Creeping mallow (Modiola caroliniana)
Creeping Mallow (Modiola caroliniana) is also known as Red Flowered Mallow, and is a rhizomatous, low growing biennial or perennial weed. It is a problem in turf, lawns and gardens.
As it is a biennial it requires two full growing seasons to complete its life cycle. Creeping Mallow tends to produce vegetative growth in its first year, and then it flowers and sets seed during the second year.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Recognise Creeping Mallow or Red Flowered Mallow.
- Know the habitat of Red Flowered Mallow.
- Know the best options to control Creeping Mallow (Modiola caroliniana).
Why is Creeping Mallow a Problem Weed?
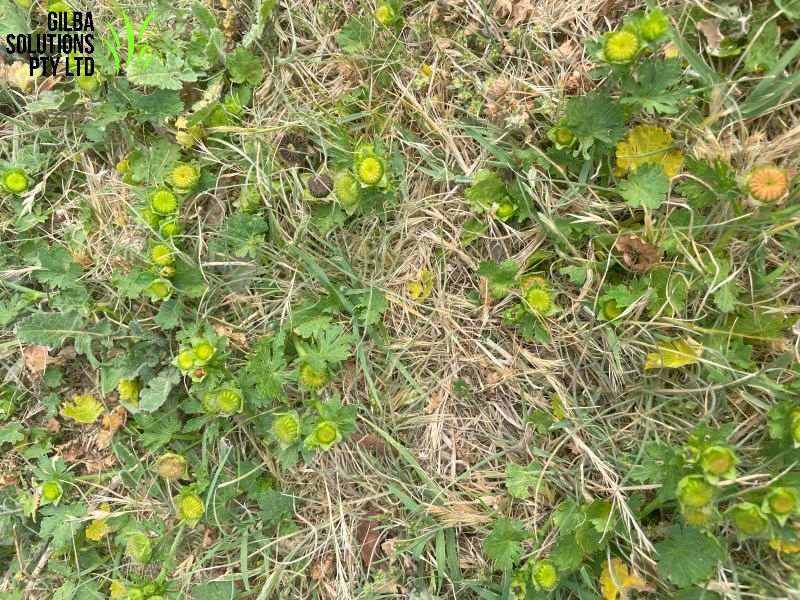
- Because of its below ground root system, Creeping Mallow spreads easily, and forms dense mats that choke out vegetation.
- It competes with other plants for water, nutrients, and sunlight.
- Creeping Mallow causes nerve disorders in sheep, cattle and goats (staggers).
- Aesthetically it is a problem in lawns, and gardens.
More on turf weeds is in our weed ID chart.
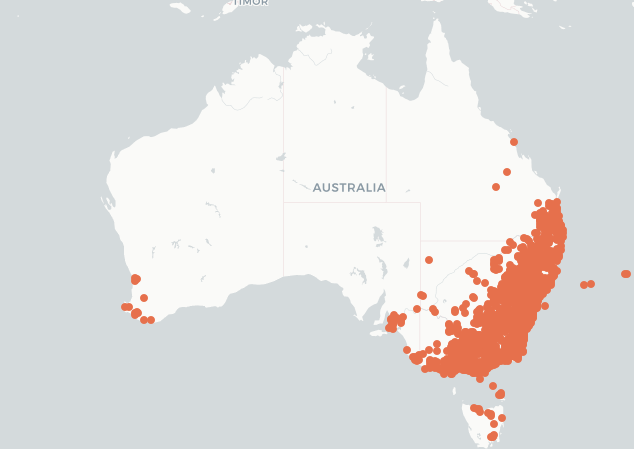
The distribution map for Creeping Mallow (Modiola caroliniana) is courtesy of The Atlas of Living Australia.
How to Identify Creeping Mallow.
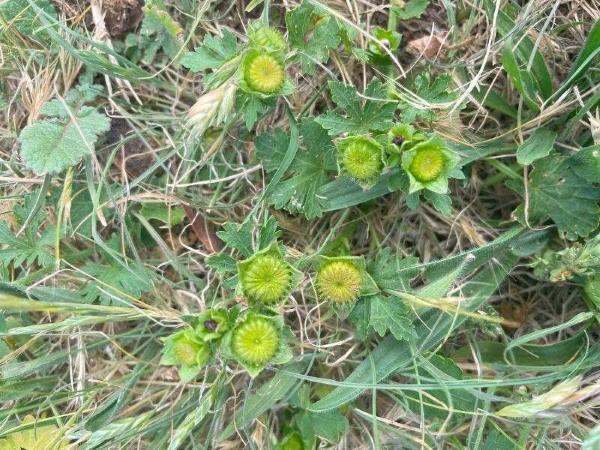
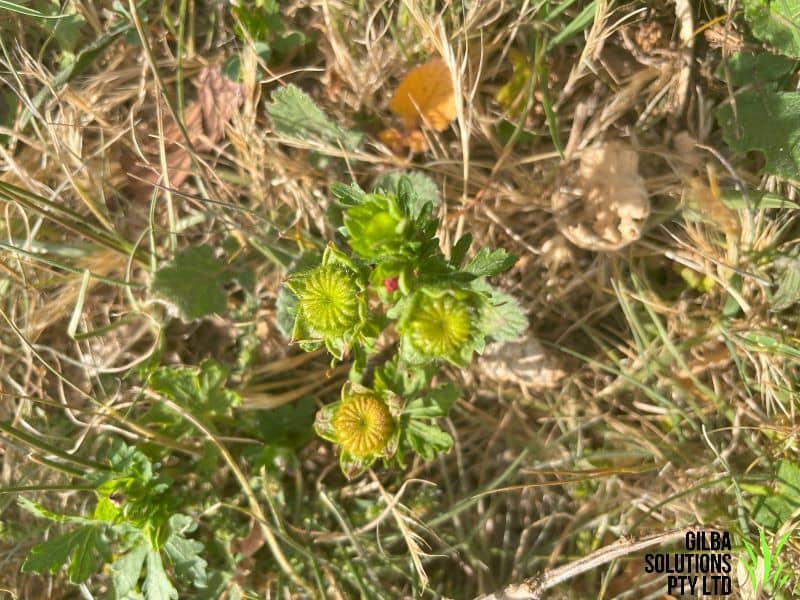
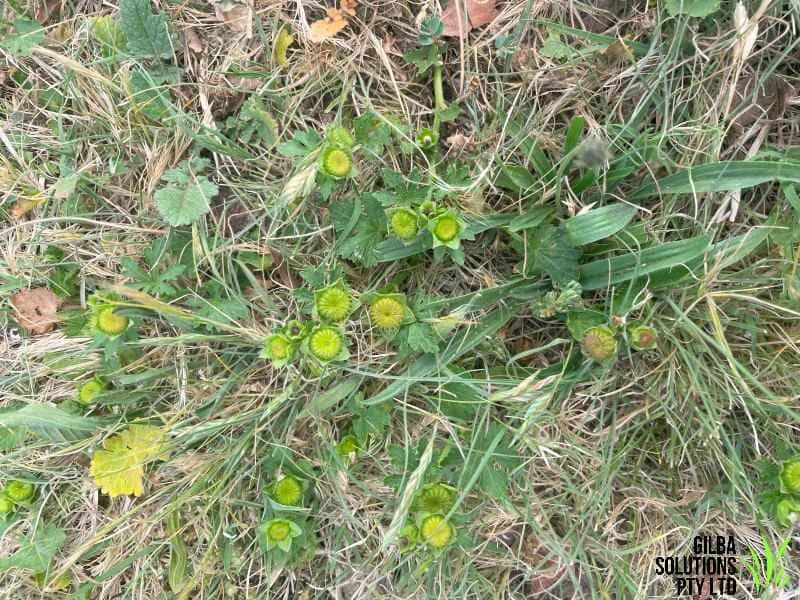
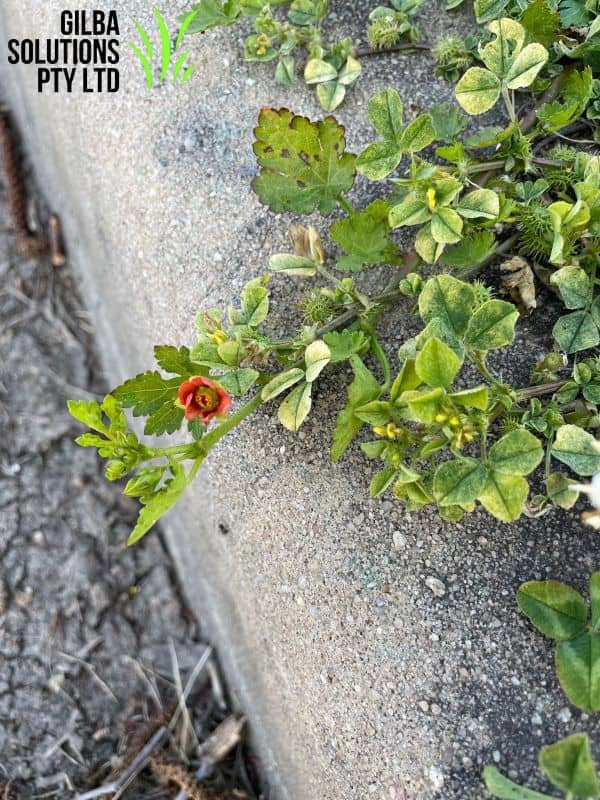
Creeping Mallow (Modiola caroliniana) is up to 25 cm in height, and its leaves have a cover of star shaped and/or simple hairs.
Photosynthetic Pathway: Creeping Mallow is a C3 weed. This means it is well-suited to temperate and cool climates.
Category: Broadleaf (Dicot)
Flowers: Creeping Mallow has single orange-red or red flowers that have yellow centres. These flowers have 5 petals and are on stalks. Creeping Mallow flowers from November to February.
Leaf length: The light green egg, shaped leaves are 3 to 4 cm long.
Leaf width: The leaves are 2 to 3 cm wide.
Stems: Red Flowered Mallow has prostrate, creeping stems that root at the nodes.
Reproduction: Creeping Mallow reproduces from seed, and produces up to 5,000 seeds per plant. The seeds normally disperse by water or animals, and they can pass through an animals digestive tract and still be viable.
Red Flowered Mallow produces both dormant and non dormant seeds.
- The dormant seed has an impermeable seed coat that stops the seeds from taking up water and causes them to be dormant. In the Summer these seeds then break out of dormancy due to natural variations in temperature or as a direct result of physical activity like scarification.
- Non dormant seed germinates over a wide range of temperatures that range from 3.3°C through to 37°C, and within a soil pH range of 4 to 10.
- The highest rate of seed germination occurs from a soil depth of 0.5 to 2 cm.
Comments: The leaves are kidney-shaped, round or shaped like a triangle with 3 to 7 toothed lobes.
Habitat: This weed is common in gardens, lawns, and playing fields, and also occurs in aquatic areas and disturbed vegetation.
How to Control Creeping Mallow.
Weed Management Timeline for Red Flowered Mallow (Modiola caroliniana).
Management Calendar for Creeping Mallow | ||||||||||||
Biennial or Perennial. | ||||||||||||
Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Flowering | ||||||||||||
Pre emergent herbicide | ||||||||||||
Post emergent herbicide | Actively Growing in the Autumn | |||||||||||
Cultural Control of Creeping Mallow.
- Maintain a thick, healthy turf cover.
- Feed your turf properly to create a thick cover that outcompetes any weeds.
- Mow at the right height as this favour turf grass over this weed.
- Grass selection plays a key role in the control of Red Flowered Mallow. Choose the wrong turf seed or turf type, and you quickly end up with a weedy lawn that is difficult to manage.
- If you intend to hand weed, do this before it produces any seed in the early Summer.
- Be aware that if any of the root system of Creeping Mallow remains in the soil, it will re-grow even if you use a pre-emergent.
Chemical Control of Creeping Mallow.
Pre-emergents for Creeping Mallow.
Pre-emergents like Specticle or granular pre-emergents like Onset 10GR have no knockdown activity, and do not work on older mallow plants. They do however, give good control of Mallow that grows from seed.
- In NZ Esplanade has a registration for Creeping Mallow.
Selective Herbicides for Creeping Mallow.
- Contra M. Do not use on Buffalo grass.
- Warhead Trio.
- Weed Blast MA .
- Straight MCPA does work against young plants, but if they are mature the results are very hit and miss.
Table of Post Emergent Herbicides for Creeping Mallow.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments | ||||
Contra M. | Dicamba + MCPA | 4 | 6.5 L | Apply in 250-400L water. DO NOT use on Buffalo grass. After use do not mow for 2 days before or after application or fertilize within two weeks. | ||||
MCPA | MCPA | 4 | 930ml -1.8L | Apply in high volume to actively growing weeds. DO NOT mow for 2 days before application. Some transitory damage may occur to fine turf grasses | ||||
Warhead | MCPA + Clopyralid + Diflufenican | 4 + 12 | 5 L | You may see discolouration on kikuyu, carpet grass and Queensland blue. Avoid overlapping. Use an NIS. | ||||
Weed Blast MA | Bromoxynil + MCPA | 6 + 4 | 3-6L | Apply in a minimum of 500L/Ha water. DO NOT mow for 2 days after treatment. | ||||
Total knockdown herbicides.
- Herbicides such as Glufosinate Ammonium do give some control of Creeping Mallow, but only brown off the top of the plant. This has no effect on the existing root system which is unaffected. As a result, Creeping Mallow sometimes regrows in the same year depending on when the herbicide was applied.
- You can spot treat with Proforce RapidFire (800g/L Glyphosate) as this moves down into the roots. You need a very high rate, plus a spray adjuvant like OptiSpread 1000 for it to be effective. (This depends on growth stage of the plant).
- When you use ProForce RapidFire 800 to control Creeping Mallow, you get the best results when you treat the weed when it is small and is newly emerged.
- If water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
Other non-selective options are:
- Numchuk Quad. Numchuk Quad kills existing weeds, and then prevents them returning for up to 12 months. This product is ideal for pavers, courtyards, driveways and fence lines.
- Cortex Duo. ProForce Cortex Duo Industrial Herbicide is a glyphosate free weed killer. It is both a non-selective knockdown & a residual herbicide that lasts up to 3 months. It also controls algae and moss, and is safe to use around trees and ornamentals.
Table of Non Selective Herbicides for Creeping Mallow.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1-6L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9-1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20-25L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5-6.5Kg |
In Conclusion.
While it’s not considered a major problem weed, Creeping Mallow can still be a nuisance in well-maintained areas. The key to its control is to maintain a healthy turf surface before you start to reach for a herbicide.