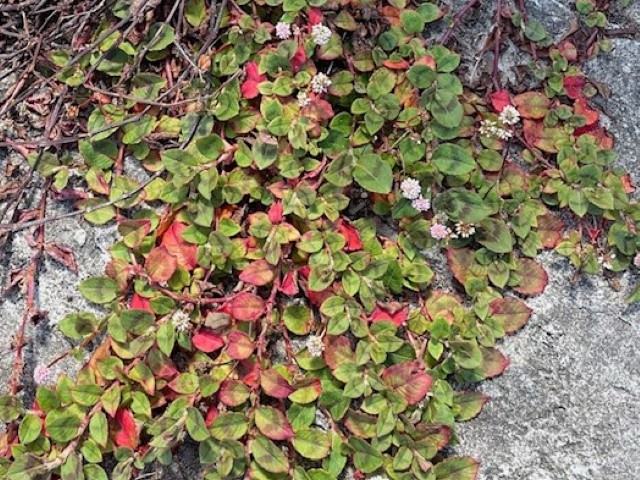
Japanese Knotweed (Persicaria capitata).
Japanese Knotweed (persicaria capitata) is a cousin of Pink-headed Knotweed. Its name comes from Persicaria which means the likeness of its leaves to a peach tree, and capitata from the latin which means head, or knob. Japanese knotweed is an environmental weed in New South Wales.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Persicaria capitata or Japanese Knotweed.
- Know the habitat of Persicaria capitata.
- Know the best cultural and chemical options to control Persicaria capitata.
Why is Japanese Knotweed a Problem Weed?
- It forms a dense carpet, that replaces most native vegetation.
- it is very aggressive, and spreads quickly.
- Persicaria capitata is very adaptable and thrives in a variety of conditions.
The distribution map is courtesy of The Atlas of Living Australia.
How to Identify Japanese Knotweed.
Japanese Knotweed quickly spreads, and forms a dense mat of foliage that smothers turf grass. It can reach maturity in under 1 growing season, and has a woody root.
Originally adapted to cope in cold mountainous conditions, this weed thrives pretty much anywhere. This includes dry and sandy soils in both sun and partial shade.
Photosynthetic Pathway: C3
Category: Japanese Knotweed is a semi-herbaceous, stoloniferous perennial weed.
Flower: Persicaria capitata has numerous distinctive pink flower heads, that are about 1.5 cm across
Height: Japanese Knotweed is prostrate and forms a mat that is less than 15 cm tall. However, it spreads horizontally for up to 1.5 m.
Leaf length: The compound, alternate leaves are 1 to 6 cm long.
Leaf width: The hairy, lance shaped leaves of Japanese Knotweed are 0.7 to 3 cm wide with pink to red bands or blotches. The leaves also have a cover of short scattered hairs.
Reproduction: Persicaria capitata reproduces both sexually and vegetatively. It sets seed, and also spreads vegetatively from its trailing stems.
Comments: The fine hairs on the leaves and stems, give Japanese Knotweed a distinctive red colour and pattern. It is susceptible to frost and has a strong urine-scented odour.
Habitat: Japanese Knotweed thrives in almost any soil. It is found on roadsides, dry banks, slopes and in open areas as it prefers to be in the full sun.
For more information check out our weed ID Chart.
How to Control Japanese Knotweed in your lawn.
You can control Japanese Knotweed by cultural and chemical means. Autumn is an ideal time carry out control of this perennial weed.
Cultural Control of Japanese Knotweed.
Unfortunately this plant is very resilient, has an extensive root system and grows vegetatively.
Because Japanese Knotweed reproduces vegetatively through its roots and rhizomes, it quickly spreads via its roots and then forms new shoots. If you leave even a small amount of vegetative material in the ground, the plant regrows and spreads.
This means when you dig it out you MUST remove all the roots and dispose of plant material offsite in landfill or a greenwaste site.
Chemical Control of Japanese Knotweed.
In Australia, a number of herbicides are registered for the control of Knotweed species. If Japanese Knotweed spreads over large areas we recommend you use a herbicide to control it.
- NZ work in 2009 shows that 2,4-D + Dicamba, MCPA, MCPA + Mecoprop + Metsulfuron, and Triclopyr + Picloram all control Persicaria capitata.
- Another option is to foliar spray Japanese Knotweed with 200 ml of glyphosate, and 3 g of metsulfuron-methyl per 10 L plus 20 ml of a good penetrant like Scrubwet.
- Other NZ work has found that it is not tolerant of MCPA.
Non Selective Control of Japanese Knotweed.
- Glufosinate-ammonium. This is a contact non selective herbicide.
Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate as a non selective option to control Japanese Knotweed. If you use Glyphosate, and water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The following are non-selective but also have a long term residual. This means that they kill the existing plants and then stop any re-growth of Japanese Knotweed.
-
- Renegade. Renegade stops the germination of Persicaria capitata for up to 12 months. It also reduces the need for multiple herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent Japanese Knotweed control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown of Persicaria capitata, and then controls it for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use around trees.