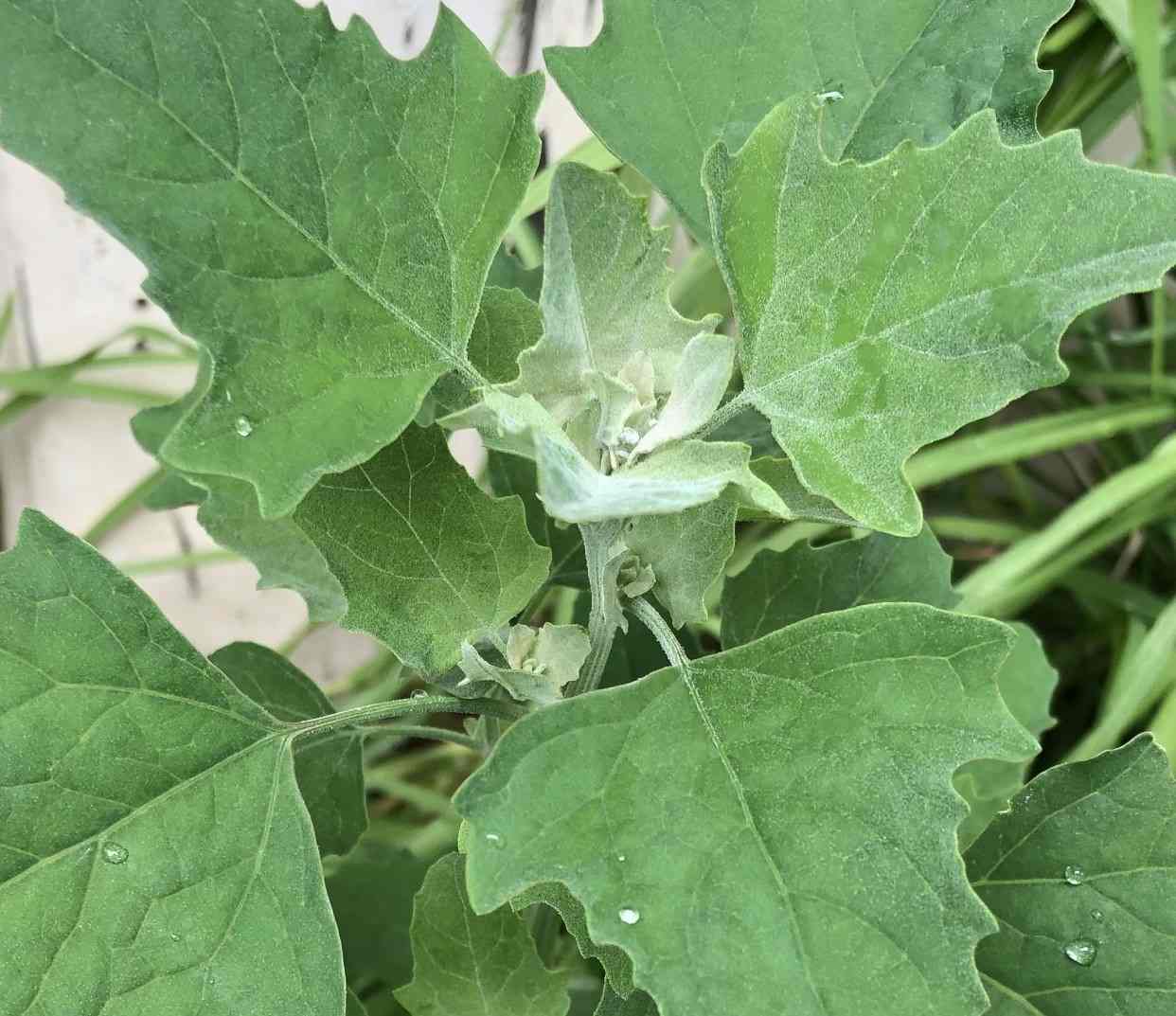
Fat Hen Weed (Chenopodium album)
Fat Hen weed is also known as White Goose foot or Common Lamb’s Quarters in Australia. It is an erect Summer annual, that is up to 2 m high and usually has stripes on its stems.
Once you read this, you will:
- Know how to ID Fat Hen weed or Goose foot.
- Know what conditions favour Goose foot or Lamb’s Quarters.
- Have a good idea of the best way to control it.
Why is Fat Hen Weed a Problem?
- This is a big problem if it grows too large. It smothers nearby plants..
- It competes with other plants for light, nutrients and moisture.
- It is a heavy seed producer.
- The seeds are viable for a long time.
- It has an advantage over many plants as it is an early Spring emerging weed that also has one of the longest emergence durations.
- Once it germinates it flowers in as little as 5 weeks.
- Goose Foot produces viable seeds two to three weeks after it flowers.
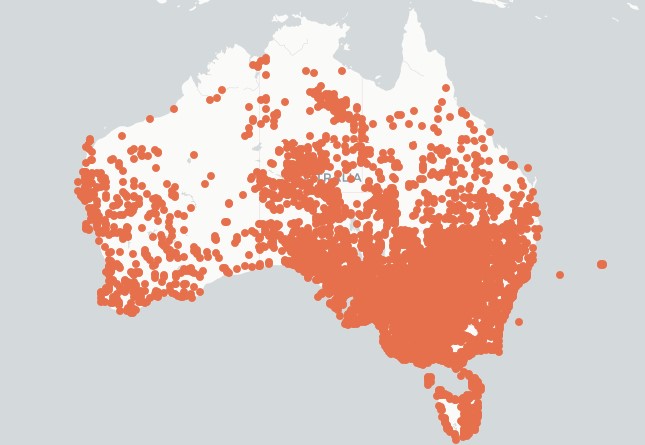
The distribution map is courtesy of The Atlas of Living Australia.
More information on lawn weeds is in our weed ID chart. What weeds reveal about soil conditions is in our blog on indicator weeds.
Fat Hen Weed Identification.
- White Goose foot is a tall, heavy seeding Summer annual or biennial herbaceous plant. It prefers high rainfall, temperate to sub-tropical conditions, and only reproduces by seed.
- The seeds germinate in the Spring, and then continue to germinate through the Summer and into the Autumn.
- It has a short, branched taproot, and it is only moderately drought tolerant.
- It is sensitive to frost.
Category: It is a Broadleaf (Dicot) weed.
Photosynthetic Pathway: Fat Hen is a C3 Weed.
Flower: Fat Hen weed has inconspicuous clusters of green or white flowers. In some cases it can flower in the Spring but it tends to mainly flower in the late Summer and the Autumn.
Height: It grows from 20 cm up to 2 metres in height.
Leaf length: The leaves of Fat Hen weed have an elliptic to diamond-shape, and are 20 to 60 mm long.
Leaf Width: The leaves are 5 to 30 mm wide, and have a pointed tip. The lower leaves sometimes have angular teeth.
Reproduction:
- Fat Hen weed reproduces only by seed.
- It is a heavy seed producer, and produces up to 75,000 seeds per plant.
- Seeds are spread by birds and mammals, with about 20% germinating immediately.
- The rest of the seeds remain viable for several decades.
Seed longevity: > 5 years.
Seed decline: 21% per year.
Germination depth: 4.8 cm.
Seeds/flower: 1.
Seeds/plant: 3,000 to 20,000.
Comments: The leaves have an oval to trowel-shape, and their edges have teeth or irregular lobes. The upper leaf surface is green, and the lower surface is a mealy white.
Habitat: Lamb’s Quarters has a preference for well-drained high pH soils but can also find it on low pH soils.
How to Control Fat Hen Weed.
You can use cultural and chemical controls to remove Goose foot.
Management Calendar for Fat Hen Weed or Goose Foot.
Management Calendar for Fat Hen | ||||||||||||
Summer annual | ||||||||||||
Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Flowering | ||||||||||||
Pre Emergent Herbicide | ||||||||||||
Post Emergent | ||||||||||||
Cultural Control of Fat Hen Weed.
- Feed your turf properly.
- Make sure that you mow at the right height of cut for the turf type present.
- Hand removal is practical if it isn’t too widespread. You should do this before it seeds in the Summer. Remove any flowering plants off site, and don’t leave them on the surface. This makes sure that viable seed isn’t left to grow back.
Lambs Quarters has a high nutrient requirement.
- It responds strongly to N and has a moderate response to P.
- High rates of N favour it.
- It has a strong response to high K levels, and it is very competitive when K levels are high. Limit N and K where possible.
Chemical Control of Fat Hen Weed.
Pre-Emergents for Fat Hen.
- ProForce Battalia.
- BASF Freehand.
- In NZ Esplanade has a label for this weed.
- Ethofumesate.
- In the USA, Specticle and Prodiamine have a label for this weed.
Post Emergents for Fat Hen Weed.
- There are several options to control Goose Foot.
- Treatment works best you use these within 3 weeks of seed germination.
- After this time, this weed tends to become woody and tricky to control.
- You will need repeat treatments to control any regrowth.
- It is difficult to wet, so use an NIS like OptiSpread 1000 at 0.25 to 0.5 v/v.
- It is difficult to wet, because Goose Foot has a crystalline leaf wax layer similar to those in grasses.
Selective post emergents include:
- 2,4-D Amine. Use when the weeds are young and actively growing. You may well need to make repeat applications.
- Dicamba. Use on growing plants. Small plants are easy to control, and you will need higher rates for large plants. Do not use when the temperature exceeds 26°C. Do not use Dicamba on Bufffalo grass.
- MCPA. This increases the spectrum of weed control if it is in a mix.
- Ethofumesate.
- Warhead Trio.
- Quali-Pro Nutmeg.
- Pylex in the USA.
You will get the best results when you:
- Only use chemicals on actively growing weeds.
- Allow time between spraying and when you mow. This gives time for the chemical to work.
- Do not spray when the weed is under stress due to drought or cold weather.
Table of Fat Hen Post Emergents.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | ||||
2,4-D | 2,4-D | 4 | 1.8-3.2 | Wet foliage. DO NOT mow lawn for 1 week before and at least 1 weed after use. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass (WA only). | ||||
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2L + 3.2L of 2,4-D Amine 625g/L | Use a minimum of 1000L/Ha water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. | ||||
MCPA | MCPA | 4 | 930ml -1.8L | Apply in high volume to actively growing weeds. DO NOT mow for 2 days before use. You may see some transitory damage on fine turf. | ||||
Nutmeg | Bentazone | 6 | 2 to 3 L/ha in 200 to 500 L of water per Ha | For best results, use on small and actively growing weeds, with good soil moisture. Several applications may be needed. Do not exceed two applications within 4 weeks. The addition of a non-ionic wetter such as Optispread 1000 at 125 mL per 100 L of the spray volume may improve weed control. | ||||
Pylex | Topramezone | 27 | 0.375 mL/ 100 m2 in 4-6 L water + 0.5% MSO | Apply 2x 21-28 days apart. You may see bleaching of Bent after 7-14 days. Do not water for 24 hrs post use. | ||||
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid overlapping. Use an NIS. | ||||
Non Selectives for Fat Hen Weed.
You cannot use any of these on lawns or turf areas to selectively remove this weed.
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks. However, it will regrow due to the limited movement of glufosinate.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate but if water quality is an issue use ProForce Manta Ray.
These are non-selective. They also have a long term residual and stop any re-growth of Lamb’s Quarters.
- Renegade. Renegade stops germination of Goose foot for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives post and pre emergent control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown, and residual control for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use near trees.
Table of Non Selectives for Fat Hen Weed.
Product | Active Ingredient | Chemical Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole + Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |