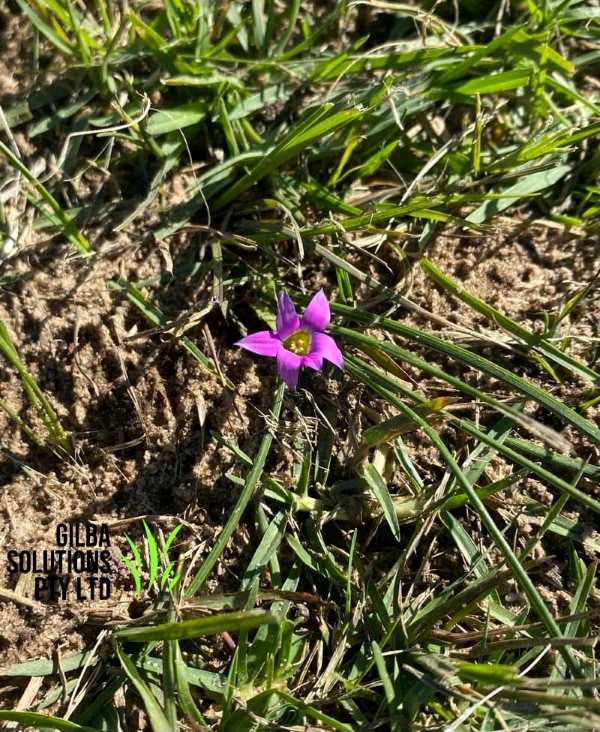
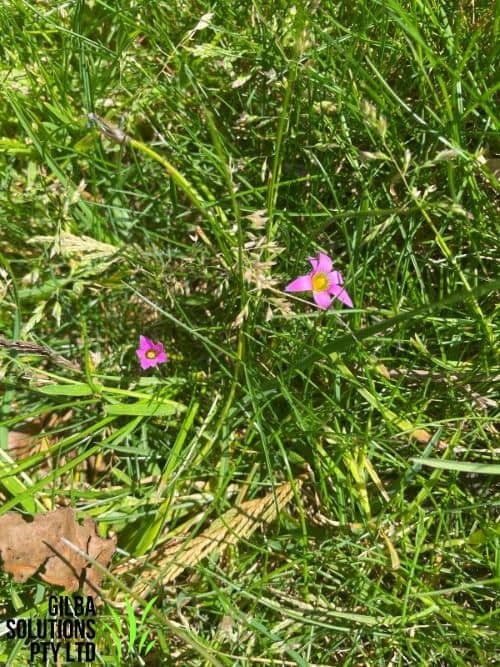
Onion Grass (Romulea rosea).
Onion Grass (Romulea rosea) is also known as Guildford Grass, and is a highly invasive small perennial herb that grows from a white bulb (corms). It has a yellow base and annual leaves with small pink, white, purple or yellow flowers.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify Onion Grass, or Guildford Grass.
- Know what conditions favour Onion Grass.
- Know the best cultural and chemical options to control Guildford Grass.
Why is Onion Grass a Problem Weed?
- It readily colonizes disturbed soils, roadsides, and pastures, where it outcompetes native plants.
- Romulea rosea grows quickly and thrives in disturbed areas.
- Onion Grass reproduces by seeds and underground bulbs, and so is very difficult to eradicate.
- Its tough leaves blunt mower blades.
Romulea rosea is a significant environmental weed in VIC and WA, and an environmental weed in SA, the ACT and NSW.
Onion Grass has very tough, shiny dark green leaves that grow from the base of the plant, and if there are leaves on the stems these are smaller. The flattened leaves, have a groove running lengthwise.
It is considered to be an environmental weed in much of Australia.
More information on common lawn weeds is in our weed ID chart. Onion Grass indicates low soil P. For more about what weeds reveal about soil conditions see our blog on indicator weeds.
The map of Onion Grass distribution is courtesy of The Atlas of Living Australia.
How to Identify Onion Grass.
Category: Perennial herb.
Photosynthetic Pathway. Onion Grass is a C4 weed.
Flower: The six petalled flowers of Onion Grass are 2 to 3 cm wide, and are small pink, white, purple or yellow. They flower in the late Winter and the Spring.
Height: Onion Grass grows up to 25 cm high.
Leaf length: The leaves are up to 18 mm long.
Reproduction: Every year the bulb regrows, and Guildford Grass reproduces by seed and corm. The seeds germinate from the Autumn to the Winter. It then grows over the Winter, and flowers from August to November.
You can see the flowers in the second year and the seedbank can persist for up to 5 years. Onion Grass needs warm temperatures to germinate, and so it favours bare ground in direct sunlight. Although a perennial, Guildford Grass behaves like an annual, and dies back at the end of the Summer.
Comments: Flowers typically open at noon and stay open only until 1 or 2 pm.
Habitat: Guildford Grass is a common weed of lawn, pasture, and sports fields.
How to Remove Onion Grass from your lawn.
You can best control Guildford Grass with herbicides.
Cultural Control of Onion Grass.
Physical removal of Romulea rosea is difficult as the bulbs at soil depths of up to 200 mm.
- You can dig or pull out small populations of Guildford Grass. However, if you hand-pull this weed, you must be careful to remove the entire plant and bulb, as any left behind re-grows. This process has to be ongoing for several years to make sure that you remove all the remaining bulbs.
- Research shows that Onion Grass does not respond to increases in soil fertility. This means that if you feed your turf it will help to control this weed as it enhances more desirable turf grass species.
- There are mixed reports in relation to the use of mowing to control Romulea rosea. The general belief is that this does not work. However, work in VIC shows that Onion grass is in fact very sensitive to close mowing.
If you mow at a height of 1 cm every three to five-weeks, it reduces the bulb mass by 70%. This also reduces seed pod density by 100% and plant density by 60%. This is compared to not mowing at all. If you cut at a height of 5 cm it reduces Onion Grass bulb mass by 58%.
Herbicides for Onion Grass.
- 6-8 weeks after Romulea rosea emerges, there is a short window when herbicides are at their most effective. This is because the old corm is exhausted, and the new corm is only just starting to develop.
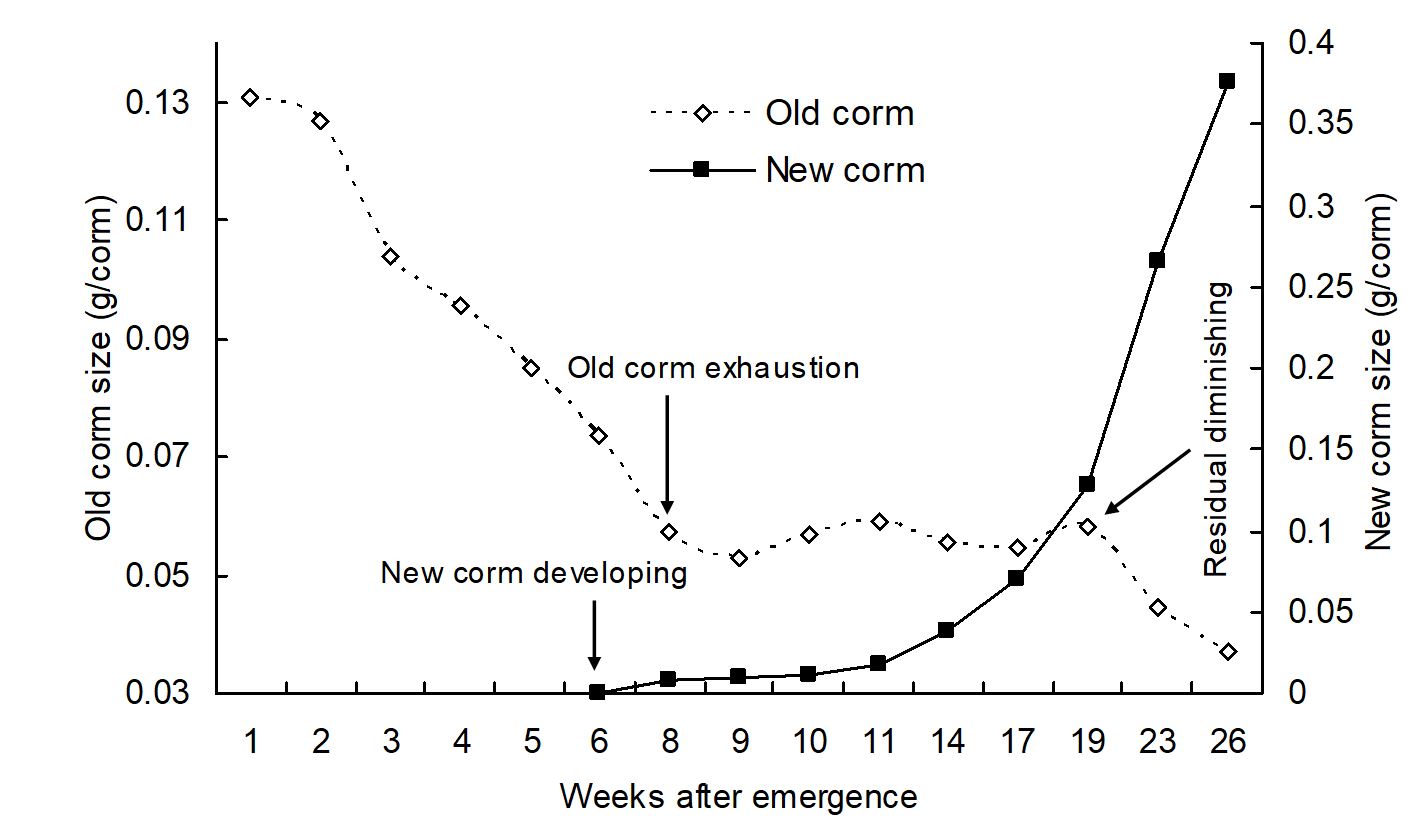
A graph showing the mean dry weight of old and new corms after emergence of onion grass plants. The most effective control with selective herbicides is when the old corm is exhausted and when the new corm starts to develop. This occurs between week six and eight after emergence.
- If you treat with a herbicide when Onion Grass flowers, it gets rid of the flowers but not the corms.
- If broadleaf weeds such as Dandelion or Bittercress are present, you can mix the herbicides below with Warhead Trio to control both types of weeds.
- The sulfonylurea herbicide, Iodosulfuron controls Onion Grass. This is in the active in ProForce Duke 100WG from Indigo Specialty Products.
- Quali-Pro Negate also controls Guildford Grass, but you cannot use this on Buffalo grass turf.
Table of Selective Post Emergent Herbicides for Onion Grass.
Product | Active | Chemical Group | Rate/Ha | Comments |
Duke | Iodosulfuron | 2 | 100g | Always use an NIS or Overtake Oil. Use in 200-500 L/ha water. |
Negate. | Rimsulfuron + Metsulfuron-methyl | 2 | 110g | Apply to growing weeds and not to stressed weeds. |
Non Selective Control of Onion Grass.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate but if water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The following are non-selective but also have a long term residual and stop re-growth of Onion Grass.
- Renegade. Renegade stops germination for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for multiple herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent control for up to 12 months
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown of Onion Grass, and residual control for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use around trees.









