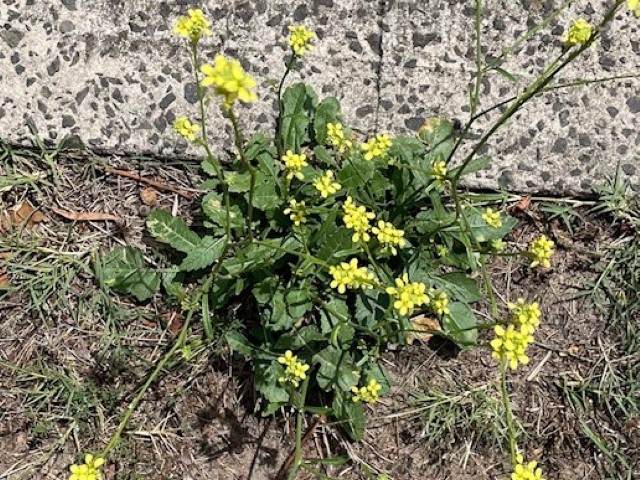
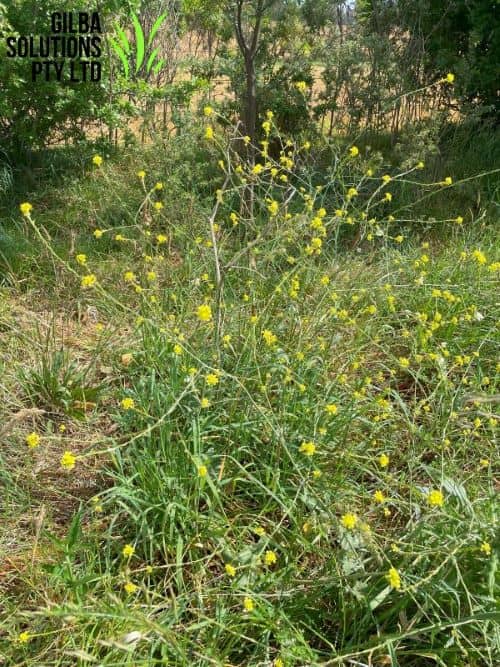
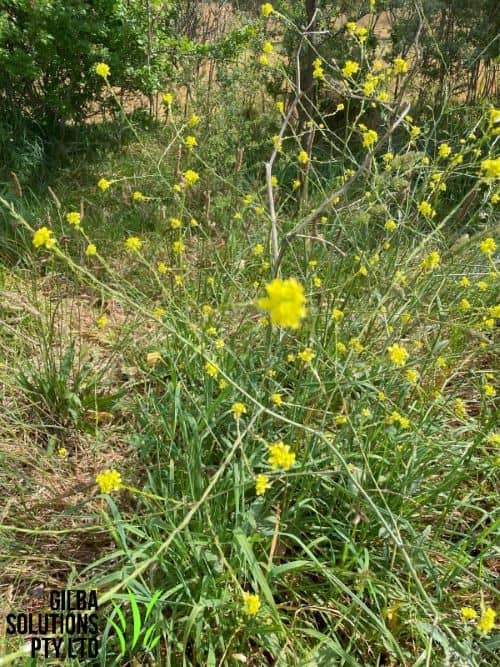
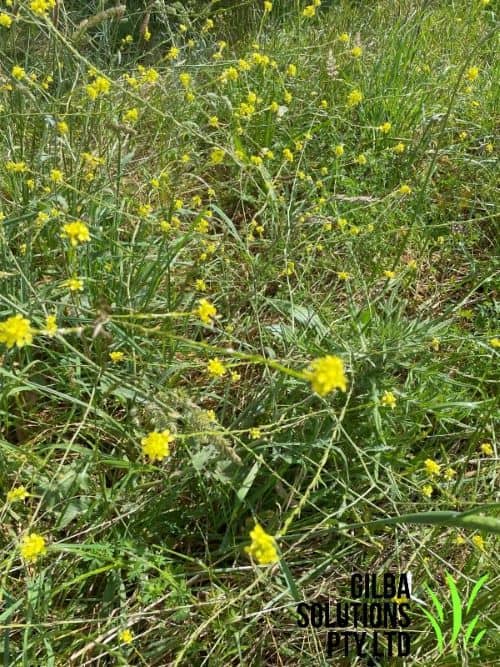
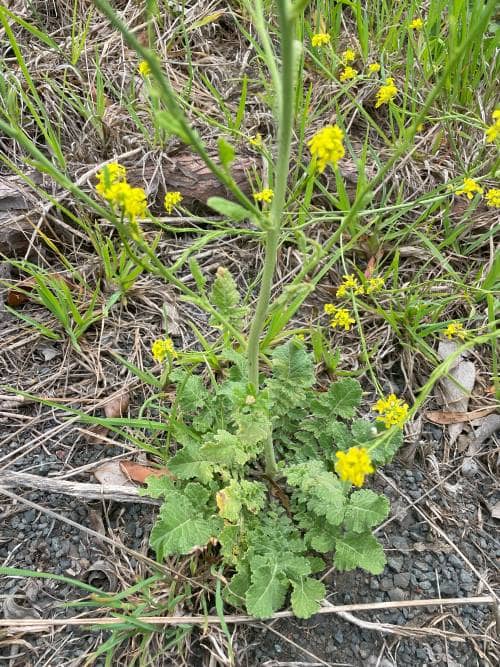
Buchan Weed (Hirschfeldia incana).
Buchan Weed aka Short Pod Mustard, and Hoary Mustard is known as Short Pod Mustard in the USA. It is an annual or biennial (sometimes perennial), herb that grows up to 100 cm tall and has pale yellow flowers. It is found in the ACT, NSW, QLD, SA, TAS, VIC, and WA.
The distribution map is courtesy of The Living Atlas of Australia.
After you read this, you will be able to:
- Identify capeweed Buchan Weed or Short Pod Mustard.
- Know the habitat of Buchan Weed or Hoary Mustard.
- Know the best options to control Buchan Weed or Short Pod Mustard.
How to Identify Buchan Weed.
Hoary Mustard has a slender, deep taproot with branching laterals in the top 300 mm of soil.
Category: Herb.
Photosynthetic Pathway: C3 Weed.
Flower: Flowers consist of four pale purple veined yellow petals, and each petal is 6 – 9 mm long.
Height: Buchan Weed can grow up to 100 cm tall.
Leaf length: The lower leaves are up to 350 mm long, deeply lobed to the stem. The upper leaves look the same as the lower leaves, but are smaller, diminishing in size, and number.
Reproduction: Hairy Brassica only reproduces by seed, that is spread by water, and human activity. Seeds germinate through the Autumn, and these grow slowly until mid-winter when flowering stems develop. It flowers from September to February.
Buchan Weed is problematic as it produces a large number of seeds that can live in the ground for several years. The seeds infest grain crops and can contaminate animal fodder.
Comments: The stems and leaves have a cover of stiff, simple bristle-like hairs.
Habitat: Buchan Weed is an indicator weed of dry or moist soil, and thrives under warm conditions in N rich soils. You often find this weed in roadsides, wasteland, degraded pastures, orchards and vineyards
More on lawn and turf grass weeds is in our weed ID chart.
How to Control Buchan Weed.
Management Calendar for Buchan Weed.
Management Calendar for Buchan Weed | ||||||||||||
Annual or biennial herb, but can also be occasionally perennial. | ||||||||||||
Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
Germination | ||||||||||||
Active Growth | ||||||||||||
Flowering | ||||||||||||
Pre emergent Herbicide | ||||||||||||
Post Emergent Herbicide | ||||||||||||
Cultural Control of Hoary Mustard:
- Dense healthy turfgrass helps prevents Short Pod Mustard from establishing.
- You can pull individual plants out by hand, but you must take care to remove as much of the taproot as possible. This is because plants are able to re-shoot from pieces of root left in the soil. If you carry on doing this over a number of years you will eventually exhaust the seed bank.
Chemical control of Buchan Weed.
Post Emergent Control of Hoary Mustard.
Currently no selective post emergent herbicides are registered to control Buchan Weed in turf grass. However, metribuzin is regsitered in agriculture.
Herbicide resistance has been seen overseas to the Group 2 Herbicide metsulfuron-methyl.
Non Selective Control of Buchan Weed.
Non selective options for Buchan Weed include:
- Glufosinate-ammonium provides control for 4 to 6 weeks, but it regrows and recovers due to the limited movement of glufosinate.
- Glyphosate. You can use Glyphosate to control Hoary Mustard but if water quality is an issue then use ProForce Manta Ray.
The following are non-selective but also have a long term residual and stop re-growth of Hoary Mustard.
- Renegade. Renegade stops germination for up to 12 months, and reduces the need for multiple herbicide applications.
- Numchuk Quad. This gives effective post and pre emergent Short Pod Mustard control for up to 12 months.
- Cortex Duo. Cortex Duo gives a rapid knockdown of Buchan Weed, and residual control for up to 3 months. It is also safe to use around trees.
Table of Non Selective Herbicides for Buchan Weed Control.
Product | Active Ingredient | Group | Use Rate/Ha |
Glufosinate 200 | Glufosinate-ammonium | 10 | 1 to 6 L |
Rapid Fire 800 | Glyphosate | 9 | 0.9 to 1.35 Kg |
Numchuk Quad | Terbuthylazine + Glyphosate + Amitrole Oxyfluorfen | 5 + 9 + 34 + 14 | 20 to 25 L |
Cortex Duo | Nonanoic Acid + Oxyfluorfen | 14 | 7 L/1000L |
Renegade | Bromacil | 5 | 3.5 to 6.5 Kg |