Praxelis (Praxelis clematidea).
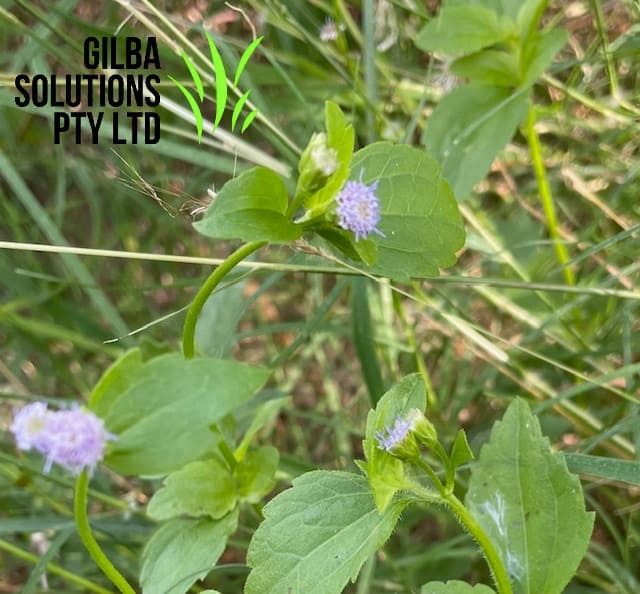
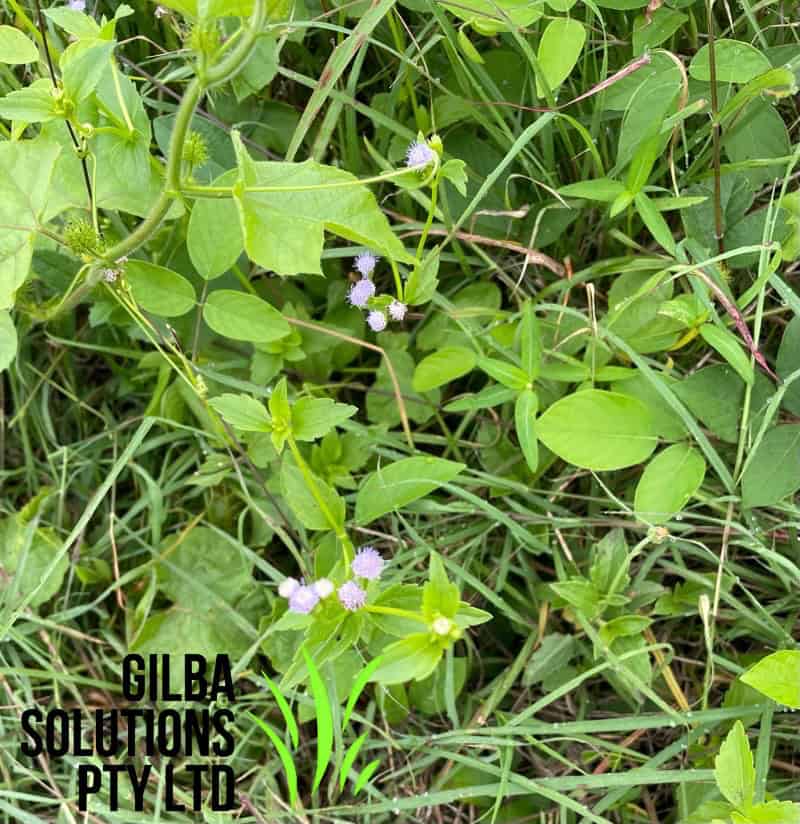
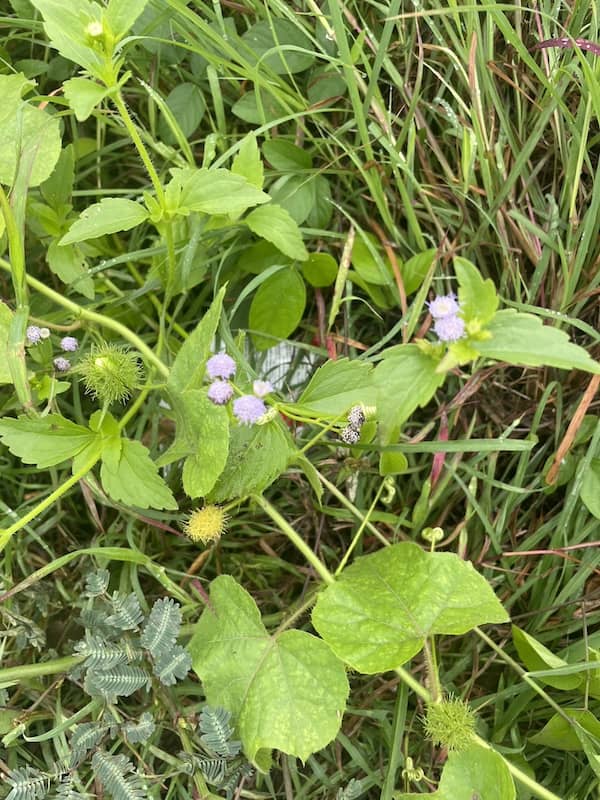
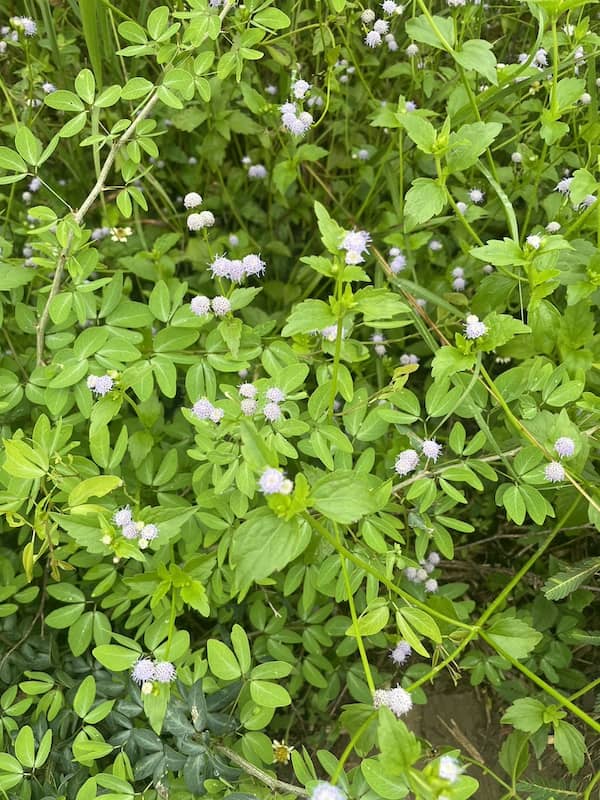
Praxelis (Praxelis clematidea) is also known as Giant Bluetop. It is an annual or short-lived perennial herb and has a fibrous root system.
This is a weed of the tropics and sub-tropics. It tolerates partial to full sun, but does not grow well in full shade.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify this weed.
- Know the habitat of Giant Bluetop.
- Know the best way to control or Giant Bluetop (Praxelis clematidea).
Why is Praxelis a Problem?
- This weed invades disturbed and undisturbed sites.
- It competes with native plants and pastures.
- Giant Bluetop contains pyrrolizidine alkaloids. These are poisonous to stock that eat it.
- It has allelopathic properties.
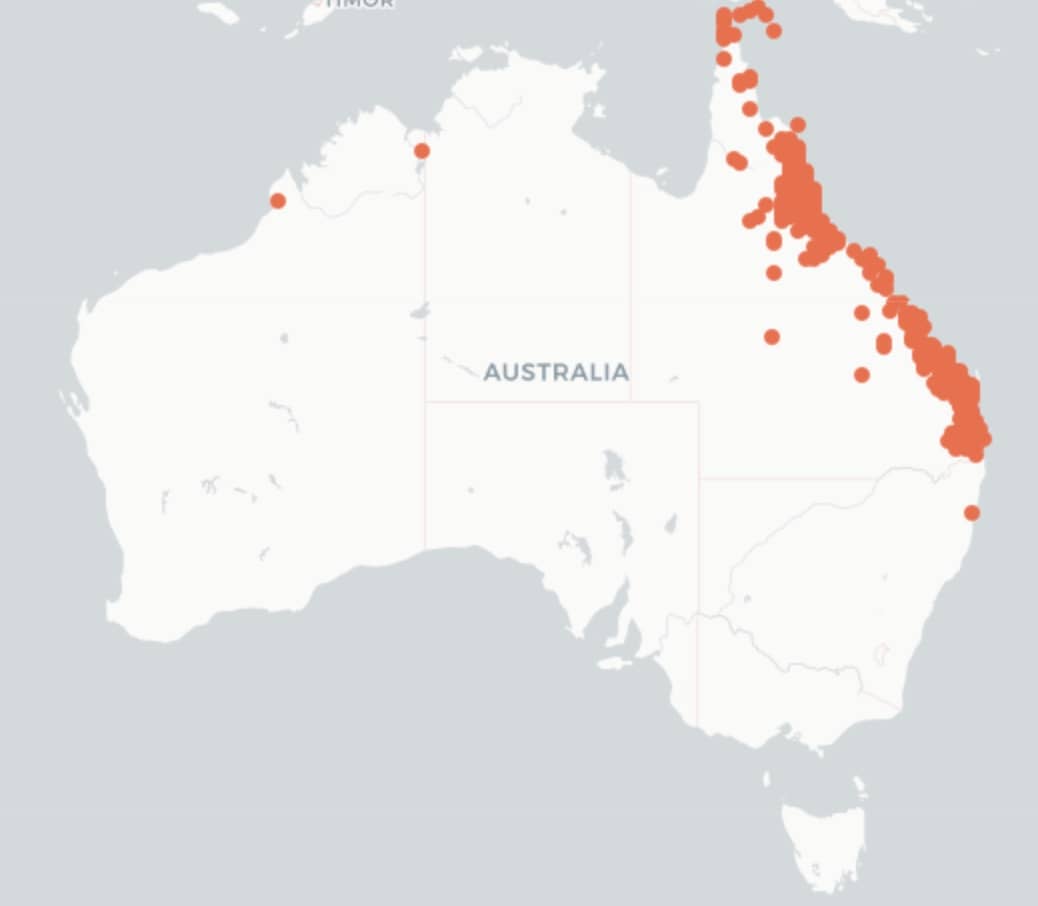
This weed is on the Alert List for Environmental Weeds. This is a list of 28 non-native plants that threaten biodiversity and cause other environmental damage. Thankfully it has never been found in NSW. It is present in Queensland.
The coverage map is courtesy of The Atlas of Living Australia.
How to Identify Praxelis.
Praxelis clematidea is an upright herb. It grows from seed and also vegetatively. Its stems have a cover of soft downy hairs.
Photosynthetic Pathway: It is a C3 weed.
Category: This is a broadleaf (Dicot) weed.
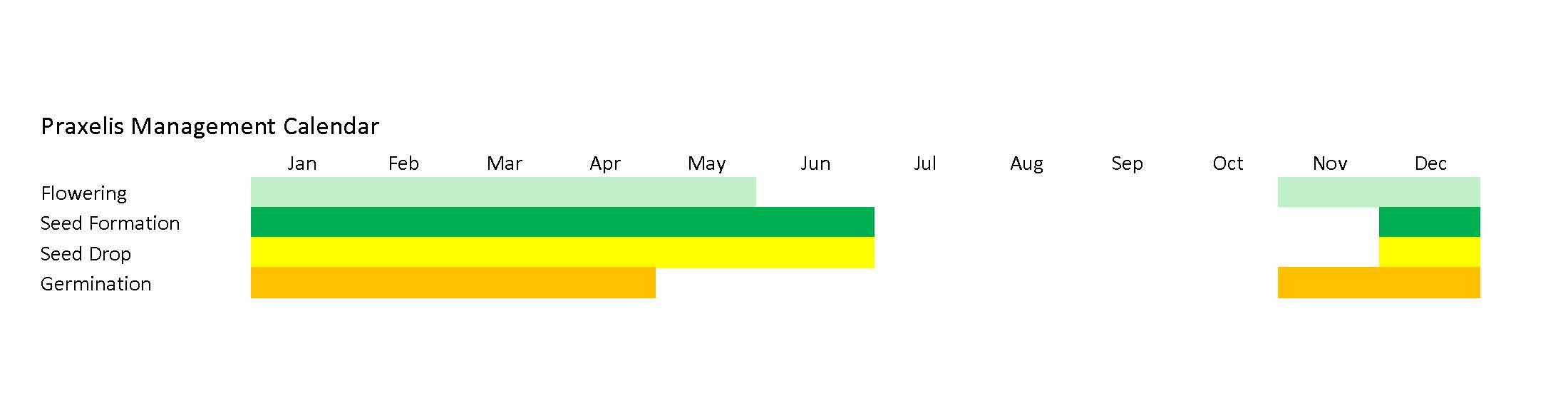
Flower: The tiny flowers of Praxelis clematidea are blue or lavender. There 35 to 40 of these flowers in clusters at the ends of hairy stems. You tend too see the flowers from January to May, but they can be present all year.
Height: It grows to a height of 40 to 50 cm
Leaf length: The leaves of Giant Bluetop are hairy underneath. They are arranged opposite to each other, and 25 to 60 mm long. The leaves have sharp teeth along their edges with 5 to 8 of these teeth on each side.
Leaf width: The leaves are 25 to 37mm wide.
Reproduction:
- After it germinates, it produces up to 1,400 small black seeds per plant.
- This takes a little as 3 or 4 months.
- Most seeds germinate after rainfall. But you can see this weed all year round in gardens or irrigated pasture.
- The seeds germinate over a temperature range of 20 to 30 °C.
- Both high (>45°C) and low (<10°C) temperatures tend to reduce germination.
- Most seed germinates at the soil surface.
- No seeds germinate more than 1 cm below the soil surface.
- The seeds have a “pappus” or a cluster of barbed bristles that helps them to spread.
- It spreads by wind or water, or attach to animal fur and feathers, clothes, or machinery.
- This weed is also capable of vegetative growth. This occurs when roots and new plantlets form along branches in contact with the soil.
Management Calendar.
Comments: If you crush the leaves they smell of cat’s urine.
Habitat: You tend to find this weed in disturbed areas along roads, in pastures, along railway lines, in open woods, and on fence lines.
For more information on weeds check out our weed ID Chart.
How to Control Praxelis.
- You can control this weed by cultural and chemical means.
- However, due to its high seed production, you will only achieve long-term control with the use of pre and post emergents to prevent any re-growth.
Cultural Control of Praxelis:
Prevention is the most cost-effective way to manage this weed. So aim to keep areas free from this weed.
- Hand pulling is not recommended, even if it’s only in small areas. This is because the seed falls off and will increase the area of infestation.
- The fact that Giant Bluetop does not grow in shade is also a control option. A thick turf cover with very few thin or bare areas stops germination.
This means:
- Mow at the right height of cut.
- Fertilise as needed. Take into account shade, the turf type and the time of year.
- Don’t over irrigate or let your turf dry out.
- Keep on top of any disease.
Chemical Control of Praxelis.
- There are few chemical controls for Giant Bluetop.
- BASF Freehand gives poor control as a pre-emergent.
- The University of Florida suggests the use of Envu Specticle herbicide. This does not have a label in Australia for this weed.
Non Selective Control of Praxelis.
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks. However it does tend to regrow due to the limited movement of glufosinate.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate to control Giant Bluetop under APVMA Permit 11463. If you use Glyphosate, and water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The following are non-selective. They also have a long term residual and stop any re-growth.
-
- Renegade. Renegade stops the germination of Giant Bluetop for up to 12 months. This reduces the need for repeat chemical applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown of Praxelis, and residual control for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use around trees.
Table on Non Selective Praxelis Herbicides.
Product | Active | Group | Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |