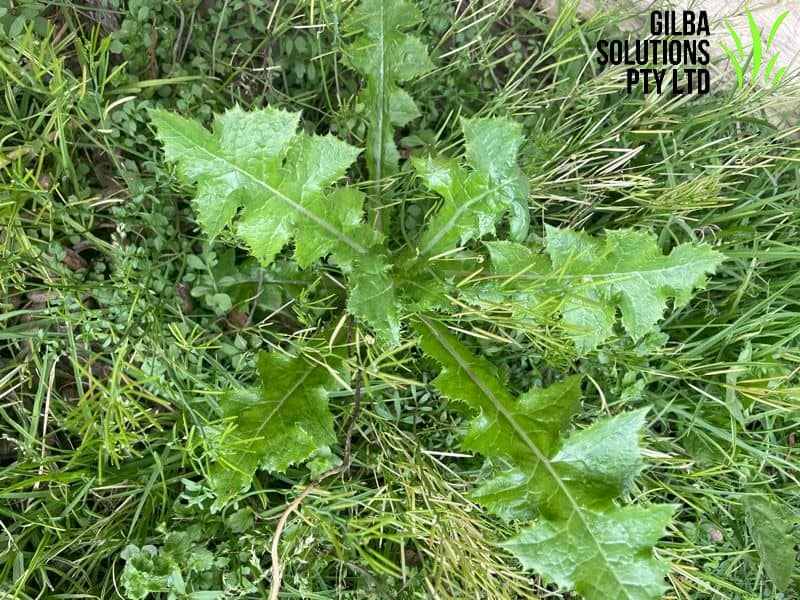
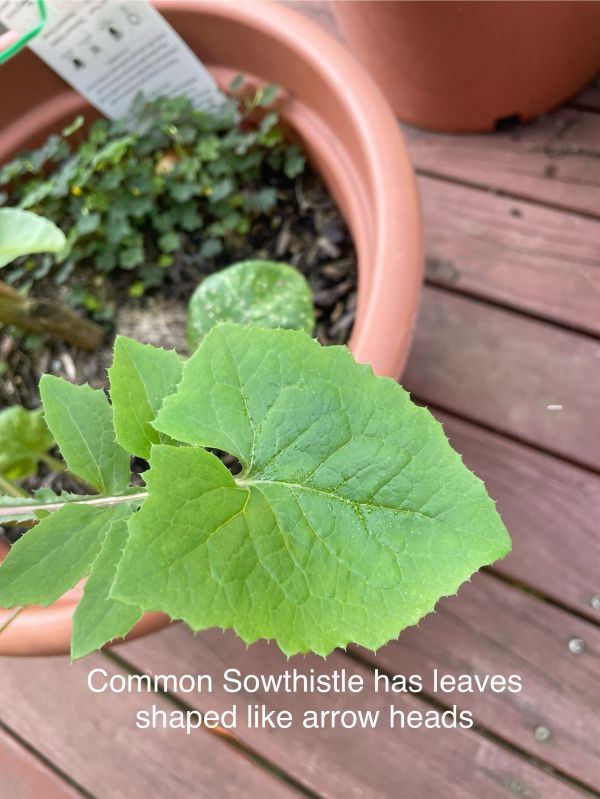
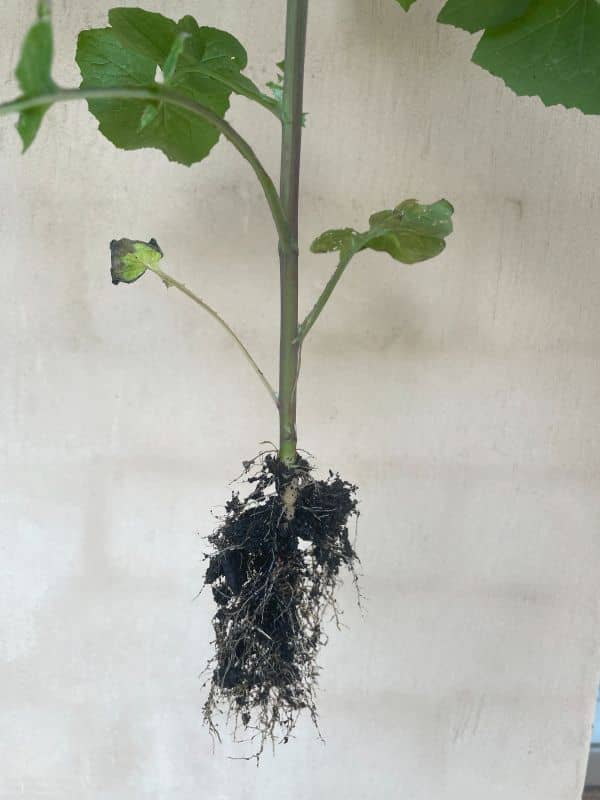
Sowthistle (Sonchus oleraceus).
Sowthistles (Sonchus sp) are annual, biennial or perennial herbs, with or without rhizomes. They are all in the genus Sonchus, and also known as Milkthistles.
There are three Sowthistles you often find in lawns and turf areas in Australia. These are:
- Annual or Common Sowthistle (Sonchus oleraceus L).
- Perennial Sow thistle (Sonchus arvensis) and
- Spiny Sowthistle (Sonchus asper L.).
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Sowthistles or Milkthistles.
- Know the habitat of Sowthistles or Milkthistles.
- Know the way to control Milkthistle.
Why are Sowthistles a Problem Weed?
- They are an invasive species. This means they spread aggressively.
- They grow quickly and produce a large number of seeds.
- They thrive in disturbed environments and outcompete other plants for sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- Sowthistles grow in a wide range of soil types.
- Some populations have developed herbicide resistance.
- They are able to survive drought conditions.
- They are a host for insects like aphids.
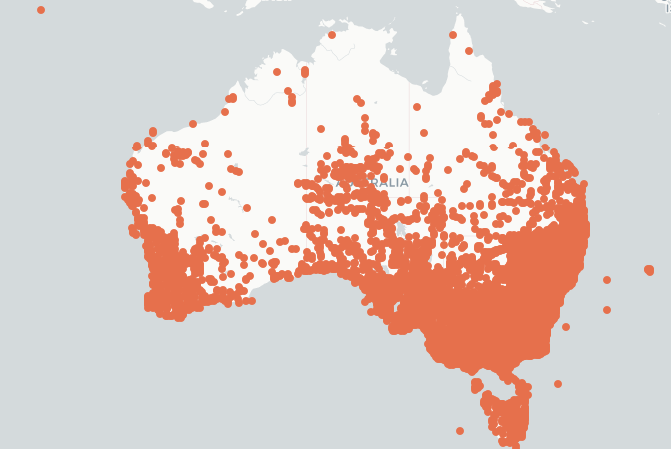
The distribution map of Sowthistles in Australia is courtesy of The Atlas of Living Australia.
How to Identify Sowthistles.
All Sowthistles have soft, irregularly lobed leaves, that clasp the stem. Young leaves form a basal rosette. The leaves are alternate, upright, hairless, and have hollow stems that sometimes branch towards the top.
Sowthistles are Often Mistaken For?
- Creeping Thistle.The easy way to tell these apart is to cut the stem. Sowthistles exude a sap when you cut them but thistles do not.
- Prickly Lettuce. This also has milky sap and similar foliage and flowers. However, Prickly lettuce leaves have raised spines along their midrib. These are not along the midribs of Spiny and Annual Sowthistle leaves.
- Dandelions. In the rosette stage young leaves look similar to Dandelions. As the plants become older identification becomes easier. Dandelions only have a few flower stalks with no leaves. Sowthistles have several branched stems with leaves.
Table of Sowthistles vs Other Similar Weeds.
Plant | Rosette | Annual or Perennial | Stems | Leaves | Flower Colour | Comments |
Sowthistle | Yes | Annual, biennial or perennial | Several branched, hollow stalks | Adult leaves are serrated and deeply lobed with a major triangle-shaped lobe at the leaf tip. | Yellow. Several flowers per stalk | Open up when the sun is out, and then close at night. |
Dandelion | Yes | Perennial | Single unbranched and hollow. Leafless or have minimal leaves. | Deeply toothed or lobed (point backwards). | Single Yellow flower per stalk. Many small florets | When the stem or leaves are cut exudes sap. |
Capeweed | Yes | Annual | Several branched with hollow core | Hairy undersides | Yellow with black centre | |
Catsear | Yes | Perennial | Multiple, branches. Leafless or have minimal leaves. | Club shaped and sometimes hairy | Yellow. Numerous tightly packed florets. | Catsear has milky sap in its stems and leaves. Needs sunlight for the flowers to open in the morning. Once open can't close for at least 3 hours. |
Gazania | Yes | Annual | Leafless | Hairless on the upper surface, woolly white hairy underneath. | Yellow | |
Fleabane | Yes | Annual, Biennial or short lived Perennial | Starts as a rosette. then grows tall, upright flower stems. | Elongated with bluntly toothed to deeply lobed margins. | Small tufted white daisy like flowers | |
Oriental Hawksbeard | Yes | Annual | Single leafy, branched main stem. | Hairy. Emit a milky sap | Yellow |
Category: This is a Dicot weed.
Photosynthetic Pathway: Milkweed is a C3 Weed.
Flower: Milkweeds have yellow flowers and these are from 12 to 25 mm in diameter. They have a ray type floret with no eye to the flower.
Height: Mature plants is 30 cm to 2 m tall.
Leaf length: The leaves are 6 to 35 cm long.
Reproduction of Sowthistle:
Milkweed grows quickly in a wide range of conditions, and their wind-borne seeds allow them to spread rapidly. Germination is favoured by light, and seedlings only emerge from the top 1 cm of the soil. The seed of Sonchus oleraceusis is viable for up to 8 years.
The Perennial Sow thistle also has long, creeping rhizomes that allow it to spread vegetatively.
The seed germinates at day/night temperatures of 25 and 10°C respectively, and Annual Sowthistle needs wet soils for optimum germination.
- If you cut the Annual Sowthistle when it flowers it will still produce viable seeds.
- Once Perennial Sow thistle establishes, it is difficult to control. This is because its perennial root system has the ability to spread vegetatively via small root fragments, and it is also reproduces via seed.
- Sonchus oleraceus produces between 4,700 and 8,000 seeds.
Comments: Milkweeds are common hosts for aphids. The young plants are very frost tolerant. Plants that emerge in the Autumn can overwinter as a rosette of leaves close to the ground, and can withstand temperatures down to -18°C.
These weeds have a robust root network. This comprises fine, spreading roots at the surface and thicker, vertical roots that penetrate deeper into the soil.
Habitat: This weed is a common weed of disturbed areas, gardens and waste places.
For more information on weeds check out our weed ID Chart.
Control of Sowthistle.
You can control Milkweed by cultural and chemical means. However, successful management of this weed is best if you adopt an integrated approach. Autumn is an ideal time carry out control of this perennial weed.
Cultural Control of Sowthistle (Sonchus sp):
- Maintain a dense turf cover. This limits the spread of this weed because it is a weak competitor.
- They are susceptible to shade. The seed needs light to germinate, and seedling emergence is limited to the top 1 cm of soil.
- You can easily hand pull Milkthistles.
- Their soft stems present little resistance to slashing or mowing.
Chemical Control of Sowthistle.
Since the seed bank is relatively short-lived, pre emergents are a good option to control Milkthistle. Post emergent herbicides work best when you target the seedling stage.
Pre-Emergent Herbicides for Sowthistle.
Pre-emergent herbicides control Milkthistle. This is because it is a shallow germinating weed.
Currently you can only legally use BASF Freehand in turf as a pre-emergent for Milkthistle. However, in agriculture you can use prodiamine (Onset 10GR) , S-Metalochlor and Pendimethalin (Battalia 440).
If Milkthistle does break through your pre-emergent barrier, the next option is to use a selective post-emergent herbicide. Luckily there are a wide range of these you can use.
Post Emergent Herbicides for Sowthistle.
Post-emergent Selective herbicides include:
- 3-D herbicide.
- Dicamba 500.
- Qualipro Crest.
- Pylex.
- 2,4-D.
- MCPA.
Table of post Emergent Sowthistle Herbicides.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | |
2,4-D | 2,4-D | 4 | 1.8-3.2 | Wet foliage. DO NOT mow lawn for 1 week before and at least 1 weed after use. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass (WA only). | |
Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Apply in 250-400L water. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass. After use do not mow for 2 days before or after use or fertilize within two weeks. | |
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2L + 3.2L of 2,4-D Amine 625g/L | Use a minimum of 1000L/Ha water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. | |
MCPA | MCPA | 4 | 930ml -1.8L | Apply in high volume to actively growing weeds. DO NOT mow for 2 days before use. Some transitory damage may occur to fine turf grasses | |
Pylex | Topramezone | 27 | 0.375 mL/ 100 m2 in 4-6 L water + 0.5% MSO | Apply to actively growing weeds. Two repeat applications 21-28 days apart are required for optimum control. You may see some minor transient bleaching of Bentgrass 7-14 days post use. For best results do not water or irrigate for 24 hrs post use. | |
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid overlapping. Use an NIS. | |
Non Selective Control of Sowthistle.
You can use Glyphosate , Numchuk Quad or Cortex Duo as a non selective options to control Milkthistle. If you use Glyphosate and water quality is an issue then we recommend the use of ProForce Manta Ray.
The following are non-selective but also have a long term residual and stop any re-growth.
-
- Renegade. Renegade stops germination for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for multiple herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown, and residual control for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use around trees.
Table of Non Selective Herbicides for Common Sowthistle (Sonchus oleraceus).
Product | Active Ingredient | Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |