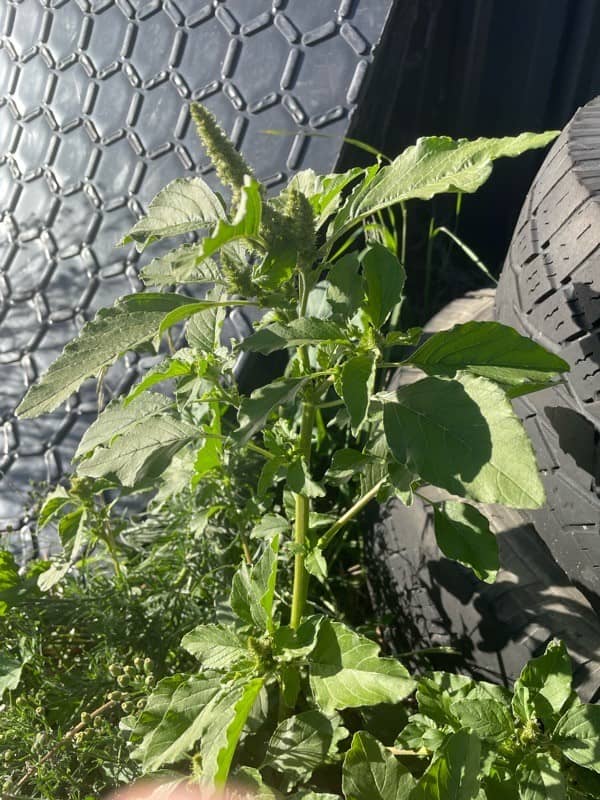
Amaranth (Amaranthus sp).
Amaranth is a very invasive Summer annual weed, that germinates in the Spring and then flowers from the late Summer onwards. There are two main varieties in Australia and these are A.viridis (Green Pigweed) and A. retroflexus (Redroot Pigweed).
It survives Winter as seed, but in the topics and sub-tropics it tends to flower all year round. In these climatic zones it produces up to two generations a year. Amaranth is a common cause of Summer allergies.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Amaranth or Redroot Pigweed.
- Know the habitat of Green or Red Pigwweed in Australia.
- Know the best options to control this weed.
Why is Amaranth a Problem Weed?
Amaranth is a problem weed because it is very competitive. This is because:
- It emerges early and grows rapidly.
- It germinates in low light conditions.
- Amaranth has a C4 photosynthetic pathway. This enables it to thrive under heat and drought conditions better than many other species.
- Redroot Pigweed has Allelopathic properties.
- It has a rapidly growing root system.
- It is a large seed producer.
- The seed remains viable for a long time.
- In warmer climates it grows all year-round.
- There are a lack of herbicides options for its management in turf grass systems.
Redroot Pigweed.
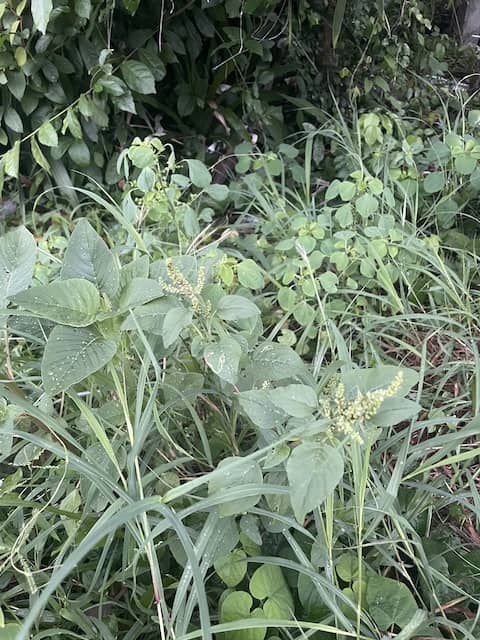
- This is a hairy, annual herb that grows up to 1 m tall. The very hairy stems are red towards the base, and it has a red taproot.
- It contains toxic nitrates and oxalates in its roots and leaves. Cattle are at risk of nitrate poisoning if they eat large amounts of immature Red Pigweed stems. It also causes kidney damage.
- You often find this weed in wet areas.
- Amaranthus retroflexus produces at least twice the root length of most other weeds in the first month of growth. This fast-growing root system allows it to quickly access soil moisture in competition with other species.
- Redroot pigweed is most common in new turf areas where turf grass is not very dense or competitive.
Green Pigweed.
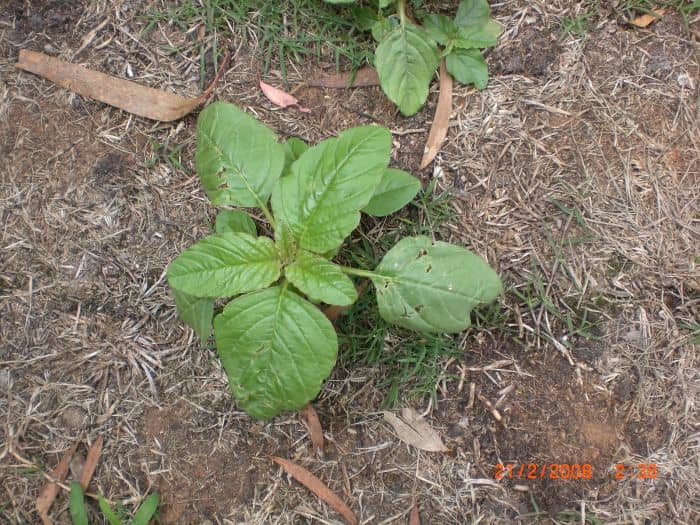
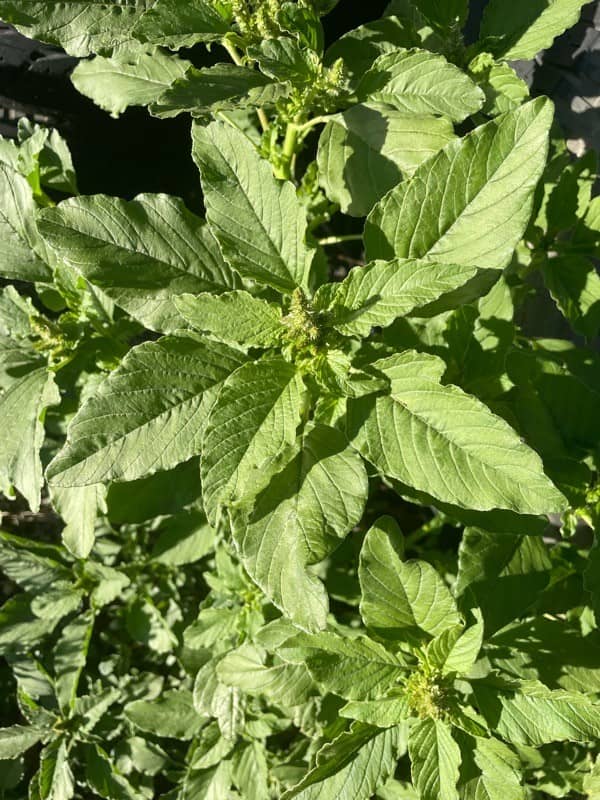
- Amaranthus viridis is a short-lived herbaceous plant that grows to 1 m tall. Its leaves are light green, have no hairs and often have notched tips.
- Green pigweed is often mistaken for Redroot Pigweed but it does not have a red taproot.
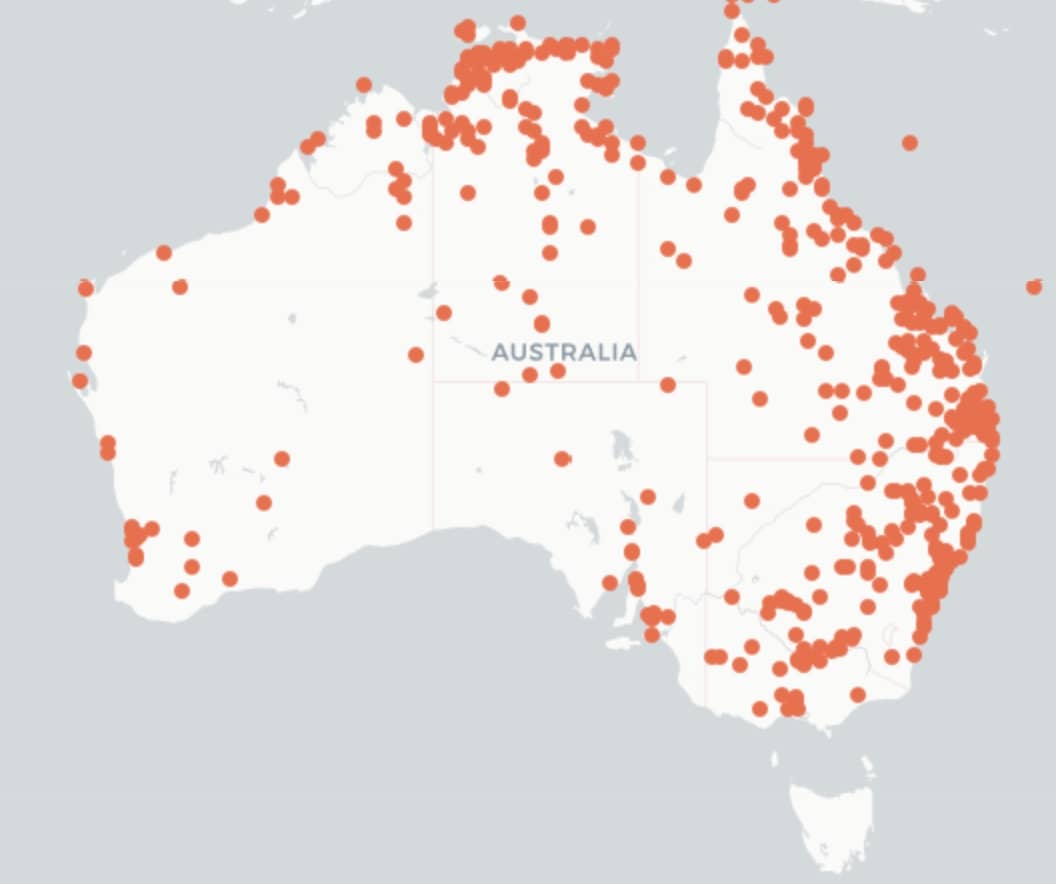
The distribution map of Green Pigweed is courtesy of The Atlas of Living Australia.
How to Identify Amaranth.
Green Pigweed is found in all the mainland states of Australia, while you tend to only find Redroot Pigweed in the South-East of Australia.
Category: It is a Broadleaf (Dicot) weed.
Photosynthetic Pathway: Amaranth is a C4 Weed.
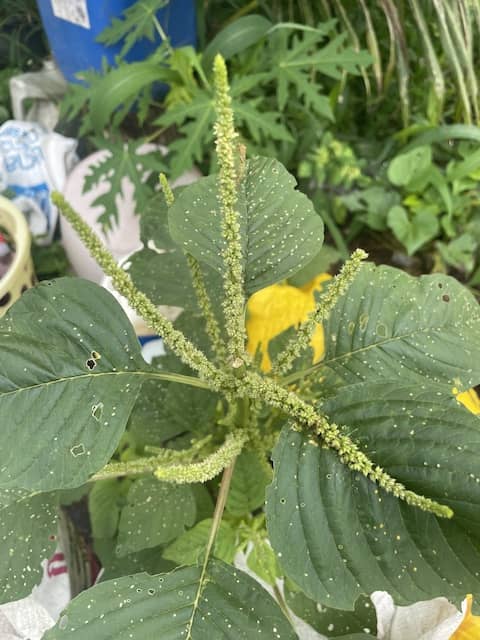
Flower: Amaranth has green flowers, and there are male and female flowers on the same plant.
An easy way to identify this weed is the presence of slender, soft, green or brown spikes at ends of branches. The terminal spike tends to be 40 to 70 mm long, 5 mm in diameter and often has a red tinge.
Height: It is up to 70 cm tall.
Leaf length: The hairless leaves are alternate, have an egg shape, and have raised white veins on their underside. They are 3 to 9 cm in length, and are a darker green on their upperside.
Leaf width: The leaves are 2 to 6 cm wide.
Amaranth Reproduction.
- This weed only reproduces by seed, and Redroot Pigweed seeds favours temperatures of 20ºC to germinate.
- Redroot Pigweed needs soil disturbance to germinate. It emerges mainly in the late Spring and early Summer, and then through the season. As the days become shorter it tends to flower, and then seeds over a short period.
- Amaranth plants produce between 230,000 and 500,000 seeds. These remain viable for up to 40 years but most are not viable after 6 to 10 years.
- It takes 3 years to reduce the seedbank by 50%, and about 20 years for a 99% reduction.
- As the seed burial depth increases above 1 cm, seed dormancy increases.
- Seed spreads by wind, water, birds and livestock, and machinery. However, without any wind the seeds only tend to fall within 2 m of the parent plant.
Comments:
- It is able to germinate in low levels of light, and grows all year-round in warm climates.
- It has a primary root, and deep secondary fibrous roots.
- Frost kills Amaranth, and it is moderately drought tolerant.
Habitat:
- This is a weed of disturbed areas.
- It grows in a wide range of soils, but prefers moist soils.
- It is less suited to acidic soils.
For more information on weeds check out our weed ID Chart.
How to Control Amaranth.
You can manage Amaranth by cultural and chemical means, but successful management of this weed is best if you adopt an integrated approach.
Cultural Control of Amaranth:
- If you maintain a healthy dense turf cover it reduces seedling emergence, flowering and seed set. This is because the turf grass competes for light, soil nutrients and water. Its poor shade tolerance means that a thick turf cover limits the amount of light that reaches any seedlings.
- It is important that you make the right grass selection in order to out compete Amaranth. Whether this is turf seed or vegetative material is open to discussion, and depends on your climatic zone.
- Hand weeding is effective to remove this weed. However, it is only effective if the population is not too high or most of the plants are young. Once it matures control is much more difficult.
- Remove all flowering plants offsite, rather than leave them on the ground. This ensures that no viable seed remains to regrow.
- Redroot Pigweed does not last in closely mown turf. However, it does establish in cool-season lawns when the mowing frequency is reduced due to high temperatures and minimal soil moisture.
Management Calendar for Amaranthus sp.
Management Calendar for Amaranthus | ||||||||||||
Summer annual | ||||||||||||
Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Flowering | ||||||||||||
Pre Emergent Herbicide | ||||||||||||
Post Emergent | successful until the 4-6 leaf stage | successful until the 4-6 leaf stage | ||||||||||
Chemical Control of Amaranth.
In turf the only selective post emergent herbicide in Australia is Pylex Herbicide. In vegetable crops Metalochlor, Ethofumesate and Propyzamide are registered.
Work in India on couch has shown that Metsulfuron at 5 g/Ha controls Green Pigweed.
The key to manage this weed is to reduce the seedbank. On this basis the pre-emergent herbicide BASF Freehand is worth a look. This is labelled to control Amaranth (Amaranthus cruentus).
- Apply herbicides at the early growth stage for the best results.
- Aim to apply herbicides when weeds are small, and ideally no greater than 5 cm in height or diameter.
- Ensure weeds are actively growing for the best results.
- Best weed control occurs when the soil is wet to a depth of 5 to 7.5 cm within 4 weeks of application.
Non Selective Control of Amaranth.
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks, but it regrows due to the limited movement of glufosinate.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate but if water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The following are non-selective but also have a long term residual and stop any re-growth.
- Renegade. Renegade stops seed germination for up to 12 months, and reduces the need for multiple herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent Amaranthus sp control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown of Amarath, and residual control for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use around trees.
Table of Non Selective Herbicides for Amaranthus.
Product | Active Ingredient | Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |