Salicylic Acid for Plants.
Salicylic acid (SA) or salicylate is an elicitor of plant response, and is as a key signalling molecule for plant immunity.
You can apply plant elicitors to turfgrass to activate plant defence mechanisms. These defence mechanisms provide plants resistance against a wide range of pathogens.
When a plant is exposed to these threats, it triggers their defence mechanisms. This leads to a build up of salicylic acid in the affected tissues.
This blog dovetails with our article on DIY pest control, and research into two novel bioactive compounds.
The Role of Salicylic Acid in Plants.
Salicylic acid (SA) is an important plant hormone and plays a vital role in turf health. It impacts turf growth and development, and the ability of plants to resist biotic and abiotic stress.
- SA supercharges plant defence mechanisms. It makes plants less prone to disease attack.
- SA improves root growth, and protects old and stressed plants from oxidative damage.
- The role of salicylic acid in plants is as a defence signal from inside the plant.
- Salicylic acid is an elicitor of plant response (EPR), and triggers a natural defence against pathogens. However, plant often do not make SA fast enough to prevent pathogens from causing damage. Applications of foliar SA speed up this process.
- Even in ideal conditions, there are inefficiencies that affect free radicals and anti-oxidants.
- Free radicals are the “bad guys” and disrupt plant functions. Anti-oxidants are the ‘good guys” and these deactivate or neutralise the free radicals.
- The production of anti-oxidants is natural. However, if carbohydrates are low or conditions are not favourable, anti-oxidants become scarce.
- In a plant, chemical by-products have to be dealt with for the plant to remain healthy.
- When conditions are not ideal there are more of these nasty by-products. These in turn impact turf health. For example, photochemical efficiencies of health turf are around 0.7. When turf is under stress this drops to 0.55 or less.
Salicylic Acid and Disease.
- PR proteins like chitinases and glucanases, directly attack pathogens.
- Antimicrobial compounds like phytoalexins accumulate, and then strengthen the plant defences.
Salicylic Acid (SA) is a key component of aspirin, and extracts from Witch Hazel have been used to treat pain and inflammation for thousands of years. In 1933, SA was first proposed to develop acquired immunity after disease infection.
SA Affects Plant Processes.
Exogenous applications of Salicylic Acid on plants has several benefits. It regulates plant processes depending on the concentration that you apply. Low concentrations tend to induce a response and high concentrations of SA tend to inhibit them.
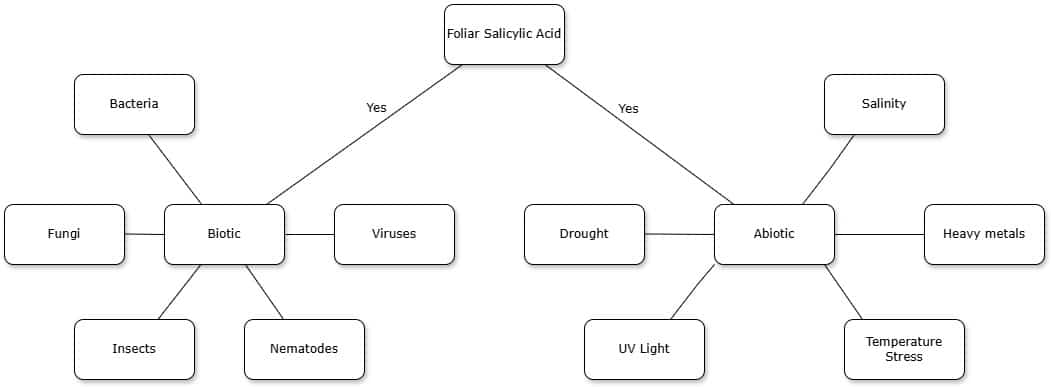
- Abiotic stresses. SA impacts on several abiotic stresses that include a plants cold tolerance, how it copes with temperature extremes, its tolerance to drought and UV radiation, and its tolerance to soil salinity.
- SA induces disease resistance.
Foliar applications of SA affect several aspects of plant growth and development1Hayat Q, Hayat S, Irfan M, Ahmad A. Effect of exogenous salicylic acid under changing environment: A review. Environ Exp Bot. 2009;68:14–25. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.08.005. 2Khan MIR, Fatma M, Per TS, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Salicylic acid-induced abiotic stress tolerance and underlying mechanisms in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:462. 3Malamy, J., Hennig, J., and Klessig, D. F. (1992). Temperature-dependent induction of salicylic acid and its conjugates during the resistance response to tobacco mosaic virus infection. Plant Cell 4, 359. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.3.359.
Exogenous use of SA on plants affect:
- Seed germinaton.
- Plant growth.
- Root growth.
- Photosynthesis.
- Plant respiration and
- the Krebs cycle.
Salicylic Acid vs Other Plant Hormones/Bio-stimulants:
There is a detailed overview of Bio-stimulants in these two blogs. Article 1 and Article 2. However, SA has some unique properties in comparison to other plant hormones or bioactive compounds.
Salicylic Acid.
SA affects the ability of plants to cope with abiotic stresses like salinity, drought, cold, heavy metals and heat stress.
Plant processes that SA regulates include:
- Photosynthesis.
- The opening and closing of stomata.
- Enzyme function.
- Nutrient uptake and
- Overall plant growth and development.
Salicylic Acid vs Common Organic Compounds.
Plant Growth Regulators and Organics Comparison | ||||||
Characteristic | Salicylic Acid | Humic Acid | Fulvic Acid | Cytokinin | Gibberellic Acid | Abscisic Acid |
Source | Made by plants | Decomposed OM | Decomposed OM | Made in roots/shoots | Fungus Gibberella fujikuroi | Made by plants |
Primary Function | Defence signaling, stress response | Soil conditioner, nutrient chelation | Nutrient transport | Cell division, shoot development | Stem elongation, germination | Growth inhibition, stress response |
Mode of Action | Activates defence genes, induces SAR | Improves soil structure, chelates nutrients | Helps nutrient take up | Promotes cytokinesis, delays senescence | Promotes cell elongation, breaks dormancy | Inhibits growth, closes stomata |
Effect on Growth | Indirect (stress tolerance) and direct (root growth) | Indirect | Indirect | Promotes growth | Promotes growth | Inhibits growth |
Application Timing | Preventive or stress periods | Growing season | Growing season | Growth periods | Germination, early growth | Stress conditions |
Plant Response Time | Hours to days | Weeks to months | Days to weeks | Days to weeks | Hours to days | Hours to days |
Target Tissues | Whole plant | Root zone, whole plant | Whole plant | Shoot tips, young leaves | Growing points, stems | Leaves, buds, roots |
Seed Germination | Increases | Increases | Increases | Slight Increase | Increases | Increases |
Stress Tolerance | Increases (biotic, abiotic) | Increases (drought, salinity) | Increases (nutrient stress) | Slight increase | Minimal effect | Maximizes (water stress) |
Disease Resistance | Strong | Some | Slight | Very Little | Minimal | Minimal |
Root Development | Moderate | Strong | Strong | Promotes roots | Minimal effect | Inhibits and promotes root growth. |
Application Method | Foliar spray | Soil application, fertigation | Foliar spray | Foliar spray | Foliar spray, seed treatment | Foliar spray |
Best Use Cases | Disease prevention, stress management | Improves the soil and nutrient efficiency | corrects nutrient deficiency | Plant and root health | Seed germination, height control | Specific stress management |
Synergistic Partners | Humic/fulvic acids, cytokinins | All nutrients | All nutrients | Auxins, gibberellins | Cytokinins, auxins | Used alone |
Application Guidelines: | ||||||
For General Plant Health: | ||||||
Salicylic Acid: Apply before stress periods | ||||||
For Stress Management: | ||||||
Salicylic Acid: Best for disease and abiotic stress | ||||||
Systemic Acquired Resistance (SAR).
- Systemic Acquired Resistance (SAR) is a long lasting and broad spectrum plant defence mechanism. SAR occurs when a pathogen infects a turf grass plant.
- After infection, a pathogen triggers the SA pathway.
- The SA pathway then induces the defence response genes in the plant.
- This results in PR protein production.
- These PR proteins play an important role in plant defence.
The other role of SA in turf grass management, is as a plant hormone that helps regulate various physiological processes.
Disease Resistance with Salicylic Acid for Plants:
SA boosts a plant’s immune system. It enhances a plant’s resistance to several diseases, and in particular to fungi or bacteria.
It activates defence mechanisms inside a plant, which makes a plant less prone to infection. For example, foliar of SA cause SAR in plants, and provide protection against various biotic stresses.4Yang Y, Shah J, Klessig DF. 1997. Signal perception and transduction in plant defence responses. Genes ant1 Develop 11:1621-39.
When a pathogen infects a plant, SA tends to build up in the locally infected tissue. After this the SA then moves around the plant to induce SAR in the non-infected parts of the plant.
Fungal diseases.
- SA improves turf resistance against diseases such as Dollar Spot and Brown Patch. It does this by activating defence responses in the plant. These responses include the production of antimicrobial compounds, and the reinforcement of cell walls. The end result is that it becomes much more difficult for fungi to infect the turf grass.
- SA is very effective against grey leaf spot on perennial ryegrass. It significantly reduces this disease when you apply it as a foliar 5Rahman A, Kuldau GA, Uddin W. Induction of salicylic acid-mediated defence response in perennial ryegrass against infection by Magnaporthe oryzae. Phytopathology. 2014 Jun;104(6):614-23..
Bacterial diseases.
- SA helps turf grass combat bacterial diseases like bacterial wilt and bacterial leaf blight. Research shows that preventative treatments with SA, reduce bacterial wilt in both ‘Penn-A4’ and ‘Tyee’ creeping bentgrass.
- SA reduces bacterial disease in both ideal and high temperature treatments. At 23 °C and 35 °C, disease severity in plants + SA is less than in the control.6Sha Liu, Joseph Vargas, Emily Merewitz, Jasmonic and salicylic acid effects on bacterial etiolation and decline disease of creeping bentgrass, Crop Protection Volume 109, July 2018, Pages 9-16
- SA stimulates the plant’s immune system to produce defence-related proteins, enzymes, and chemicals. All of these inhibit bacterial growth and limit disease progression.
Viral diseases.
While SA doesn’t directly target viruses, it indirectly enhances the resistance of turf grass to them. It activates SAR, and helps the plant to produce antiviral proteins that slow down the spread of viruses.
Nematode Resistance with Salicylic Acid:
- SA increases turf grass resistance against nematodes. Nematodes are microscopic worms that damage turf grass roots, and result in poor growth and turf decline.
- SA induces defence mechanisms in the plant, such as the production of nematode-repellent chemicals which deter nematode feeding7Molinari S, Salicylic acid as an elicitor of resistance to root-knot nematodes in Tomato, ISHS Acta Horticulturae 789: XV Meeting of the EUCARPIA Tomato Working Group 8El-Sherif, A.G.;* Gad, S. B.; **Khalil, A.M. & ***Mohamedy, Rabab H.E. 2015. Impact of Four Organic Acids on Meloidogyne Incognita Infecting Tomato Plants under Greenhouse Conditions, Global Journal of Biology, Agriculture and Health Sciences, Vol.4(2):94-100.
- Tomato plants + SA show a 20 to 25% reduction in root knot egg numbers in comparison to a control9Molinari, Sergio. (2008). Salicylic Acid as an Elicitor of Resistance to Root-Knot Nematodes in Tomato. Acta horticulturae. 789. 119-125. 10.17660/ActaHortic.2008.789.15. . Similar results were seen in 2017 by Martínez-Medina et al10Martínez-Medina A., Fernandez I., Lok G. B., Pozo M. J., Pieterse C. M. J., Van Wees S. C. M. (2017). Shifting from priming of salicylic acid- to jasmonic acid-regulated defences by Trichoderma protects tomato against the root knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. New Phytol. 213, 1363–1377. 10.1111/nph.14251.
Insect effects.
- SA repels certain insects such as thrips11O. Ozinger, Effects of methy salicylate, methyl jasmonate and Cis-Jasmone on thrips Tabaci Lindeman, 2012,University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna Division of Plant Protection , caterpillars12Iversonlo A, Inverson L, and Eshita S, The Effects of Surface-Applied Jasmonic and Salicylic Acids on Caterpillar Growth and Damage to Tomato Plants, OHIO J SCI 101 (5):S)O-94, 2001, and has indirect effects on mite mortality13Homayoonzadeh M, Moeini P, Khalil Talebi K, Allahyari H,Torabi E, Michaud JP, Physiological responses of plants and mites to salicylic acid improve the efficacy of spirodiclofen for controlling Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) on greenhouse tomatoes, Exp Appl Acarol. 2020 Nov;82(3):319-333 .14Vilela de Resende JT, Rafael Matos R, Zeffa DM, Constantino LV, Alves SM, Ventura MU, Resende NCV, Youssef K, Relationship between salicylic acid and resistance to mite in strawberry, Folia Hort. 33(1) (2021): 107–119.
Stress Tolerance with Salicylic Acid:
Turf grass often faces extreme stresses like drought, heat, or cold. SA helps plants cope with these as it regulates various stress-responsive genes and biochemical pathways. It improves the resilience of turf,and allows it to better withstand these adverse conditions.
Seed Germination.
Foliar SA improves seed germination and promotes protein synthesis. These proteins are vital for germination to successfully occur.
Growth Regulation.
SA influences the growth and development of turf. It promotes root growth, and results in a healthier and more robust root system. It also regulates shoot growth, helps to maintain balanced growth and increases the overall turf quality.
Photosynthesis and Chlorophyll Production.
SA also enhances photosynthesis, which is crucial for energy production and to maintain turf grass health. It increases chlorophyll content, which leads to greener and more vibrant turf.
Drought Stress.
SA plays a major role in how plants cope with drought stress. It influences several growth parameters when plants are under drought stress.
When you make foliar applications of SA it helps synthetize soluble sugars and the amino acid, proline, and so helps maintain the moisture status of plants.
Temperature Stress.
SA increases the tolerance of plants to both high and low temperatures, and activates enzymes that protect plants from damage.
For example, in Tall Fescue, foliar SA reduces high temperature stress by increasing photosynthetic pigments, and the build up of proline15Hayat, Q., S. Hayat, M. Irfan and A. Ahmad, 2010: Effect of exogenous salicylic acid under changing environment: A review. Environmental and Experimental Botany 68, 14-25..
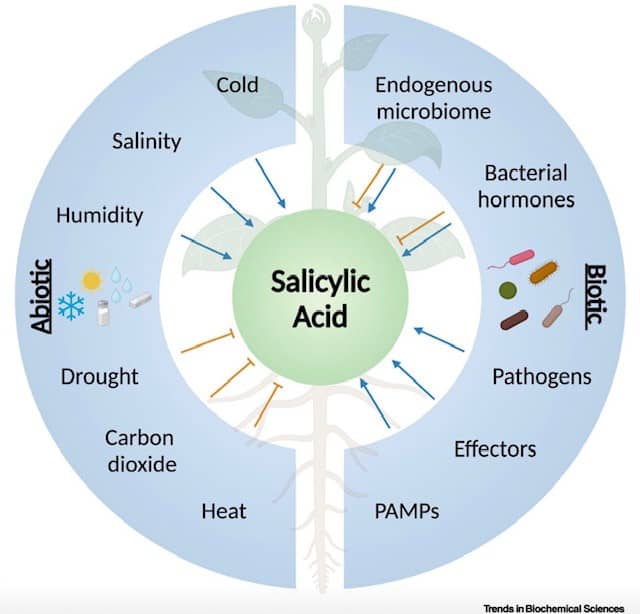
The role of SA in abiotic and biotic factors16Rossi CAM 1, Marchetta EJR, Kim JH, Castroverde CDM, Molecular regulation of the salicylic acid hormone pathway in plants under changing environmental conditions, Trends in Biochemical Sciences, Volume 48, Issue 8, August 2023, Pages 699-712 (credits: Rossi et al. 2023; DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2023.05.004).
Salicylic Acid on Cool Season Turf.
Cool-season turf is susceptible to temperature extremes which has a major impact on growth. Research shows that SA increases heat tolerance and turf quality on Kentucky Bluegrass and Tall Fescue.17Larkindale, J, and Huang, B. (2004). Thermotolerance and antioxidant systems in Agrostis stolonifera: involvement of salicylic acid, abscisic acid, calcium, hydrogen peroxide, and ethylene. J. Plant Physiol. 161, 405–413.
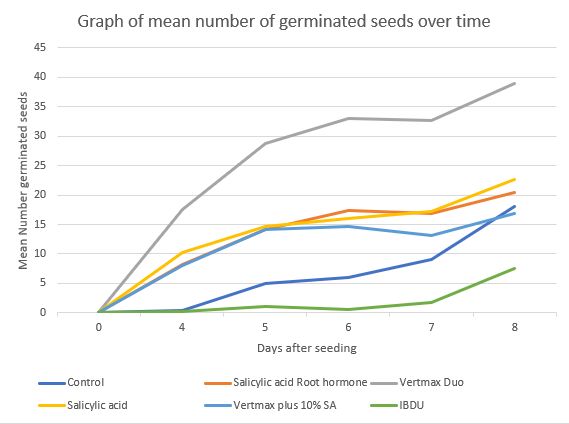
In a 2019 study18Zhang X and Goatley M, Evaluating the effects of SA and pigment sources, 2019 https://issuu.com/leadingedgepubs/docs/va-turfgrass-2019-jan-feb/s/10135194, salicylic acid + a Copper based pigment gives better colour of creeping bentgrass under heat and mild drought stress at 42 and 56 d after treatment.
These results show:
- The role of SA in plants + pigment is to block UV-B radiation. This protect the plants photosynthetic function from UV-B injury.
- There is a synergy between SA and the pigment. This results in an improvement in turf quality under heat and mild drought conditions.
How to Apply Salicylic Acid to Plants?
There have been two issues with SA and its use on plants.
- How to apply an amount that actually works? It is not water soluble. This means that you can’t simply dissolve this in water, and spray it onto plants. You will not be able to apply enough to get a result.
- How to apply high loads of SA without causing any damage to the plant.
The Development of a Salicylic Acid Bio-stimulant.
In 2019 we began to investigate how to apply high loads of SA to turf. In 2021 we developed a way to dissolve 200 g in 1 L of liquid. This is the equivalent of dissolving over 650 aspirin in a litre of water.
This high load of SA is only available in our turf pigment, Vertmax Duo. However in the future we are looking at this being available as a standalone product with no pigment.
Vertmax Duo: Turf Pigment + Salicylic Acid.
The development of Vertmax Duo began shortly after the launch of Bayer’s Stressgard range. This is a colourant and biostimulant that are pre-mixed with certain fungicides.
Vertmax Duo offers similar plant health benefits plus added flexibility when it comes to your choice of tank mix partner. You can use Vertmax Duo as a stand alone application or tank mix it with all turf pesticides.
Why Vertmax Duo?
Vertmax Duo turf pigment is the only product on the market that contains 200g/L of salicylic acid. One application gives an immediate colour response together with all the potential benefits listed below.
It’s formulation also contains adjuvants and stickers to help with coverage, longevity and uptake.
Benefits of Vertmax Duo.
- Because of its tank compatibility you can mix this with all fungicides, fertilisers and insecticides. You have not got to use one brand to get the benefits of SA.
- Salicylic acid increases disease, heat and drought resistance of turf.
- It does not stain once it dries.
- Increases root growth and lateral branching.
- We carry out a continual program of turf pigment research and improvement.
- Higher quality playing surfaces.
Please feel free to check out more information on Vertmax Duo or contact us directly. To put it another way, why prevent your playing surface from being at its best?
Buy Vertmax Duo.
Vertmax Duo comes in 1 L containers.
Buy Here. If you wish to purchase this unique colourant and bio-stimulant packed full of the plant health benefits of Salicylic Acid.
FAQ
What Does Salicylic acid Do in Plants?
In plants salicylic acid (SA) is an important plant hormone. It impacts plant growth and development, and the ability of plants to resist biotic and abiotic stress.
Salicylic acid regulates:
- The ability of plants to fight against diseases.
- Root growth.
- It reduces oxidative damage on plants under stress.
- seed germination.
- Photosynthesis.
- The opening and closing of stomata.
- Enzyme function.
- The uptake of nutrients.
- Plant growth and development.
How to Apply Salicylic Acid to Plants?
Salicylic acid (SA) is very good for plants and especially turf grass. The problem has always been to be able to apply a high enough amount to produce a plant response without damaging the plant.
Professional turf managers are able to apply a high loading of Salicylic acid by using Vertmax Duo turf pigment. However, this is not practical for anyone growing plants for two reasons.
- The pigment Vertmax Duo contains is not required.
- The high loading of salicylic acid in Vertmax Duo would dame name plants if you use it as a standalone application.
Under these circumstances try can simply dissolve aspirin in water and simply spray this onto the foliage with a pump pack or knapsack sprayer. A suitable rate is 1 aspirin per Litre of water applied as a foliar every 2 weeks.
References

Jerry Spencer
Graduated from Newcastle University with an Hons Degree in Soil Science in 1988, Jerry then worked for the Sports Turf Research Institute (STRI) as a turf agronomist before emigrating to Australia in 1993.
He followed this by gaining a Grad Dip in Business Management from UTS. He has worked in a number of management roles for companies as diverse as Samsung Australia, Arthur Yates and Paton Fertilizers.
He has always had a strong affinity with the Australian sports turf industry and as a result he established Gilba Solutions as an independent sports turf consultancy in 1993. Jerry has written over 100 articles and two books on a wide range of topics such as Turf Pesticides and Nutrition which have been published in Australia and overseas.