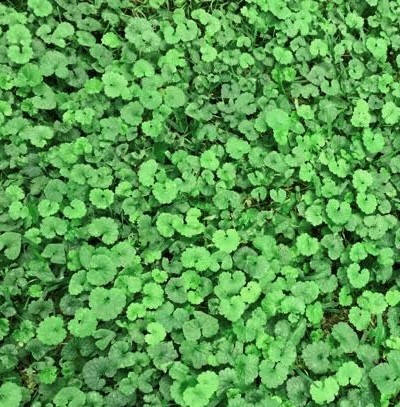
Creeping Charlie (Glechoma hederacea).
Creeping Charlie (Glechoma hederacea) is also known as Ground Ivy. It is a perennial aggressive weed, that flowers in the early Spring and the Summer. It is very difficult to control once it gets a foothold.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Creeping Charlie.
- Know the habitat of Ground Ivy plant.
- Know the best options to control Creeping Charlie (Glechoma hederacea).
Why is Creeping Charlie a Problem Weed?
Creeping Charlie (Glechoma hederacea) or Ground Ivy, is a problem weed because:
- It is very aggressive and spreads rapidly.
- It thrives in a range of conditions. These include shade and full sun areas.
- Creeping Charlie quickly forms dense mats that smother other plants.
- The Creeping Carlie root system is able to root at the node where it comes into the soil. This makes it difficult to remove completely and lead to frequent re-emergence.
- The Ground Ivy Plant regrows from even small root fragments. This makes it difficult to control by hand weeding.
- It is toxic to horses if they eat it in large quantities.
The Ground ivy plant is a low growing perennial weed commonly found in lawns and landscape beds. Creeping Charlie has a shallow root system, and has a minty odour when you crush or cut it.
It has kidney-shaped or rounded leaves with scalloped edges that grow low to the ground. The stems can root at each leaf node.
Glechoma hederacea is a good indicator weed of wet soils and turf under stress. The distribution map is courtesy of The Atlas of Living Australia.
For more information, please check out our weed ID chart.
Ground Ivy Identification.
Creeping Charlie (Glechoma hederacea) spreads aggressively by seeds and creeping stems that root at the nodes to form dense patches.
It is often mistaken for Deadnettle or Henbit. These all have square stems, are members of the mint family and have small purple flowers.
However the key differences are:
- The upper leaves of Deadnettle are smaller than the lower leaves.
- Deadnettle is an annual that flowers in the early Spring and then dies in the late Spring.
- Deadnettle has long stalks on its lower leaves and short stalks on its upper leaves. The leaves of Creeping Charlie are on long stalks.
Differences Between Creeping Charlie, Deadnettle and Henbit.
Plant | Growth Habit | Flowering | Creeping | Stem | Leaf Stalks | Leaf Shape | Teeth on Leaf |
Creeping Charlie | Perennial | Late Spring | Yes | Square | Long | Kidney | Yes |
Deadnettle | Winter Annual | Early Spring | Yes | Square | Long on lower leaves and short on upper leaves. | Hairy oval- to egg-shaped | Rounded teeth on edges |
Henbit | Winter Annual | Early Spring | Yes | Square | On lower not on upper | Hairy oval- to egg-shaped | Yes |
Category: Creepng Charlie is a broadleaf (Dicot) weed.
Photosynthetic Pathway: C3 Weed.
Flower: Creeping Charlie flowers in the late Spring. It has flowers that are funnel shaped, about 2.5 cm in diameter, and are blue to purple in colour. You find the flowers in 3 to 7 clusters, and you see these from April to June.
Height: Prostrate
Leaf Length: Creeping Charlie has kidney shaped leaves that are opposite each other and on long stalks. These leaves have rounded teeth along their edges.
Leaf Width: The leaves are 6 to 37 mm in diameter.
Reproduction: Creeping Charlie reproduces by seed in the Summer and Autumn, and also by producing roots along its creeping stems.
Root system: The Creeping Charlie root system is shallow and fibrous. It spreads horizontally across the soil surface and can root at any point where the stem nodes come into contact with the soil. This ability of the Creeping Charlie root system to root down makes it even more of a challenge to completely remove this weed.
Comments: The stems of the Ground Ivy plant are square (four-sided). During the hot Summer weather, it has a tendency to become dormant.
Habitat: Creeping Charlie is an aggressive weed that prefers moist, partly shaded areas. However it also grows well in the full sun. It spreads quickly into turf areas and flower beds.
How to Remove Creeping Charlie from your Lawn.
Weed Management Timeline for Creeping Charlie.
Management Calendar for Creeping Charlie | ||||||||||||
Perennial. | ||||||||||||
Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Vegetative Growth | Plant overwinters as a rosette | |||||||||||
Flowering | ||||||||||||
Pre emergent herbicide | Will only prevent seed germination; no effect on stolons | |||||||||||
Post emergent herbicide | ||||||||||||
Cultural Control of Creeping Charlie.
- If the turf grass is under stress, try to improve the turf health and its density. This means mow it at the correct height, and fertilize and water the grass properly.
- US works shows that the use of the organic herbicide Iron HEDTA controls Ground Ivy. You need to use this early in the season.
- Adopt the correct N fertilization practices (≥ 0.5Kg N/100 m2). This approach is known to reduce Creeping Charlie in comparison to unfertilized turf (Kohler et al., 2004)
- Keep in mind that although it prefers shade, Creeping Charlie also grows well in full-sun areas.
- If you see Ground Ivy early, hand remove it and destroy all of the roots. Don’t put Creeping Charlie in a compost bin because it will take root there. This means that you must remove all plants off-site.
- If Creeping Charlie has spreads over a large area, it is difficult to control by only hand-weeding.
Chemical Control of Ground Ivy.
- Chemical control of Ground Ivy is variable and takes time.
- The best time for post emergent control is in the Autumn. This is when it moves carbohydrates into its root system, and is usually when daytime temperatures have dropped to 16 to 21°C.
- Apply post emergents when no rain is forecast for 48 hours. You need to make several applications over multiple seasons to get complete control.
The other thing to note is that no pre-emergents work against this weed. Contrary to what some might say Prodiamine, Pendimethalin and Dithiopyr will not work.
Post Emergent Ground Ivy Control.
- Post-emergent control of Creeping Charlie is best in the Autumn.
- Use a weed killer that contains Dicamba (not registered in Australia for this). This is found in products like ProForce Contra M.
- For best results, make a second application after 3 to 4 weeks.
- If you see it again in the Spring, spray again.
- Ground Ivy is very susceptible to herbicides when it flowers.
- In the US, you can use Pylex Herbicide for the control of the Ground Ivy plant.
- US work shows that 2,4-D Amine works on Creeping Charlie (Kohler et al 2004). However, timing, rate and formulation all play a role in the results you get.
- Certain broadleaf herbicides such as (2,4-D) + Quinclorac (Quinstar) are effective against Ground Ivy in the Summer.
Non Selective Ground Ivy Options.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate. However, if you use Glyphosate and water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks. Be aware that Ground Ivy will however regrow due to the limited movement of glufosinate.
The following are non-selective but also have a long term residual that stops any weed re-growth.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent weed control for up to 12 months
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown of Creeping Charlie, and stops other weeds for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use around trees
Table of Non Selective Ground Ivy Herbicides.
Product | Active Ingredient | Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |