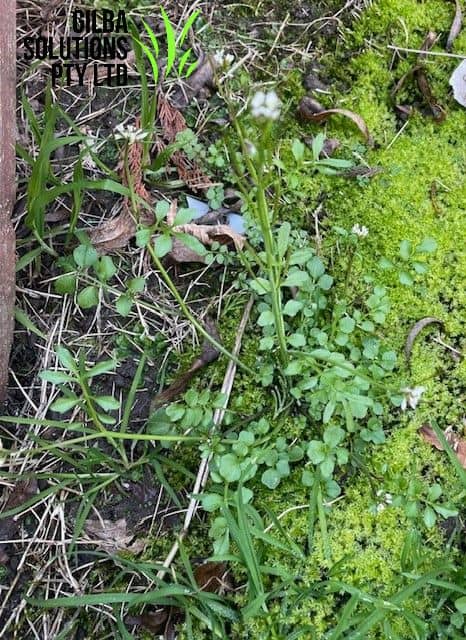
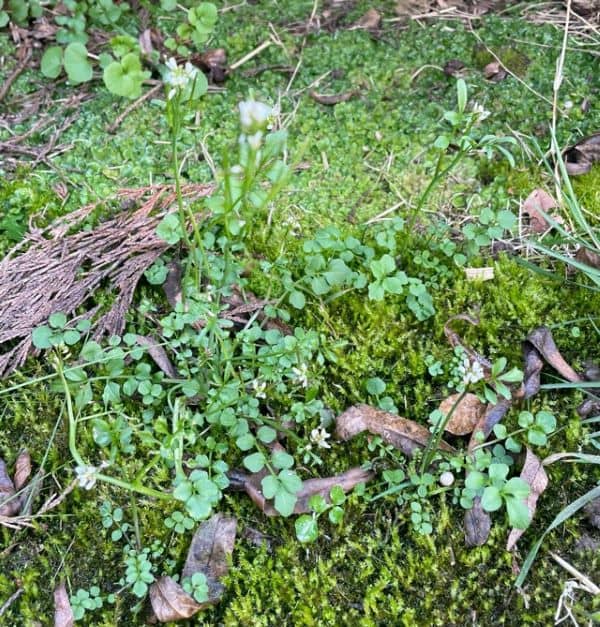
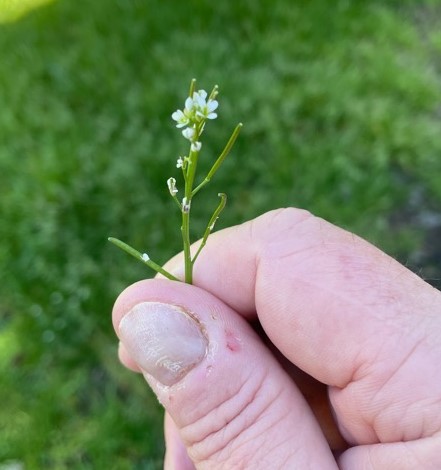
Hairy Bittercress (Cardamine hirsuta).
Hairy Bittercress is also called Swinecress and Flick Weed. It is a Winter annual broadleaf weed and is a member of the mustard family.
For more information, please check out our weed ID chart.
This weed is a good indicator of poorly drained, wet soils. It is often is found in disturbed areas.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Swinecress and Flick Weed.
- Know its habitat.
- Know the best cultural and chemical options to control it.
Why is Bittercress a Weed?
- This weed produces a large number of seeds.
- The seeds germinate immediately or stay dormant for several years.
- The seeds are sticky so disperse easily.
- In a moist environment like the Southern Highlands of NSW, this weed germinates, and grows at any time of the year.
- It is a host plant for aphids.
This weed is typically one of the first weeds to appear in the Spring. However, it can grow all the year-round when suitable conditions exist.
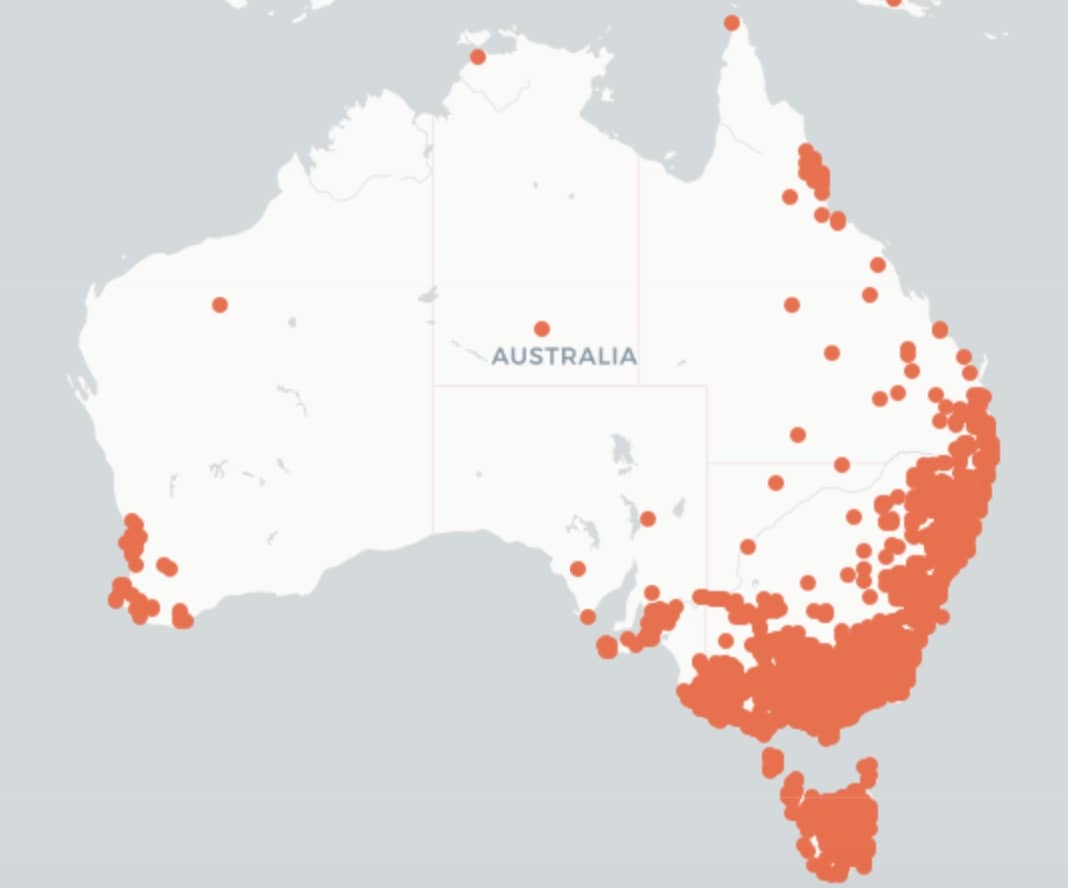
The distribution map is courtesy of The Living Atlas of Australia.
Bittercress Identification.
Flick Weed is a weed in the ACT, NSW, NT, QLD, SA, TAS, VIC, and WA.
Category: It is a broadleaf (Dicot) weed.
Photosynthetic Pathway: This weed is a C3 Weed.
Flower: The white flowers are tiny with four white petals. They are around 3 mm long.
Height: It is a Slender annual herb that grows to a height of 35 cm.
Leaves: Flick Weed has thin, sparsely hairy leaves that form a rosette at the base. These leaves have 1 to 7 leaflets. The side leaflets are circular and the terminal leaflets have a kidney shape. On both sides of the leaves are numerous tiny hairs.
Reproduction:
- Bittercress forms lime green seed pods up to 25 mm long.
- These flick the seeds out when they are ripe. The seeds can travel 1 to 2 metres from the plant.
- Each plant produces up to 5,000 seeds.
- These can germinate immediately.
- However, if conditions they can survive for several years.
Comments: The seeds tend to germinate in the Autumn or Winter. They stay dormant in cold weather. In the Spring they resume their growth, and then produce more seeds. It has a 12-week lifecycle.
Habitat: This weed inhabits most gardens and thin lawns. It is common in damp, sunny or disturbed soils.
How to Remove Bittercress from your Lawn.
Cultural Control of Bittercress.
- Prevention is the best way to manage this weed.
- Hand weeding is very effective to manage small populations. However, you must repeat this regularly.
- It is also important to hand weed before it flowers. This is because the seeds will still disperse when you handle the plants.
- Once you pull it up, remove the plant from the area and dispose of it.
- The seeds tend to not germinate where there is competition or shade i.e. dense turf grass. This means that turf grass selection for your site is important.
- Proper fertilising, mowing, and watering will encourage turf growth. This also reduces the chances of weed establishment.
- If you frequently mow in the Spring, this removes the flowers before any seeds develop.
- However, as this weed grows from a rosette, it tends to tolerate mowing.
Management Calendar for Bittercress.
Being a temperate weed there are some geographical variations with the timings. However this does give you a good place to start.
- Note the importance of regular mowing and hand pulling of this weed.
- Also, be aware of the short period between germination and seed production.
Management Calendar for Bittercress | ||||||||||||
Winter annual | ||||||||||||
Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Hand Pull/Mow | ||||||||||||
Pre emergent Herbicide | ||||||||||||
Post Emergent Herbicide | ||||||||||||
Chemical Control of Bittercress.
Several post-emergents are available to control this weed. Treatment is best over the entire area rather than spot treating.
Pre-emergents for Bittercress.
- Currently only BASF Freehand and Pendimethalin (ProForce Battalia 435 Herbicide) have a label for this weed in Australia.
- In the US, pre-emergents include: Dimethenamid-P + Pendimethalin, Indaziflam, Oxadiazon, and Dithiopyr.
Post Emergents for Bittercress.
Post emergents include:
- 2,4-D.
- Warhead Trio. Safe on Buffalo grass.
- Contra M herbicide. Do not use Contra M on Buffalo grass.
- MCPA.
- Weed Blast MA. Safe on Buffalo grass.
- Dicamba. Don’t use Dicamba on Buffalo grass..
- Quali-Pro Negate.
Rate Table for Post Emergent Bittercress Herbicides.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | ||||
2,4-D | 2,4-D | 4 | 1.8-3.2 L | Wet foliage. DO NOT mow lawn for 1 week before and at least 1 weed after use. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass (WA only). | ||||
MCPA | MCPA | 4 | 930 ml -1.8 L | Use in a high water volume to actively growing weeds. DO NOT mow for 2 days before use. Some transitory damage may occur to fine turf grass. | ||||
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2 L + 3.2 L of 2,4-D Amine 625 g/L | Use a minimum of 1000 L/Ha water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. | ||||
Negate. | Rimsulfuron + Metsulfuron-methyl | 2 | 110 g | Apply to growing weeds and not to weeds under stress weeds. | ||||
Weed Blast MA. | Bromoxynil + MCPA | 6 + 4 | 3-6 L | Apply in a minimum of 500 L/Ha water. DO NOT mow for 2 days after use. | ||||
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid overlapping. Use an NIS like Optispread. | ||||
Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Use in 250-400 L water. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass. After use do not mow for 2 days before or afterwards or fertilise within two weeks. | ||||
Non Selective Control of Bittercress.
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks. However this weed will regrow after you treat it.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate. If water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The list below is of non-selective with a long term residual. This stops re-growth of this weed.
- Renegade. Renegade stops seed germination for up to 12 months. It reduces the need for herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent Flick Weed control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown. It then has a 3 month residual. It is also safe to use near trees.
Table of Non Selective Herbicides for Bittercress.
Product | Active | Group | Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |