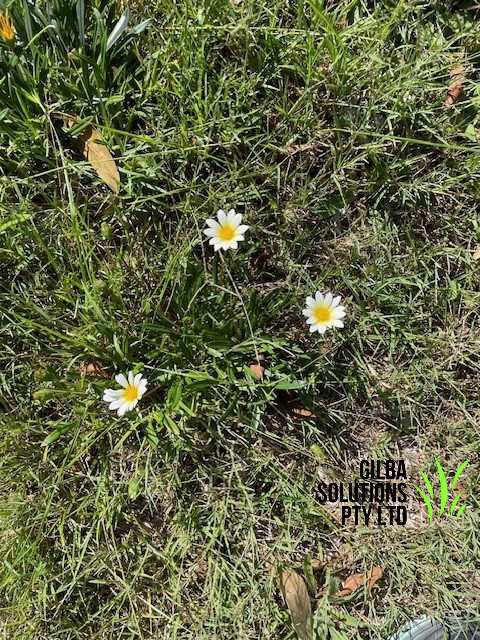
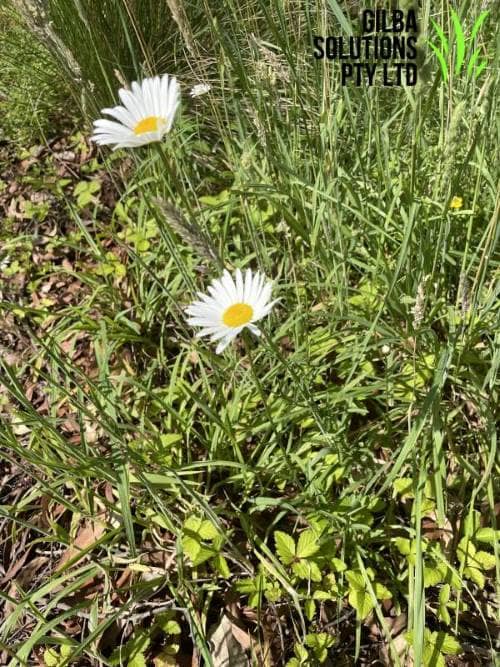
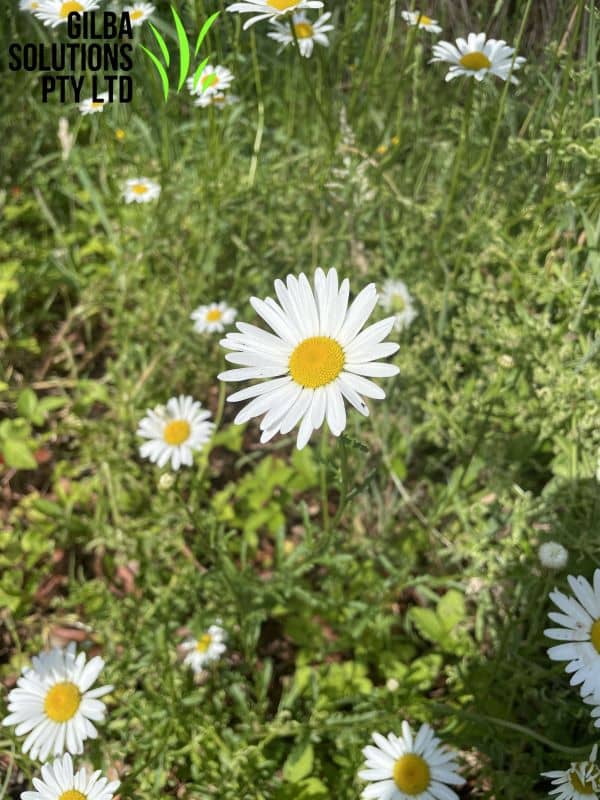
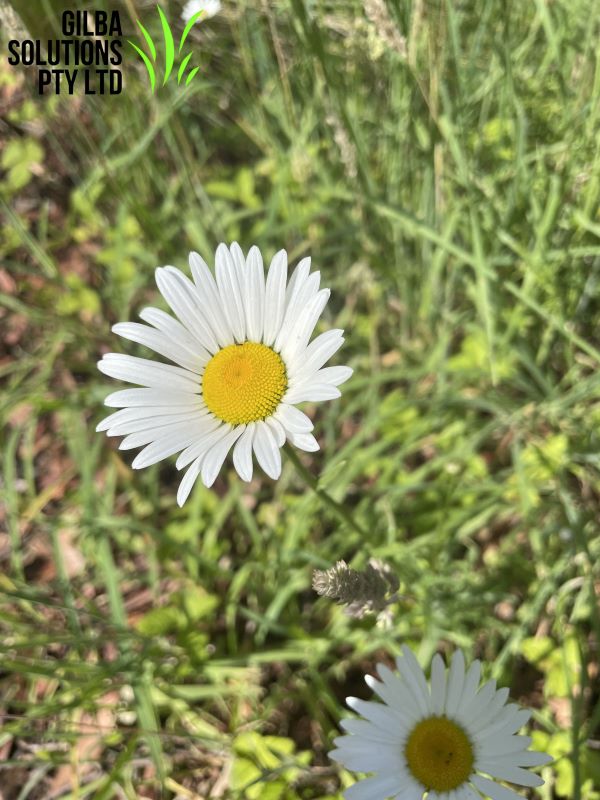
Oxeye Daisy or Dog Daisy Plant (Leucanthemum vulgare).
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Oxeye Daisy or Dog Daisy.
- Know what conditions favour Dog Daisy or Leucanthemum vulgare.
- Know the best options to control it.
Why is Oxeye Daisy a Weed?
- This weed produces a large numbers of seeds. It also regrows from rhizomes. These reasons make is hard to control.
- It is a host for Root-knot nematodes.
- It spreads rapidly, and forms dense infestations.
- This weed thrives in disturbed areas. Once it establishes it then aggressively invades the surrounding areas.
- Dense stands outcompete other plants, and this causes soil erosion. It also depletes soil organic matter when the above ground plant parts die.
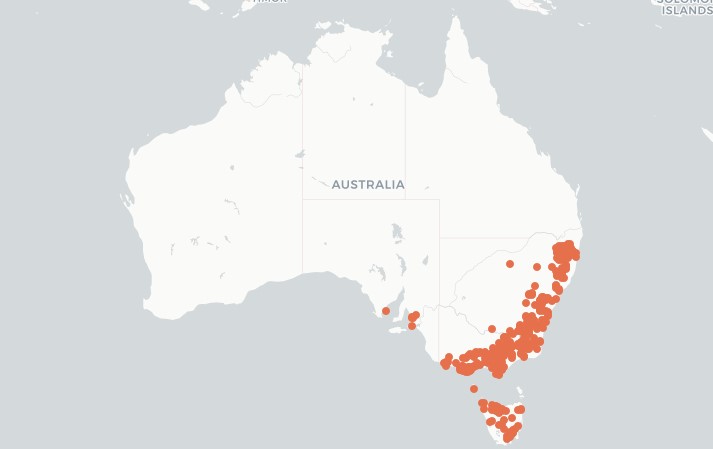
Thanks to the Atlas of Living Australia for the distribution map for Dog Daisy.
Oxeye Daisy Identification.
This is an upright perennial that spreads by seed and rhizomes. It is much larger than a White Daisy.
The Oxeye Daisy at first grows as a rosette. It then forms upright, flower stems.
- Leucanthemum vulgare starts life as a rosette. After this it grows long stems that have small leaves with a lance shape.
- Over the Summer, the above ground plant parts die. It then regrows from the remaining roots.
- It has dark green rosette leaves on stalks. These have a spoon shape, and a jagged edge.
- The stem leaves of this weed are dark green, but don’t have stalks. They have up to 15 jagged teeth, that are alternately arranged.
Category: This is a broadleaf (Dicot) weed.
Photosynthetic Pathway. It is a C3 weed. It struggles in drought, and in dry weather it closes its stomata to save water
Flower: The flowers of Leucanthemum vulgare have 15 to 35 white petals. These petals surround a yellow button shaped centre up to 5 cm across. It flowers from the late Spring to the early Summer.
Height: It grows up to 1 m tall.
Leaf length: The basal leaves are 4 to 15 cm long. Toward the top of the plant the leaves are shorter, and around 7.5 cm long.
- Reproduction: It reproduces from seeds and rhizomes. In one season it can produce up to 26,000 seeds. These seeds germinate in the Autumn or the Spring. They then spread by animals, vehicles and water.
- Up to 80% of the seeds remain viable for up to 6 years.
- It needs temperatures of 25°C to germinate.
Comments: When you crush the plant it has a sour smell.
Habitat: You find this weed in disturbed soils by the side of roads, and waste areas. It favours high nutrient, moist soils.
How to Control Oxeye Daisy.
The best way to control Leucanthemum vulgare is by cultural control. This is because there are very few registered post emergents on the market.
In Australia there are currently no pre-emergents registered to control this weed in turf.
Cultural Control of Oxeye Daisy.
- Hand Removal. You can hand pull small populations or use hand tools. It is important that you remove any roots from at least 10 cm below the ground to avoid re-growth. It is easier to do this when the soil is damp and loose.
- Maintain a full turf cover. Establish and maintain turf grass to outcompete this weed. This weed does not tolerate shade.
- It is not competitive with turf grass in high N soils. This means fertilising is a good way to control this weed.
- Don’t mow too low as this weed quickly invades bare ground. Mow once after it produces a flower stalk but before it flowers.
- It is important to mow again four weeks later to prevent it flowering later in the season.
- Mowing stimulates this weed to grow lateral branches and rhizomes, and works well in combination with herbicides.
- Mowing tends to produce a more uniform plant with a greater leaf area to absorb herbicides.
Biological Control of Oxeye Daisy.
- Dichrorampha aeratana feeds on roots, and looks like a good candidate to control Oxeye Daisy.
- Cyphocleonus trisulcatus, is a root feeding weevil. This is also under investigation to control this weed.
- Other potential agents for this weed include: the shoot-mining moth Dichrorampha consortana, the root-gall fly Oxyna nebulosa, and a fly that attacks the flowerhead called Tephritis neesii.
Chemical Control of Oxeye Daisy.
Selective Control of Oxeye Daisy.
- Dicamba. Spray large infestations when this weed is in the early flowering stage. Remember that you cannot use Dicamba on Buffalo lawns.
- MCPA does not work very well.
- 2,4-D Amine boom spraying gives some control. However, it often recovers and grow back.
- The best time to boom spray is in the Spring. This is when the plants are actively growing.
Post Emergent Herbicides for Oxeye Daisy.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments |
2,4-D | 2,4-D | 4 | 1.8-3.2 L | Wet foliage. DO NOT mow lawn for 1 week before and at least 1 weed after use. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass (WA only). |
Dicamba | Dicamba | 4 | 1.2 L + 3.2 L of 2,4-D Amine 625 g/L | Use a minimum of 1000 L/Ha water. Do not spray on Buffalo or Bent Grass. |
The following are not registered in Australia for this weed in turf grass, but are overseas.
- Clopyralid. Apply Clopyralid in the Spring. Target the rosette to the bud stage of growth.
- Picloram. Apply Picloram in the Spring to actively growing plants, or to the new rosettes in the Autumn.
- Metsulfuron.
- Triclopyr.
Non Selective Control of Oxeye Daisy.
- Renegade. This stops Oxeye Daisy germination for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for multiple herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. Numchuk gives effective post and pre-emergent weed control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown and then residual control for up to 3 months. Cortex Duo is safe to use around trees.
- Rapid Fire 800. You can use Glyphosate to control Oxeye Daisy. However, if water quality is an issue, then add Manta Ray to your spray mix.
Table of Non Selective Herbicides for Leucanthemum vulgare.
Product | Active Ingredient | Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |