Dock Weed (Rumex spp)
Dock Weeds are annual or perennial weeds that have thick taproots. Docks contain oxalates and are toxic to dogs, cats and horses
In well irrigated areas it can become a major problem. It grows in meadows, pastures, ditches, and waste ground.
Once you read this you will be able to:
- Identify Docks.
- Know the habitat of the Dock Weed.
- Know the best cultural and chemical options to control Dock.
Why is Dock a Problem Weed?
Docks are a problem weed because of their aggressive growth, ability to produce a huge number of seeds, and the fact that they are difficult to control.
- Compete for Resources. The large leaves and roots of Dock weeds means that they are very effective to compete with other plants for sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- Aggressive Growth and Spread. Docks produce huge numbers of viable seeds, and they also regrow from small small root fragments.
- Difficult to Control. They have deep taproots and regenerate from fragments which means they are difficult to control.
- Toxic to Livestock. Some Docks accumulate oxalates and nitrates, which are toxic to livestock in large quantities, particularly horses.
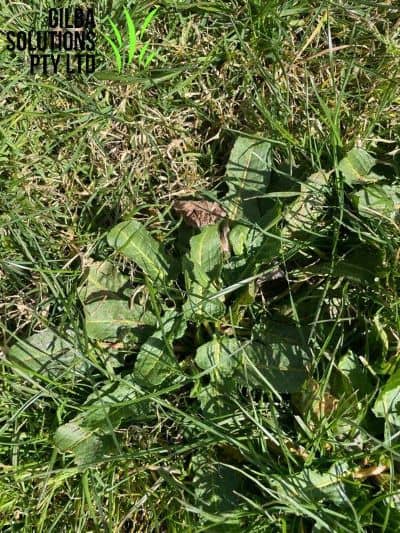
Both Curly Dock Weed (Rumex crispus) and Broadleaf Dock ((Rumex obtusifolius) are common weeds of turfgrass. Their hairless leaves form a basal rosette, and have an erect, branched flowering stem. Depending on the species, the leaves may be narrow or broad.
- Broad Leaf Dock is up to 1.5 m tall, with pointed oval leaves 4 to 24 cm long.
- Curly Dock Weed is 50 to 120 cm tall, though it may grow higher. It has long coarse basal leaves with wavy margins. Its leaves are 4 to 8 times longer than the leaves of Broad Leaf Dock.
- Broad Leaf Dock is an aggressive weed that competes with turfgrass for space, light, moisture and nutrients.
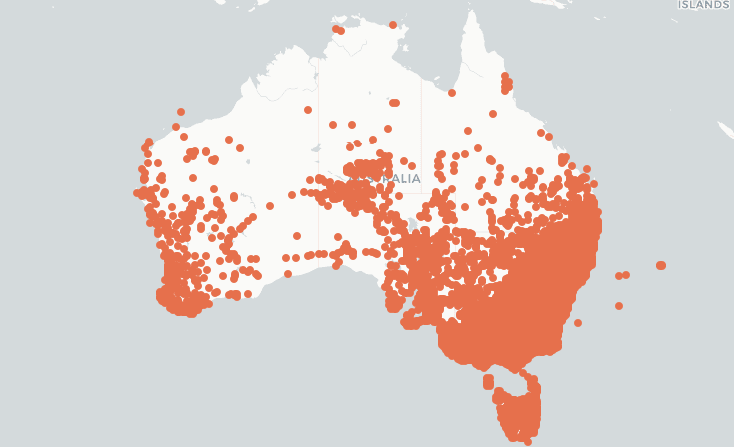
The Dock Weed Distribution map for Australia is courtesy of The Atlas of Living Australia.
Dock Weed Identification.
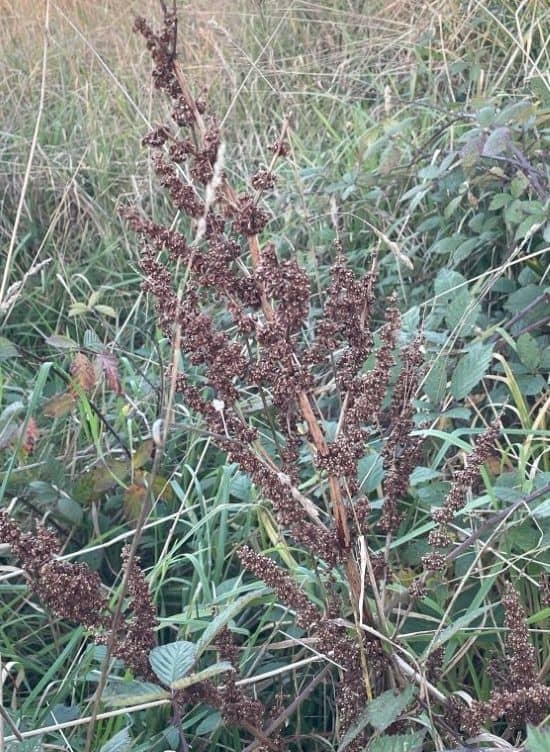
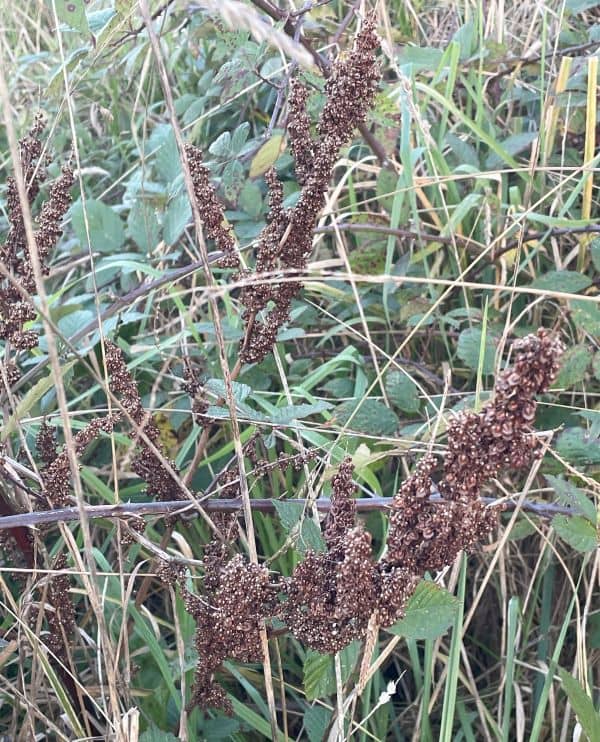
In Australia, Docks start to grow in the Winter, and flower and fruit by the early Summer. This is when the above-ground branches die and turn brown.
Spring and Autumn are the main germination periods. Young Dock Weed plants overwinter as a rosette, and above ground growth is slow until a taproot develops.
Category: Broadleaf (Dicot).
Photosynthetic Pathway: C3 Weed.
Flower: Dock flowers are small, green and in clusters at the end of the upright stems. The flower clusters of Broadleaf Dock are not as dense and closely spaced as those of Curly Dock Weed. Once the flowers die, the fruit takes on a rusty-brown colour, and tend to stay on the plant over the Winter.
Height: Dock Weeds are 50 to 130 cm tall.
Leaf length: The leaf blade is thin, egg-shaped, and around 25 cm long. It has a blunt to pointed tip and its base is round-lobed.
Leaf width: The leaves are about 12 cm wide.
Reproduction of Dock Weed.
Broadleaf and Curly Dock Weeds spread by seed, which falls close to the plant. The seed also spreads due to animals, machinery or humans that brush against them. They also disperse by wind.
The fruit can disperse long distances by water, due to a corky appendage called a callosity that allows them to float.
Seeds of Broadleaf Dock survive at least 40 years under favourable conditions, and Curly Dock seeds can remain viable in the soil for up to 80 years.
| Broadleaf Dock | Curled Dock |
| Seed longevity: >5 years. | Seed longevity: >5 years |
| Germination depth: 5 cm. | Germination depth: 3 cm |
| Seeds/flower: 1. | Seeds/head: 1 |
| Seeds/plant: 7,000. | Seeds/plant: 3,000–40,000 |
About half of the Curly Dock Weeds die after they flower, and a typical plant lives about three years. Both species are relatively short-lived perennials. Less than 2% of Broadleaf Dock and 4 to 24% of Curly Dock survive for more than four years.
The crown and upper taproot also regrow from fragments left behind during soil cultivation.
Comments: Both Curly Dock and Broadleaf Dock Weed are big seed producers. Docks are an aggressive weed, and have a deep root system that depletes the soil of nutrients and moisture. They are frost and drought tolerant.
Habitat: Docks indicate moist to wet ground, which is at least occasionally waterlogged. Swamps and marshes are its common habitats. Curly dock is an indicator of compaction.
For more information on weeds check out our weed ID Chart.
How to Control Dock Weed.
You can control Dock Weed by cultural and chemical means, but successful management of this weed is best if you adopt an integrated approach. Autumn is an ideal time carry out control of this perennial weed.
Dock Weed Management Timeline.
Management Calendar for Dock | ||||||||||||
Perennial. | ||||||||||||
Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Vegetative Growth | Plant overwinters as a rosette | |||||||||||
Flowering | ||||||||||||
Pre emergent herbicide | ||||||||||||
Post emergent herbicide | ||||||||||||
Cultural Control of Dock Weed.
- Both Curly and Broadleaf Dock Weed are difficult to control by hand due to their deep taproot. If the root breaks off while you try and hand remove the plant it regrows from the part that remains in the soil. A better option is to cut them off about 50 mm below the surface with a shovel.
- Regular mowing before Dock Weed seeds is effective to reduce seed production.
- Anything that increases the ability of desirable turf grasses to out compete Docks is a good thing. So deal with any soil compaction, and encourage a dense grass cover.
- Avoid scalping or mowing too short as this will limit any gaps in the canopy for Dock Weeds to emerge. Work in Ireland actually shows that docks germinate and grow better when there are high K levels in the soil.
- Dock Weed seeds need light to germinate, and so a thick, dense grass cover helps prevent it establishing. Once this weed gets too big, say around the 5 to 6 leaf stage onwards, turf grass will not outcompete this weed.
- Another key to its management is to have a fertile soil. This means adequate levels of N, P and K, plus the right soil pH for the grass you have.
Chemical Control of Dock Weed.
The aim of control with this weed is to reduce the seedbank and keep it at a low level.
Pre-Emergents for Dock Weed.
- ProForce Battalia is worth looking at.
- In NZ Esplanade is registered for Dock Weed.
- In the USA, Specticle and Prodiamine are labelled for this weed.
Post Emergent Herbicides for Dock Weed.
Selective post emergent Curly Dock Weed killers include:
- 2,4-D Amine. Apply when weeds are young and actively growing. Repeat applications may be necessary.
- Dicamba. Apply to rapidly growing Dock Weeds. Smaller plants are more easily controlled. Use higher rates for larger plants. Do not apply when outside temperatures exceed 26°C. Do not use on Bufffalo.
- Contra M. Do not use on Buffalo.
- Casper Turf Herbicide. Add a non ionic surfactant at 0.25 to 0.5 v/v. We recommend OptiSpread 1000. Do not use on Buffalo.
- Recondo Herbicide. Do not use on Buffalo.
- Warhead Trio.
You will need repeat treatments to control regrowth. Dicamba is effective on Curly Dock but not on Broadleaf Dock Weed.
You will get the best results when you:
- Only apply herbicides to actively growing Dock Weeds.
- Only apply any chemical, after you mow off any seed stalks and let it regrow.
- Allow adequate time between spraying and mowing for the herbicide to work. This is especially important if it has a deep taproot.
- Do not spray when Dock Weed is under stress due to drought or cold weather.
Table of Post Emergent Dock Weed Herbicides.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | ||||
2,4-D | 2,4-D | 4 | 1.8-3.2 | Wet foliage thoroughly. DO NOT mow lawn for 1 week before and at least 1 weed after application. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass (WA only). | ||||
Casper | Prosulfuron + Dicamba | 2 + 4 | 800g-1Kg | Apply from Autumn to Spring. Use high rates in cool months or if high weed pressure. Control takes 4 to 6 weeks. Use an NIS at a rate of 0.25 to 0.5% v/v. | ||||
Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Apply in 250-400L water. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass. After use do not mow for 2 days before or after application or fertilize within two weeks. | ||||
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2L + 3.2L of 2,4-D Amine 625g/L | Use a minimum of 1000L/Ha water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. | ||||
Recondo. | Trifloxysulfuron | 2 | 225g | Use an NIS at 0.25% v/v (1000 g ai/L), 0.42% v/v (600 g ai/L) or Overtake Oil at 1%v/v. Ensure uniform placement onto leaves & into crowns. Water volume is 400 to 800 L/ha. You may need a repeat application in 4 to 6 weeks. Allow at least 6 weeks before overseeding. You may see discolouration on Qld Blue and Zoysia. | ||||
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid overlapping. Use an NIS. | ||||
Non Selective Herbicides for Dock Weed.
You can use Glyphosate as a non selective option to control this weed, although herbicide resistance has been reported overseas. If you use Glyphosate for Dock Weeds and water quality is an issue then we recommend the use of ProForce Manta Ray.
Other options for Dock Weed include:
Table of Non Selective Herbicides for Dock Weed.
Product | Active Ingredient | Chemical Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole + Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000 L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |