Recondo Herbicide.
Table of Selective Post Emergent Mouse Ear Chickweed Herbicides.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | ||||
Casper | Prosulfuron + Dicamba | 2 and 4 | 800g-1Kg | Apply from Autumn to Spring. Use high rates in cool months or if high weed pressure. Control takes 4 to 6 weeks. Use an NIS at a rate of 0.25 to 0.5% v/v. | ||||
Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Apply in 250-400L water. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass. After use do not mow for 2 days before or after application or fertilize within two weeks. | ||||
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2L + 3.2L of 2,4-D Amine 625g/L | Use a minimum of 1000L/Ha water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. | ||||
Stature | MCPA + Bromoxynil + Diflufenican | 4 + 6 + 12 | 2L | Apply to actively growing weeds. Complete control may take 4 to 6 weeks. A repeat application maybe needed in 4 – 6 weeks. Use a surfactant for difficult to wet weeds. Apply in 200 to 500 L of water. Transient discolouration may occur up to 21 days following application. | ||||
Duke | Iodosulfuron | 2 | 100g | Always use an NIS or Overtake Oil. Use in 200-500 L/ha water. | ||||
Recondo | Trifloxysulfuron | 2 | 225g | Use an NIS at 0.25% v/v (1000 g ai/L), 0.42% v/v (600 g ai/L) or Overtake Oil at 1%v/v. Ensure uniform placement onto leaves & into crowns. Water volume is 400 to 800 L/ha. You may need a repeat application in 4 to 6 weeks. Allow at least 6 weeks before overseeding. You may see discolouration on Qld Blue and Zoysia. | ||||
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid overlapping. Use an NIS. | ||||
Non Selective Control.
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks, but Mouse Ear Chickweed regrows and recovers due to the limited movement of glufosinate.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate but if water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The following are non-selective but also have a long term residual and stop re-growth of Mouse Ear Chickweed.
- Renegade. Renegade stops germination for up to 12 months, and reduces the need for multiple herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent control for up to 12 months
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown of Mouse Ear Chickweed, and residual control for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use around trees.